Thomas S. Hatsukami
Deep Open Snake Tracker for Vessel Tracing
Jul 19, 2021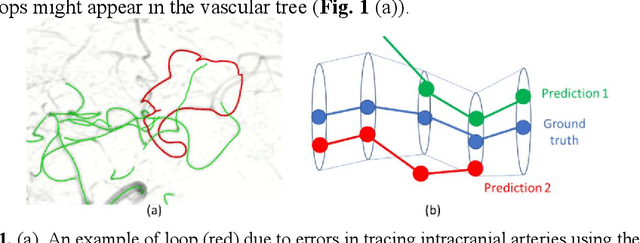
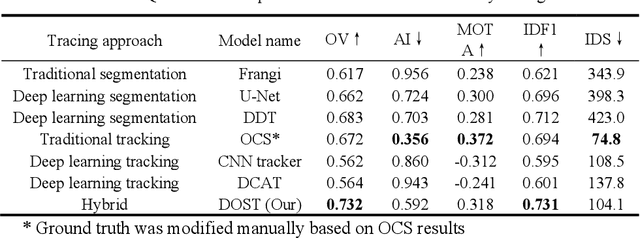
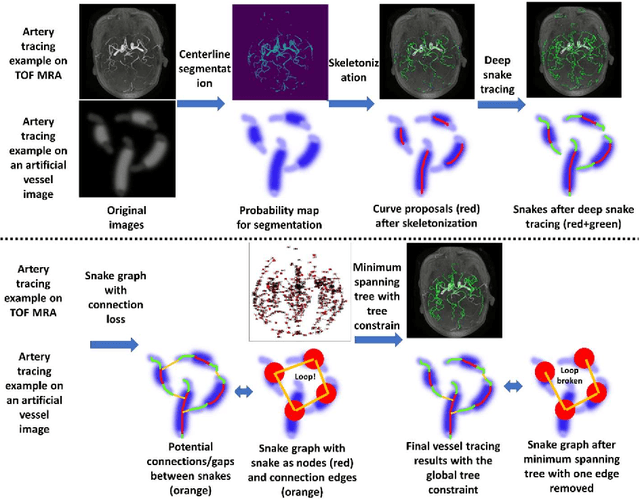
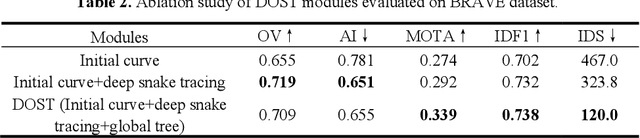
Abstract:Vessel tracing by modeling vascular structures in 3D medical images with centerlines and radii can provide useful information for vascular health. Existing algorithms have been developed but there are certain persistent problems such as incomplete or inaccurate vessel tracing, especially in complicated vascular beds like the intracranial arteries. We propose here a deep learning based open curve active contour model (DOST) to trace vessels in 3D images. Initial curves were proposed from a centerline segmentation neural network. Then data-driven machine knowledge was used to predict the stretching direction and vessel radius of the initial curve, while the active contour model (as human knowledge) maintained smoothness and intensity fitness of curves. Finally, considering the nonloop topology of most vasculatures, individually traced vessels were connected into a tree topology by applying a minimum spanning tree algorithm on a global connection graph. We evaluated DOST on a Time-of-Flight (TOF) MRA intracranial artery dataset and demonstrated its superior performance over existing segmentation-based and tracking-based vessel tracing methods. In addition, DOST showed strong adaptability on different imaging modalities (CTA, MR T1 SPACE) and vascular beds (coronary arteries).
Y-net: 3D intracranial artery segmentation using a convolutional autoencoder
Dec 19, 2017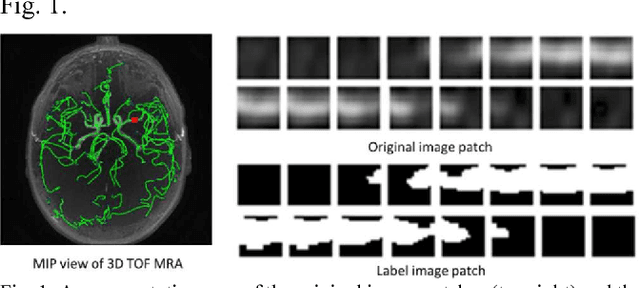
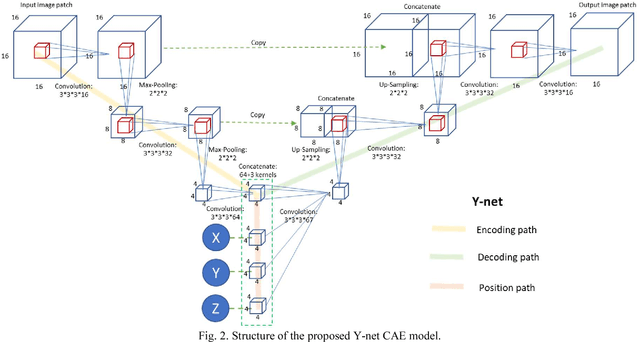
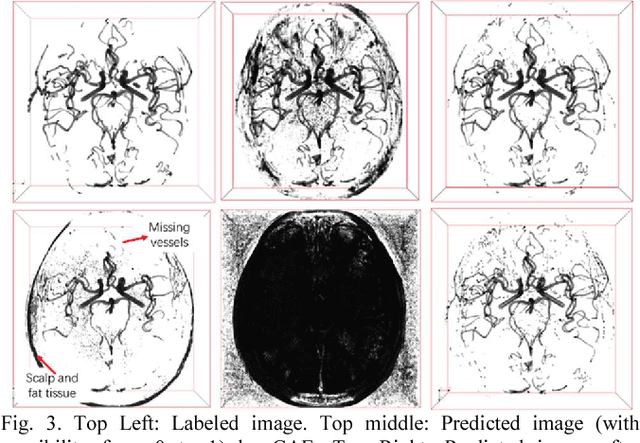
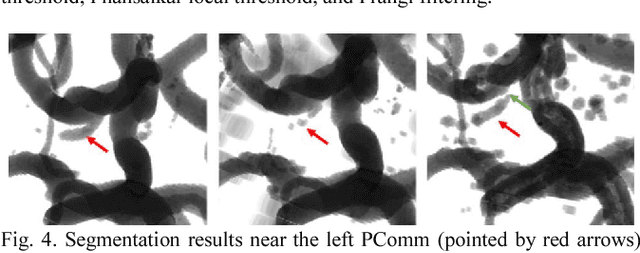
Abstract:Automated segmentation of intracranial arteries on magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) allows for quantification of cerebrovascular features, which provides tools for understanding aging and pathophysiological adaptations of the cerebrovascular system. Using a convolutional autoencoder (CAE) for segmentation is promising as it takes advantage of the autoencoder structure in effective noise reduction and feature extraction by representing high dimensional information with low dimensional latent variables. In this report, an optimized CAE model (Y-net) was trained to learn a 3D segmentation model of intracranial arteries from 49 cases of MRA data. The trained model was shown to perform better than the three traditional segmentation methods in both binary classification and visual evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge