Thomas Roland Barillot
BlackRock Inc
Blowfish: Topological and statistical signatures for quantifying ambiguity in semantic search
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:This works reports evidence for the topological signatures of ambiguity in sentence embeddings that could be leveraged for ranking and/or explanation purposes in the context of vector search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. We proposed a working definition of ambiguity and designed an experiment where we have broken down a proprietary dataset into collections of chunks of varying size - 3, 5, and 10 lines and used the different collections successively as queries and answers sets. It allowed us to test the signatures of ambiguity with removal of confounding factors. Our results show that proxy ambiguous queries (size 10 queries against size 3 documents) display different distributions of homologies 0 and 1 based features than proxy clear queries (size 5 queries against size 10 documents). We then discuss those results in terms increased manifold complexity and/or approximately discontinuous embedding submanifolds. Finally we propose a strategy to leverage those findings as a new scoring strategy of semantic similarities.
Modelling the semantics of text in complex document layouts using graph transformer networks
Feb 18, 2022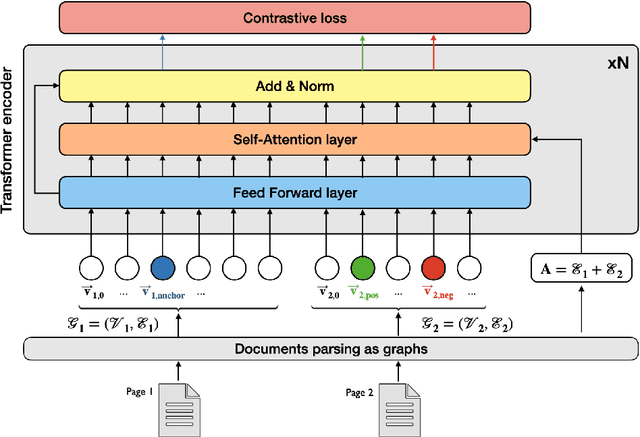
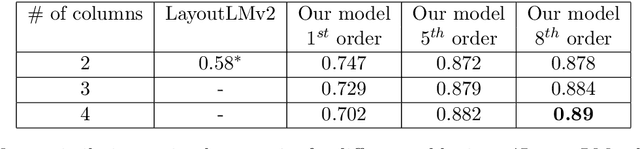
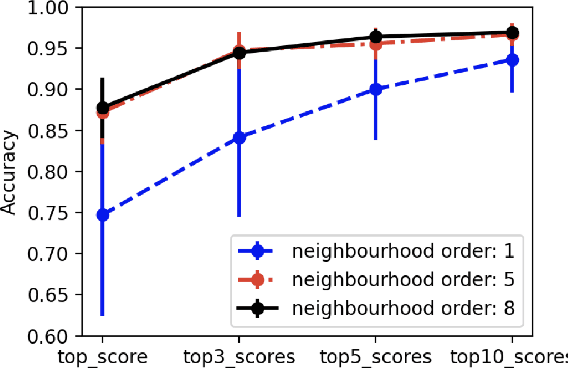
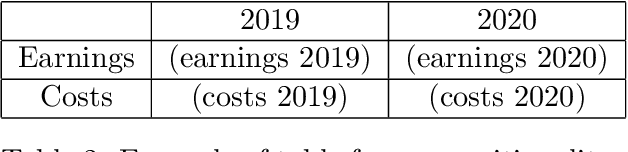
Abstract:Representing structured text from complex documents typically calls for different machine learning techniques, such as language models for paragraphs and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for table extraction, which prohibits drawing links between text spans from different content types. In this article we propose a model that approximates the human reading pattern of a document and outputs a unique semantic representation for every text span irrespective of the content type they are found in. We base our architecture on a graph representation of the structured text, and we demonstrate that not only can we retrieve semantically similar information across documents but also that the embedding space we generate captures useful semantic information, similar to language models that work only on text sequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge