Thiago Augusto Bruza Alves
Improving Random Access with NOMA in mMTC XL-MIMO
Apr 07, 2023Abstract:The extra-large multiple-input multiple-output (XL-MIMO) architecture has been recognized as a technology for supporting the massive MTC (mMTC), providing very high-data rates in high-user density scenarios. However, the large dimension of the array increases the Rayleigh distance (dRayl), in addition to obstacles and scatters causing spatial non-stationarities and distinct visibility regions (VRs) across the XL array extension. We investigate the random access (RA) problem in crowded XL-MIMO scenarios; the proposed grant-based random access (GB-RA) protocol combining the advantage of non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and strongest user collision resolutions in extra-large arrays (SUCRe-XL) named NOMA-XL can allow access of two or three colliding users in the same XL sub-array (SA) selecting the same pilot sequence. The received signal processing in a SA basis changes the dRayl, enabling the far-field planar wavefront propagation condition, while improving the system performance. The proposed NOMA-XL GB-RA protocol can reduce the number of attempts to access the mMTC network while improving the average sum rate, as the number of SA increases.
Crowded MTC Random Access in NOMA XL-MIMO
Mar 01, 2023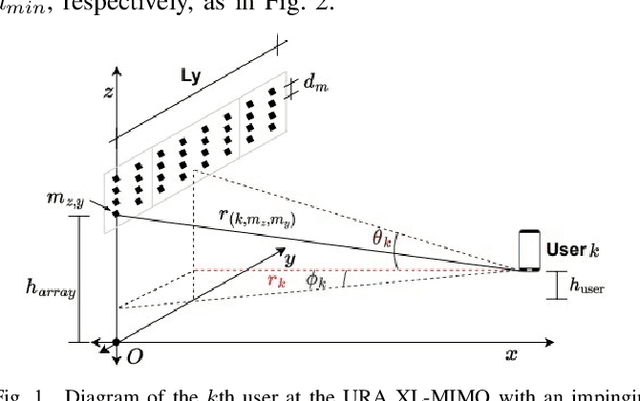
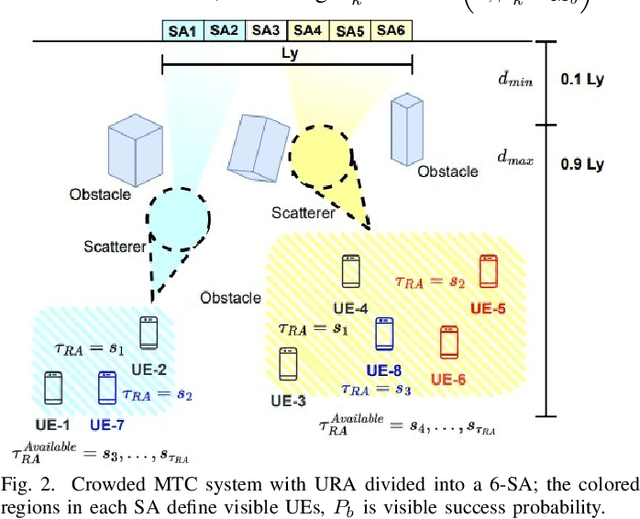
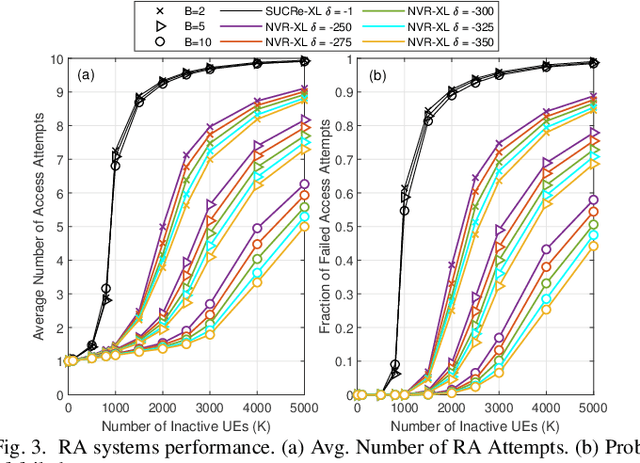
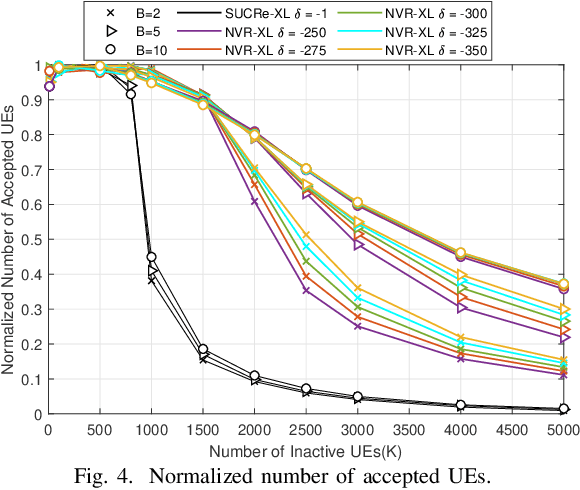
Abstract:Massive MIMO is one of the key technologies to support the growth of massive access attempts by devices, such as in massive machine type communication (mMTC). The evolution of antenna array technology brought the recent extra-large scale massive multiple input multiple output (XL-MIMO) systems, seen as a promising technology for providing very high-data rates in high-user density scenarios. Spatial non stationarities and visibility regions (VRs) occur across all huge XL array extension, since its large dimension is of the same order of the distances to the user equipment (UE). We investigate the random access (RA) problem in crowded XL-MIMO scenarios. The proposed nonorthogonal multiple access (NOMA) visible region extra large array (NVR-XL) protocol takes advantage of the power domain NOMA to allow access of two or more users colliding in the same XL sub-array (SA) selecting the same pilot sequence. The NVRXL provides a reduction in the number of attempts to access the network, while improving the average sum-rate, as the number of SA increases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge