Theodore B. Trafalis
Using Federated Machine Learning in Predictive Maintenance of Jet Engines
Feb 07, 2025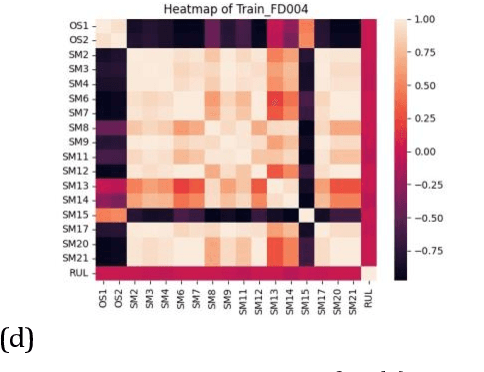
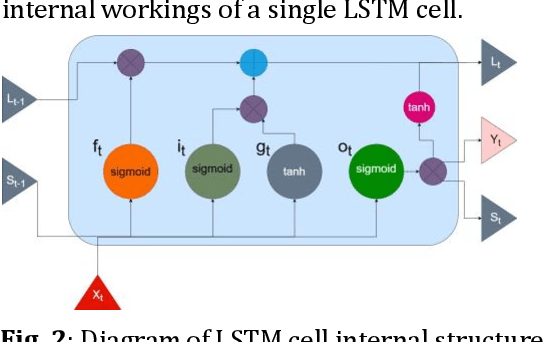
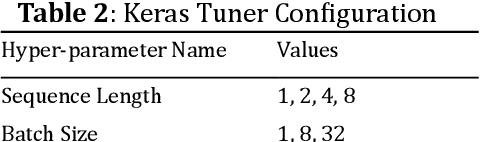
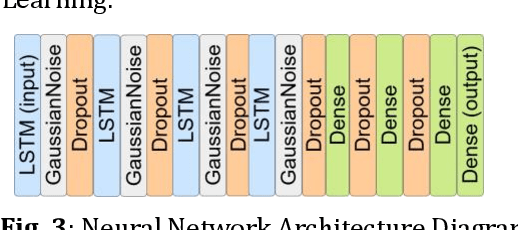
Abstract:The goal of this paper is to predict the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of turbine jet engines using a federated machine learning framework. Federated Learning enables multiple edge devices/nodes or servers to collaboratively train a shared model without sharing sensitive data, thus preserving data privacy and security. By implementing a nonlinear model, the system aims to capture complex relationships and patterns in the engine data to enhance the accuracy of RUL predictions. This approach leverages decentralized computation, allowing models to be trained locally at each device before aggregating the learned weights at a central server. By predicting the RUL of jet engines accurately, maintenance schedules can be optimized, downtime reduced, and operational efficiency improved, ultimately leading to cost savings and enhanced performance in the aviation industry. Computational results are provided by using the C-MAPSS dataset which is publicly available on the NASA website and is a valuable resource for studying and analyzing engine degradation behaviors in various operational scenarios.
Religious Affiliation in the Twenty-First Century: A Machine Learning Perspective on the World Value Survey
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:This paper is a quantitative analysis of the data collected globally by the World Value Survey. The data is used to study the trajectories of change in individuals' religious beliefs, values, and behaviors in societies. Utilizing random forest, we aim to identify the key factors of religiosity and classify respondents of the survey as religious and non religious using country level data. We use resampling techniques to balance the data and improve imbalanced learning performance metrics. The results of the variable importance analysis suggest that Age and Income are the most important variables in the majority of countries. The results are discussed with fundamental sociological theories regarding religion and human behavior. This study is an application of machine learning in identifying the underlying patterns in the data of 30 countries participating in the World Value Survey. The results from variable importance analysis and classification of imbalanced data provide valuable insights beneficial to theoreticians and researchers of social sciences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge