Terence Van Zyl
Using Machine Learning to Fuse Verbal Autopsy Narratives and Binary Features in the Analysis of Deaths from Hyperglycaemia
Apr 26, 2022
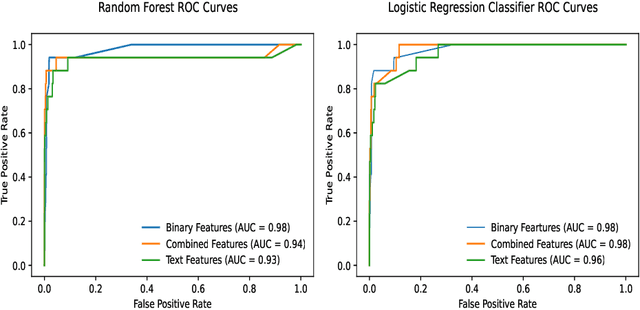
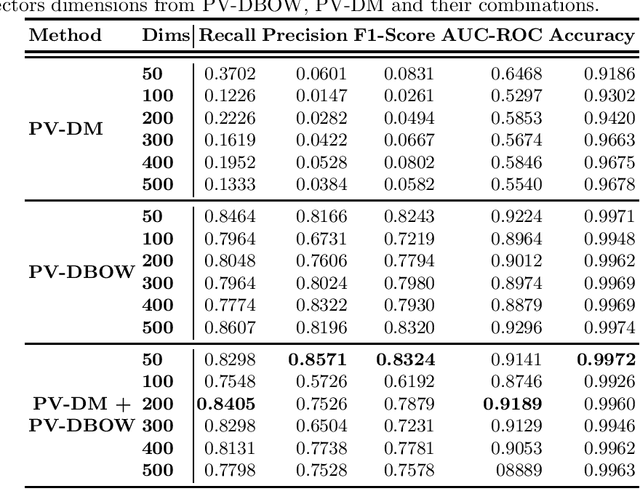
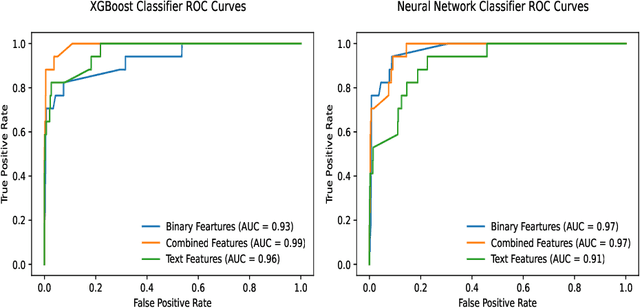
Abstract:Lower-and-middle income countries are faced with challenges arising from a lack of data on cause of death (COD), which can limit decisions on population health and disease management. A verbal autopsy(VA) can provide information about a COD in areas without robust death registration systems. A VA consists of structured data, combining numeric and binary features, and unstructured data as part of an open-ended narrative text. This study assesses the performance of various machine learning approaches when analyzing both the structured and unstructured components of the VA report. The algorithms were trained and tested via cross-validation in the three settings of binary features, text features and a combination of binary and text features derived from VA reports from rural South Africa. The results obtained indicate narrative text features contain valuable information for determining COD and that a combination of binary and text features improves the automated COD classification task. Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus, Verbal Autopsy, Cause of Death, Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing
Surrogate Parameters Optimization for Data and Model Fusion of COVID-19 Time-series Data
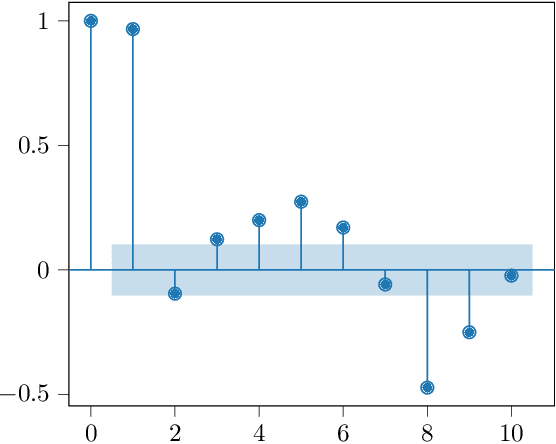
Sep 09, 2021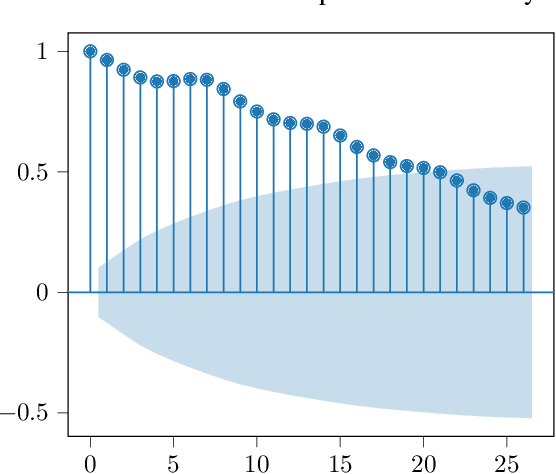
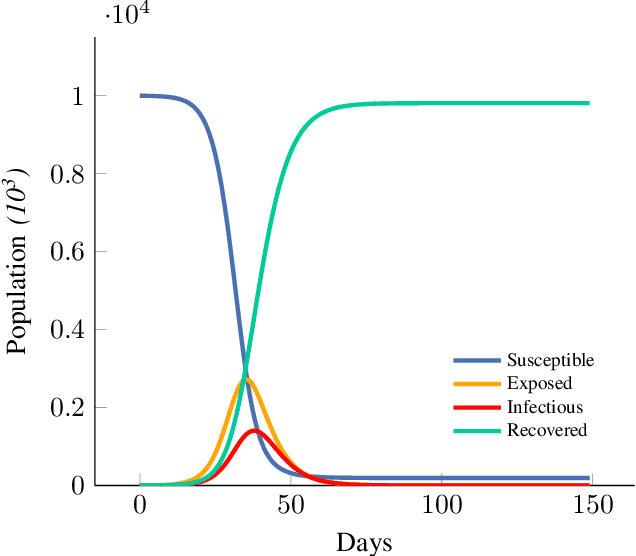
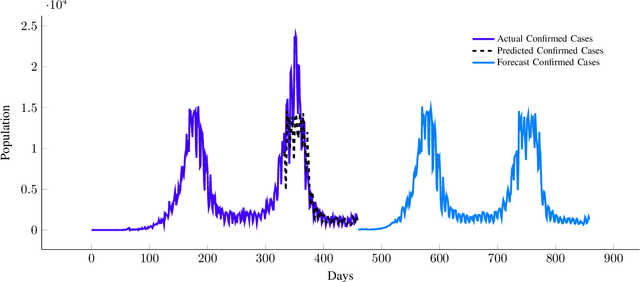
Abstract:Our research focuses on developing a computational framework to simulate the transmission dynamics of COVID-19 pandemic. We examine the development of a system named ADRIANA for the simulation using South Africa as a case study. The design of the ADRIANA system interconnects three sub-models to establish a computational technique to advise policy regarding lockdown measures to reduce the transmission pattern of COVID-19 in South Africa. Additionally, the output of the ADRIANA can be used by healthcare administration to predict peak demand time for resources needed to treat infected individuals. ABM is suited for our research experiment, but to prevent the computational constraints of using ABM-based framework for this research, we develop an SEIR compartmental model, a discrete event simulator, and an optimized surrogate model to form a system named ADRIANA. We also ensure that the surrogate's findings are accurate enough to provide optimal solutions. We use the Genetic Algorithm (GA) for the optimization by estimating the optimal hyperparameter configuration for the surrogate. We concluded this study by discussing the solutions presented by the ADRIANA system, which aligns with the primary goal of our study to present an optimal guide to lockdown policy by the government and resource management by the hospital administrators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge