Sven Nomm
PointExplainer: Towards Transparent Parkinson's Disease Diagnosis
May 04, 2025Abstract:Deep neural networks have shown potential in analyzing digitized hand-drawn signals for early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. However, the lack of clear interpretability in existing diagnostic methods presents a challenge to clinical trust. In this paper, we propose PointExplainer, an explainable diagnostic strategy to identify hand-drawn regions that drive model diagnosis. Specifically, PointExplainer assigns discrete attribution values to hand-drawn segments, explicitly quantifying their relative contributions to the model's decision. Its key components include: (i) a diagnosis module, which encodes hand-drawn signals into 3D point clouds to represent hand-drawn trajectories, and (ii) an explanation module, which trains an interpretable surrogate model to approximate the local behavior of the black-box diagnostic model. We also introduce consistency measures to further address the issue of faithfulness in explanations. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets and a newly constructed dataset show that PointExplainer can provide intuitive explanations with no diagnostic performance degradation. The source code is available at https://github.com/chaoxuewang/PointExplainer.
LSTM-CNN: An efficient diagnostic network for Parkinson's disease utilizing dynamic handwriting analysis
Nov 20, 2023


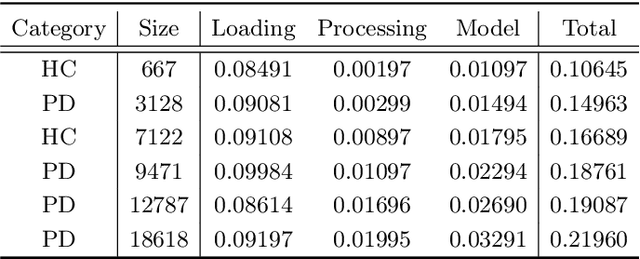
Abstract:Background and objectives: Dynamic handwriting analysis, due to its non-invasive and readily accessible nature, has recently emerged as a vital adjunctive method for the early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. In this study, we design a compact and efficient network architecture to analyse the distinctive handwriting patterns of patients' dynamic handwriting signals, thereby providing an objective identification for the Parkinson's disease diagnosis. Methods: The proposed network is based on a hybrid deep learning approach that fully leverages the advantages of both long short-term memory (LSTM) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Specifically, the LSTM block is adopted to extract the time-varying features, while the CNN-based block is implemented using one-dimensional convolution for low computational cost. Moreover, the hybrid model architecture is continuously refined under ablation studies for superior performance. Finally, we evaluate the proposed method with its generalization under a five-fold cross-validation, which validates its efficiency and robustness. Results: The proposed network demonstrates its versatility by achieving impressive classification accuracies on both our new DraWritePD dataset ($96.2\%$) and the well-established PaHaW dataset ($90.7\%$). Moreover, the network architecture also stands out for its excellent lightweight design, occupying a mere $0.084$M of parameters, with a total of only $0.59$M floating-point operations. It also exhibits near real-time CPU inference performance, with inference times ranging from $0.106$ to $0.220$s. Conclusions: We present a series of experiments with extensive analysis, which systematically demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed hybrid neural network in extracting distinctive handwriting patterns for precise diagnosis of Parkinson's disease.
A Light-weight CNN Model for Efficient Parkinson's Disease Diagnostics
Feb 02, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, deep learning methods have achieved great success in various fields due to their strong performance in practical applications. In this paper, we present a light-weight neural network for Parkinson's disease diagnostics, in which a series of hand-drawn data are collected to distinguish Parkinson's disease patients from healthy control subjects. The proposed model consists of a convolution neural network (CNN) cascading to long-short-term memory (LSTM) to adapt the characteristics of collected time-series signals. To make full use of their advantages, a multilayered LSTM model is firstly used to enrich features which are then concatenated with raw data and fed into a shallow one-dimensional (1D) CNN model for efficient classification. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves a high-quality diagnostic result over multiple evaluation metrics with much fewer parameters and operations, outperforming conventional methods such as support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF), lightgbm (LGB) and CNN-based methods.
Towards the Linear Algebra Based Taxonomy of XAI Explanations
Jan 30, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes an alternative approach to the basic taxonomy of explanations produced by explainable artificial intelligence techniques. Methods of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) were developed to answer the question why a certain prediction or estimation was made, preferably in terms easy to understand by the human agent. XAI taxonomies proposed in the literature mainly concentrate their attention on distinguishing explanations with respect to involving the human agent, which makes it complicated to provide a more mathematical approach to distinguish and compare different explanations. This paper narrows its attention to the cases where the data set of interest belongs to $\mathbb{R} ^n$ and proposes a simple linear algebra-based taxonomy for local explanations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge