Sumanshu Agarwal
Parametric Scaling of Preprocessing assisted U-net Architecture for Improvised Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Mar 18, 2022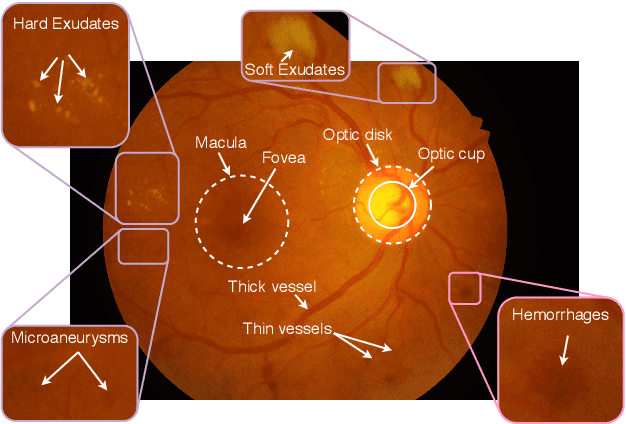
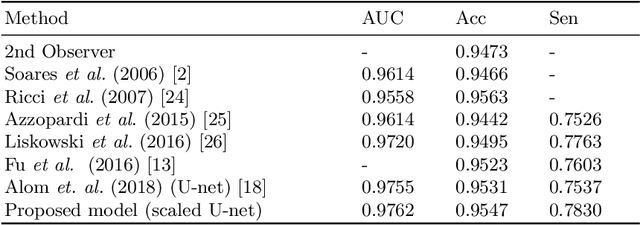
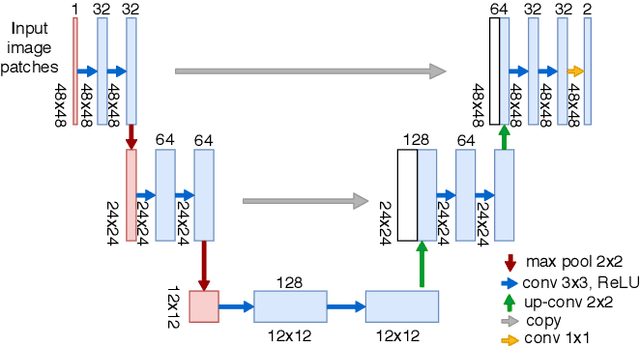

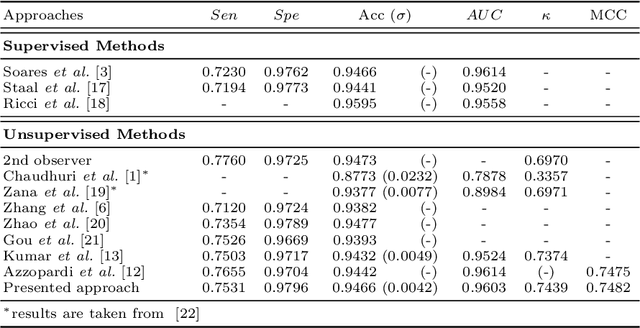
Abstract:Extracting blood vessels from retinal fundus images plays a decisive role in diagnosing the progression in pertinent diseases. In medical image analysis, vessel extraction is a semantic binary segmentation problem, where blood vasculature needs to be extracted from the background. Here, we present an image enhancement technique based on the morphological preprocessing coupled with a scaled U-net architecture. Despite a relatively less number of trainable network parameters, the scaled version of U-net architecture provides better performance compare to other methods in the domain. We validated the proposed method on retinal fundus images from the DRIVE database. A significant improvement as compared to the other algorithms in the domain, in terms of the area under ROC curve (>0.9762) and classification accuracy (>95.47%) are evident from the results. Furthermore, the proposed method is resistant to the central vessel reflex while sensitive to detect blood vessels in the presence of background items viz. exudates, optic disc, and fovea.
Application of Top-hat Transformation for Enhanced Blood Vessel Extraction
Mar 18, 2022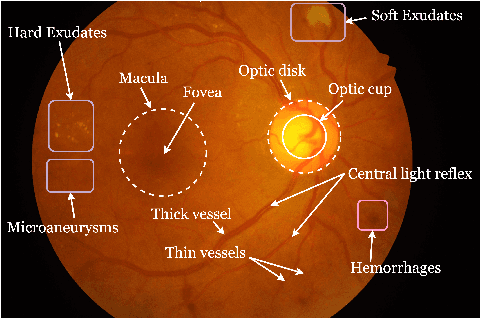
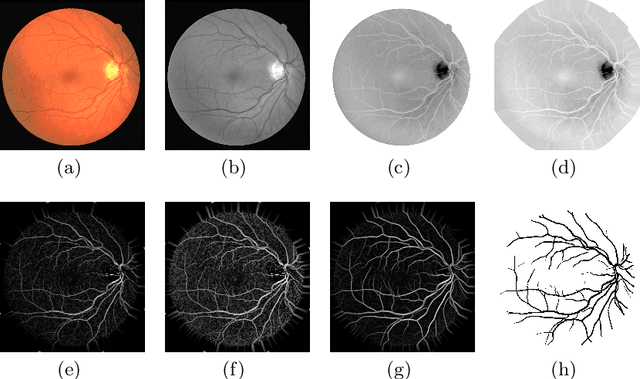
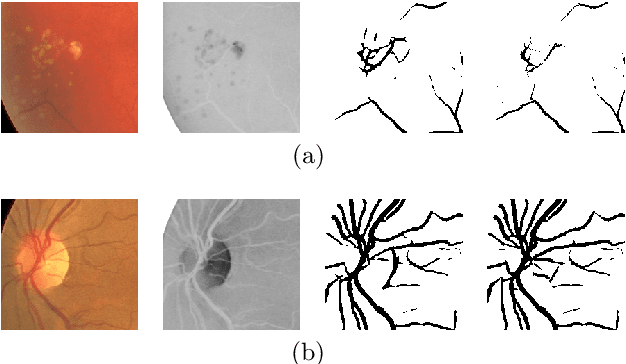
Abstract:In the medical domain, different computer-aided diagnosis systems have been proposed to extract blood vessels from retinal fundus images for the clinical treatment of vascular diseases. Accurate extraction of blood vessels from the fundus images using a computer-generated method can help the clinician to produce timely and accurate reports for the patient suffering from these diseases. In this article, we integrate top-hat based preprocessing approach with fine-tuned B-COSFIRE filter to achieve more accurate segregation of blood vessel pixels from the background. The use of top-hat transformation in the preprocessing stage enhances the efficacy of the algorithm to extract blood vessels in presence of structures like fovea, exudates, haemorrhages, etc. Furthermore, to reduce the false positives, small clusters of blood vessel pixels are removed in the postprocessing stage. Further, we find that the proposed algorithm is more efficient as compared to various modern algorithms reported in the literature.
Blood Vessel Detection using Modified Multiscale MF-FDOG Filters for Diabetic Retinopathy
Oct 26, 2019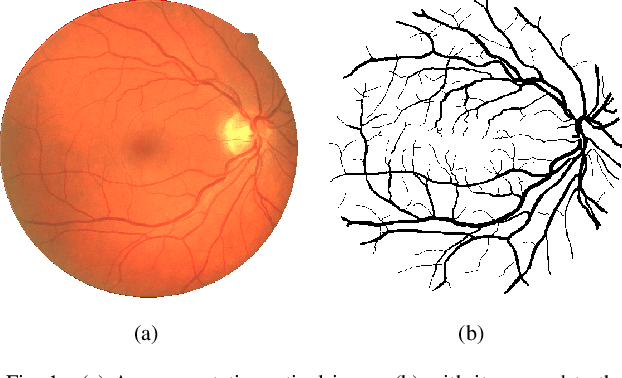
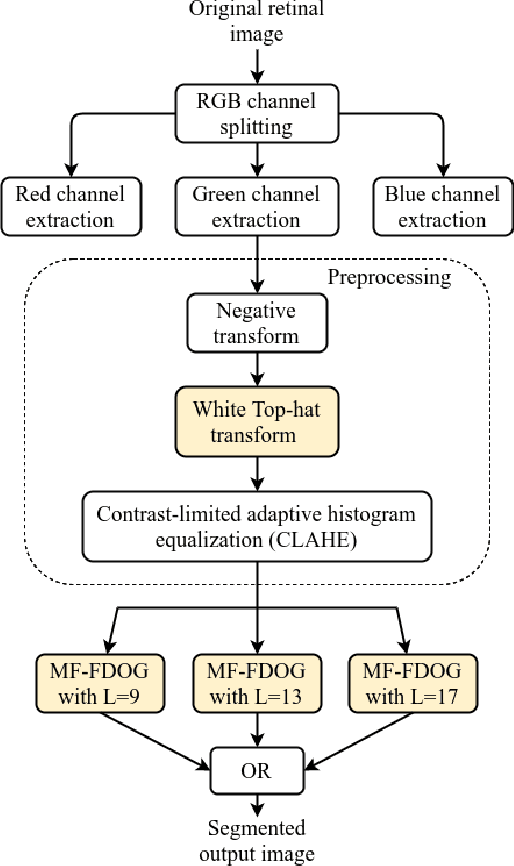
Abstract:Blindness in diabetic patients caused by retinopathy (characterized by an increase in the diameter and new branches of the blood vessels inside the retina) is a grave concern. Many efforts have been made for the early detection of the disease using various image processing techniques on retinal images. However, most of the methods are plagued with the false detection of the blood vessel pixels. Given that, here, we propose a modified matched filter with the first derivative of Gaussian. The method uses the top-hat transform and contrast limited histogram equalization. Further, we segment the modified multiscale matched filter response by using a binary threshold obtained from the first derivative of Gaussian. The method was assessed on a publicly available database (DRIVE database). As anticipated, the proposed method provides a higher accuracy compared to the literature. Moreover, a lesser false detection from the existing matched filters and its variants have been observed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge