Sukjin Han
How Well Do LLMs Predict Human Behavior? A Measure of their Pretrained Knowledge
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used to predict human behavior. We propose a measure for evaluating how much knowledge a pretrained LLM brings to such a prediction: its equivalent sample size, defined as the amount of task-specific data needed to match the predictive accuracy of the LLM. We estimate this measure by comparing the prediction error of a fixed LLM in a given domain to that of flexible machine learning models trained on increasing samples of domain-specific data. We further provide a statistical inference procedure by developing a new asymptotic theory for cross-validated prediction error. Finally, we apply this method to the Panel Study of Income Dynamics. We find that LLMs encode considerable predictive information for some economic variables but much less for others, suggesting that their value as substitutes for domain-specific data differs markedly across settings.
Copyright and Competition: Estimating Supply and Demand with Unstructured Data
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Copyright policies play a pivotal role in protecting the intellectual property of creators and companies in creative industries. The advent of cost-reducing technologies, such as generative AI, in these industries calls for renewed attention to the role of these policies. This paper studies product positioning and competition in a market of creatively differentiated products and the competitive and welfare effects of copyright protection. A common feature of products with creative elements is that their key attributes (e.g., images and text) are unstructured and thus high-dimensional. We focus on a stylized design product, fonts, and use data from the world's largest online marketplace for fonts. We use neural network embeddings to quantify unstructured attributes and measure the visual similarity. We show that this measure closely aligns with actual human perception. Based on this measure, we empirically find that competitions occur locally in the visual characteristics space. We then develop a structural model for supply and demand that integrate the embeddings. Through counterfactual analyses, we find that local copyright protection can enhance consumer welfare when products are relocated, and the interplay between copyright and cost-reducing technologies is essential in determining an optimal policy for social welfare. We believe that the embedding analysis and empirical models introduced in this paper can be applicable to a range of industries where unstructured data captures essential features of products and markets.
Mining Causality: AI-Assisted Search for Instrumental Variables
Sep 21, 2024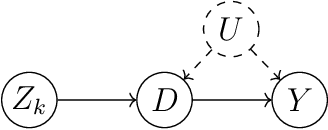
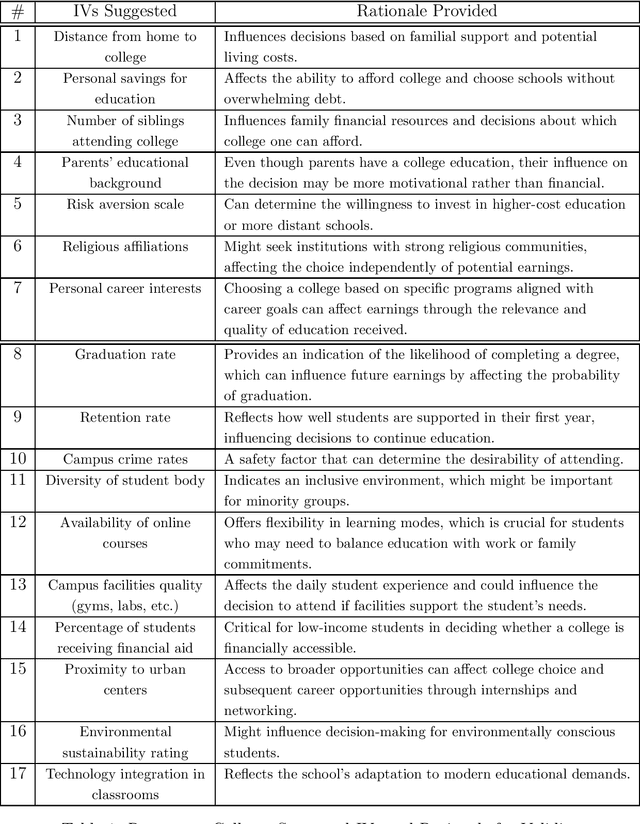
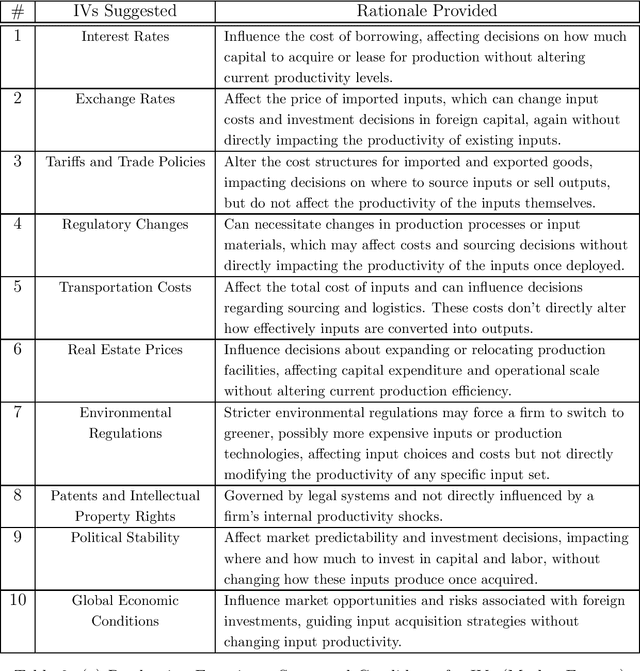
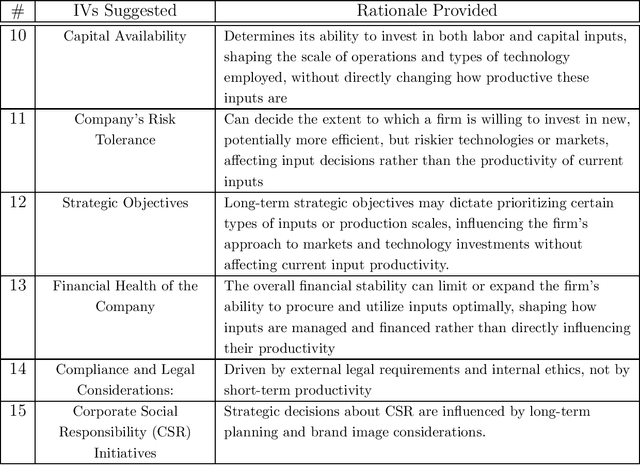
Abstract:The instrumental variables (IVs) method is a leading empirical strategy for causal inference. Finding IVs is a heuristic and creative process, and justifying its validity (especially exclusion restrictions) is largely rhetorical. We propose using large language models (LLMs) to search for new IVs through narratives and counterfactual reasoning, similar to how a human researcher would. The stark difference, however, is that LLMs can accelerate this process exponentially and explore an extremely large search space. We demonstrate how to construct prompts to search for potentially valid IVs. We argue that multi-step prompting is useful and role-playing prompts are suitable for mimicking the endogenous decisions of economic agents. We apply our method to three well-known examples in economics: returns to schooling, production functions, and peer effects. We then extend our strategy to finding (i) control variables in regression and difference-in-differences and (ii) running variables in regression discontinuity designs.
Individualized Treatment Allocations with Distributional Welfare
Nov 27, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we explore optimal treatment allocation policies that target distributional welfare. Most literature on treatment choice has considered utilitarian welfare based on the conditional average treatment effect (ATE). While average welfare is intuitive, it may yield undesirable allocations especially when individuals are heterogeneous (e.g., with outliers) - the very reason individualized treatments were introduced in the first place. This observation motivates us to propose an optimal policy that allocates the treatment based on the conditional \emph{quantile of individual treatment effects} (QoTE). Depending on the choice of the quantile probability, this criterion can accommodate a policymaker who is either prudent or negligent. The challenge of identifying the QoTE lies in its requirement for knowledge of the joint distribution of the counterfactual outcomes, which is generally hard to recover even with experimental data. Therefore, we introduce minimax optimal policies that are robust to model uncertainty. We then propose a range of identifying assumptions under which we can point or partially identify the QoTE. We establish the asymptotic bound on the regret of implementing the proposed policies. We consider both stochastic and deterministic rules. In simulations and two empirical applications, we compare optimal decisions based on the QoTE with decisions based on other criteria.
Shapes as Product Differentiation: Neural Network Embedding in the Analysis of Markets for Fonts
Jul 06, 2021
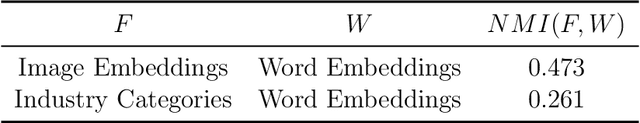
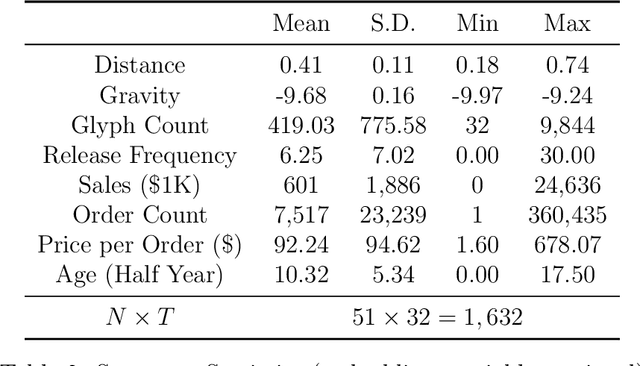
Abstract:Many differentiated products have key attributes that are unstructured and thus high-dimensional (e.g., design, text). Instead of treating unstructured attributes as unobservables in economic models, quantifying them can be important to answer interesting economic questions. To propose an analytical framework for this type of products, this paper considers one of the simplest design products -- fonts -- and investigates merger and product differentiation using an original dataset from the world's largest online marketplace for fonts. We quantify font shapes by constructing embeddings from a deep convolutional neural network. Each embedding maps a font's shape onto a low-dimensional vector. In the resulting product space, designers are assumed to engage in Hotelling-type spatial competition. From the image embeddings, we construct two alternative measures that capture the degree of design differentiation. We then study the causal effects of a merger on the merging firm's creative decisions using the constructed measures in a synthetic control method. We find that the merger causes the merging firm to increase the visual variety of font design. Notably, such effects are not captured when using traditional measures for product offerings (e.g., specifications and the number of products) constructed from structured data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge