Soumi Ray
An Automatic Method for Complete Brain Matter Segmentation from Multislice CT scan
Oct 22, 2018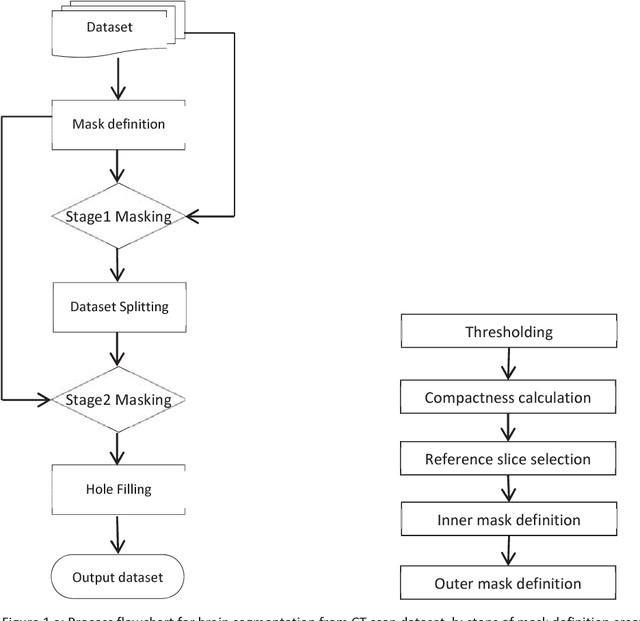
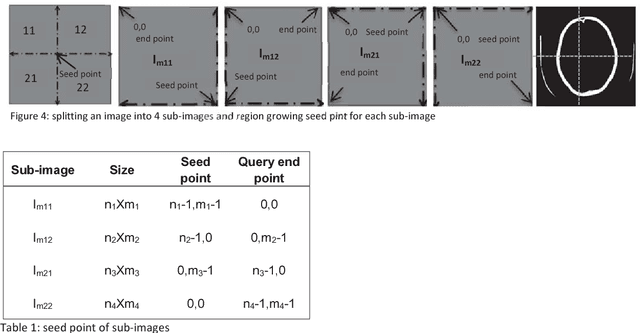
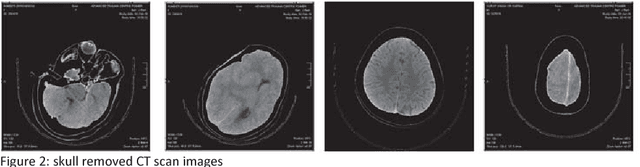
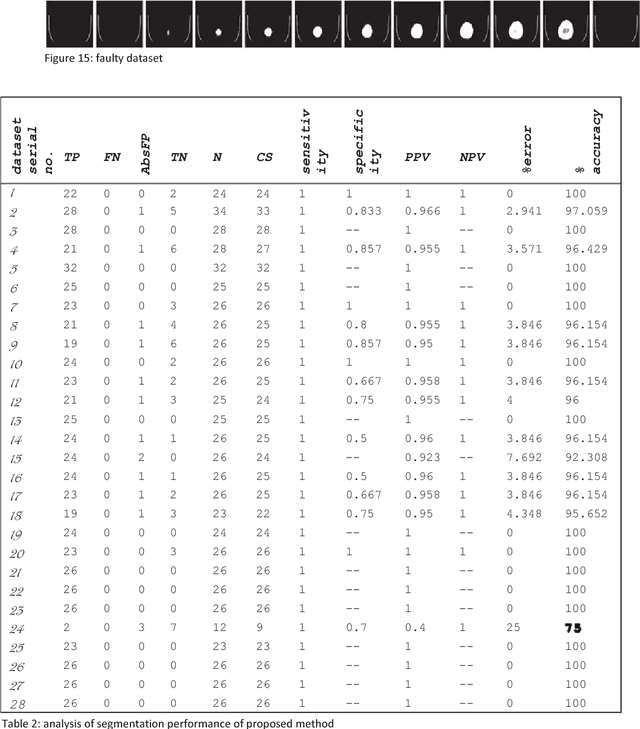
Abstract:Computed tomography imaging is well accepted for its imaging speed, image contrast & resolution and cost. Thus it has wide use in detection and diagnosis of brain diseases. But unfortunately reported works on CT segmentation is not very significant. In this paper, a robust automatic segmentation system is presented which is capable of segment complete brain matter from CT slices, without any lose in information. The proposed method is simple, fast, accurate and completely automatic. It can handle multislice CT scan in single run. From a given multislice CT dataset, one slice is selected automatically to form masks for segmentation. Two types of masks are created to handle nasal slices in a better way. Masks are created from selected reference slice using automatic seed point selection and region growing technique. One mask is designed for brain matter and another includes the skull of the reference slice. This second mask is used as global reference mask for all slices whereas the brain matter mask is implemented on only adjacent slices and continuously modified for better segmentation. Slices in given dataset are divided into two batches, before reference slice and after reference slice. Each batch segmented separately. Successive propagation of brain matter mask has demonstrated very high potential in reported segmentation. Presented result shows highest sensitivity and more than 96% accuracy in all cases. Resulted segmented images can be used for any brain disease diagnosis or further image analysis.
Binary Image Features Proposed to Empower Computer Vision
Aug 14, 2018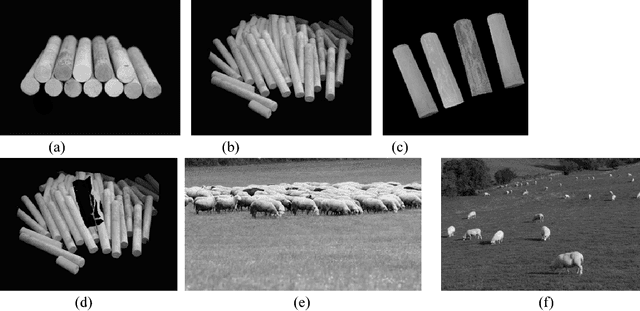
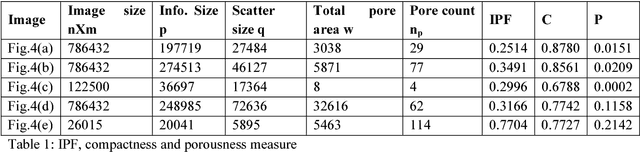

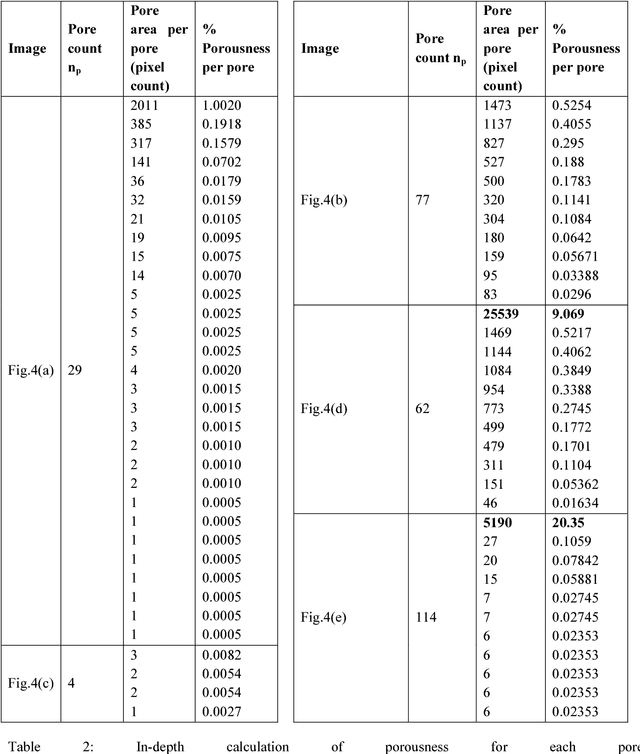
Abstract:This literature has proposed three fast and easy computable image features to improve computer vision by offering more human-like vision power. These features are not based on image pixels absolute or relative intensity; neither based on shape or colour. So, no complex pixel by pixel calculation is required. For human eyes, pixel by pixel calculation is like seeing an image with maximum zoom which is done only when a higher level of details is required. Normally, first we look at an image to get an overall idea about it to know whether it deserves further investigation or not. This capacity of getting an idea at a glance is analysed and three basic features are proposed to empower computer vision. Potential of proposed features is tested and established through different medical dataset. Achieved accuracy in classification demonstrates possibilities and potential of the use of the proposed features in image processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge