Sonia Bergamaschi
Face Landmark-based Speaker-Independent Audio-Visual Speech Enhancement in Multi-Talker Environments
Nov 06, 2018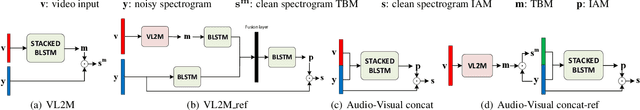
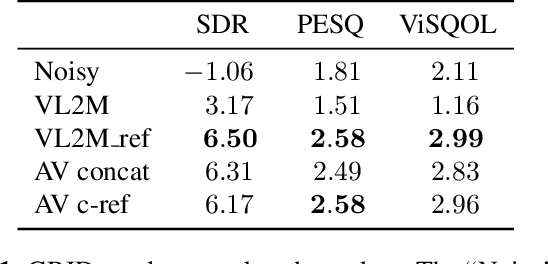
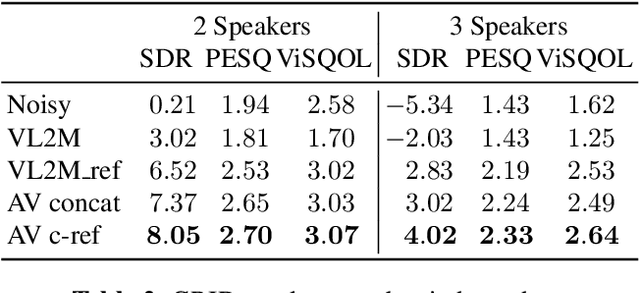
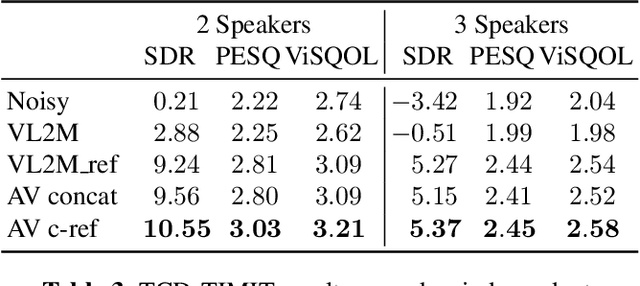
Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of enhancing the speech of a speaker of interest in a cocktail party scenario when visual information of the speaker of interest is available. Contrary to most previous studies, we do not learn visual features on the typically small audio-visual datasets, but use an already available face landmark detector (trained on a separate image dataset). The landmarks are used by LSTM-based models to generate time-frequency masks which are applied to the acoustic mixed-speech spectrogram. Results show that: (i) landmark motion features are very effective features for this task, (ii) similarly to previous work, reconstruction of the target speaker's spectrogram mediated by masking is significantly more accurate than direct spectrogram reconstruction, and (iii) the best masks depend on both motion landmark features and the input mixed-speech spectrogram. To the best of our knowledge, our proposed models are the first models trained and evaluated on the limited size GRID and TCD-TIMIT datasets, that achieve speaker-independent speech enhancement in a multi-talker setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge