Solomon Tesfamariam
State-of-the-Art Review of Design of Experiments for Physics-Informed Deep Learning
Feb 13, 2022

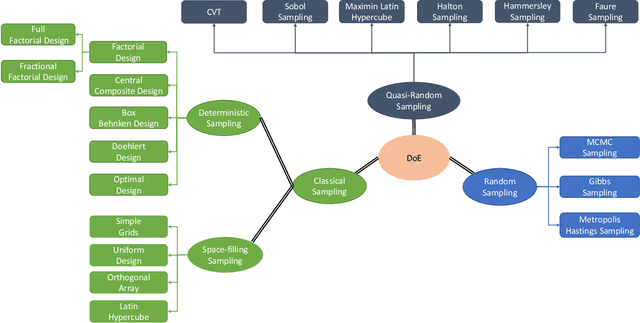
Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive review of the design of experiments used in the surrogate models. In particular, this study demonstrates the necessity of the design of experiment schemes for the Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN), which belongs to the supervised learning class. Many complex partial differential equations (PDEs) do not have any analytical solution; only numerical methods are used to solve the equations, which is computationally expensive. In recent decades, PINN has gained popularity as a replacement for numerical methods to reduce the computational budget. PINN uses physical information in the form of differential equations to enhance the performance of the neural networks. Though it works efficiently, the choice of the design of experiment scheme is important as the accuracy of the predicted responses using PINN depends on the training data. In this study, five different PDEs are used for numerical purposes, i.e., viscous Burger's equation, Shr\"{o}dinger equation, heat equation, Allen-Cahn equation, and Korteweg-de Vries equation. A comparative study is performed to establish the necessity of the selection of a DoE scheme. It is seen that the Hammersley sampling-based PINN performs better than other DoE sample strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge