Silvia Chiacchiera
Multiscale modelling and simulation of physical systems as semiosis
Apr 01, 2020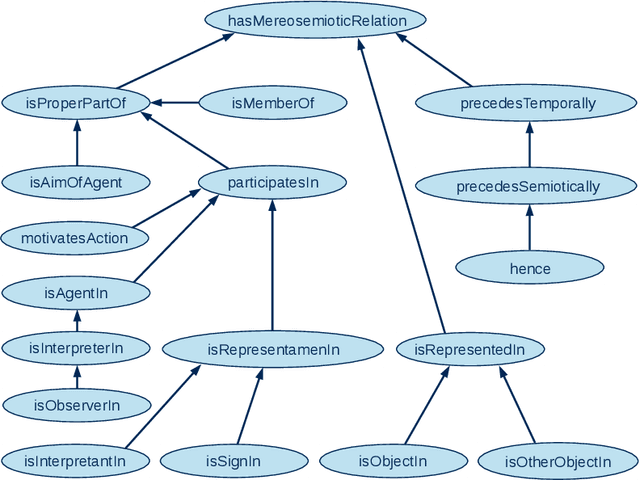
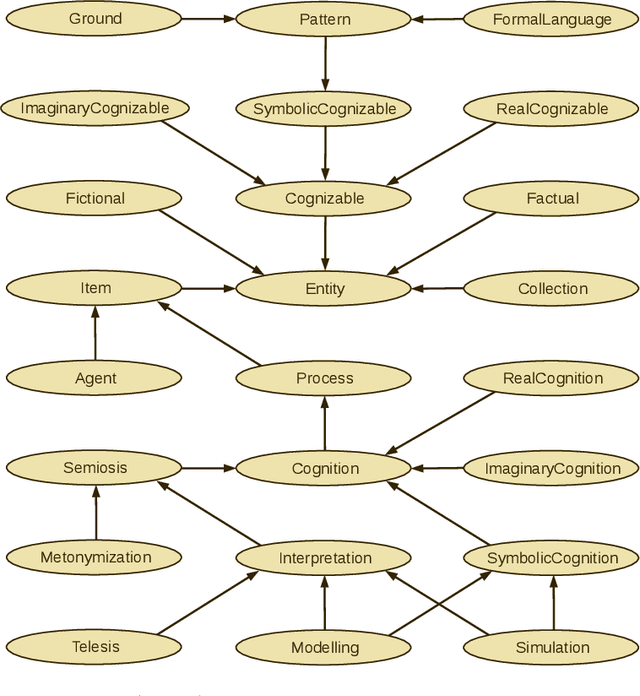
Abstract:It is explored how physicalist mereotopology and Peircean semiotics can be applied to represent models, simulations, and workflows in multiscale modelling and simulation of physical systems within a top-level ontology. It is argued that to conceptualize modelling and simulation in such a framework, two major types of semiosis need to be formalized and combined with each other: Interpretation, where a sign and a represented object yield an interpretant (another representamen for the same object), and metonymization, where the represented object and a sign are in a three-way relationship with another object to which the signification is transferred. It is outlined how the main elements of the pre-existing simulation workflow descriptions MODA and OSMO, i.e., use cases, models, solvers, and processors, can be aligned with a top-level ontology that implements this ontological paradigm, which is here referred to as mereosemiotic physicalism. Implications are discussed for the development of the European Materials and Modelling Ontology, an implementation of mereosemiotic physicalism.
Ontologies for the Virtual Materials Marketplace
Dec 03, 2019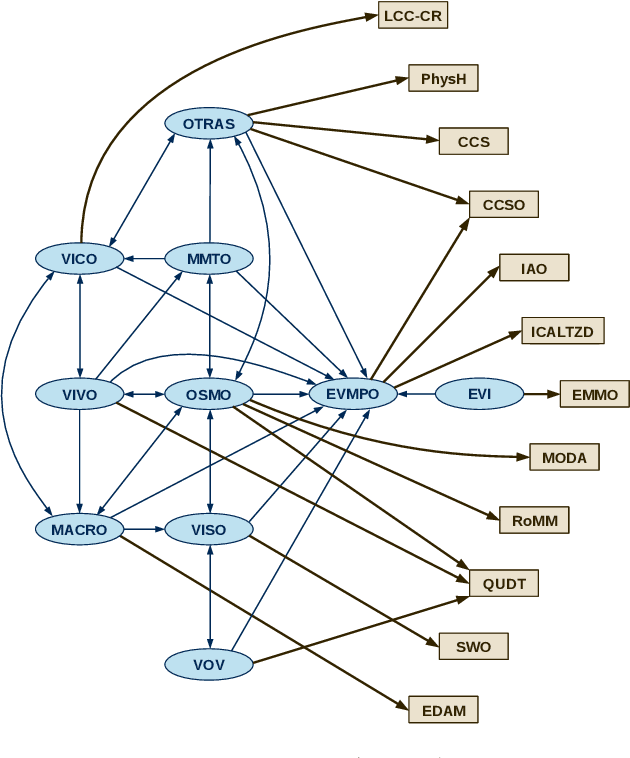
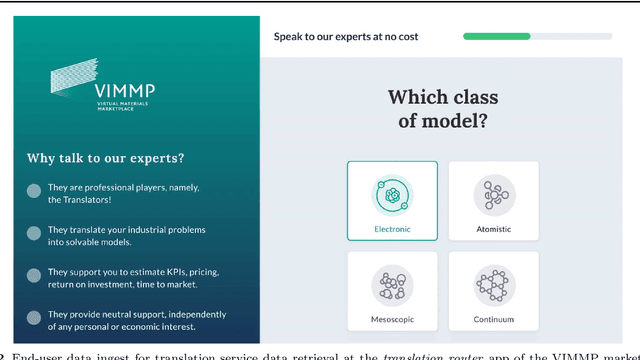
Abstract:The Virtual Materials Marketplace (VIMMP) project, which develops an open platform for providing and accessing services related to materials modelling, is presented with a focus on its ontology development and data technology aspects. Within VIMMP, a system of marketplace-level ontologies is developed to characterize services, models, and interactions between users; the European Materials and Modelling Ontology (EMMO), which is based on mereotopology following Varzi and semiotics following Peirce, is employed as a top-level ontology. The ontologies are used to annotate data that are stored in the ZONTAL Space component of VIMMP and to support the ingest and retrieval of data and metadata at the VIMMP marketplace frontend.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge