Sibi Chakkaravarthy Sethuraman
SimplyMime: A Control at Our Fingertips
Apr 22, 2023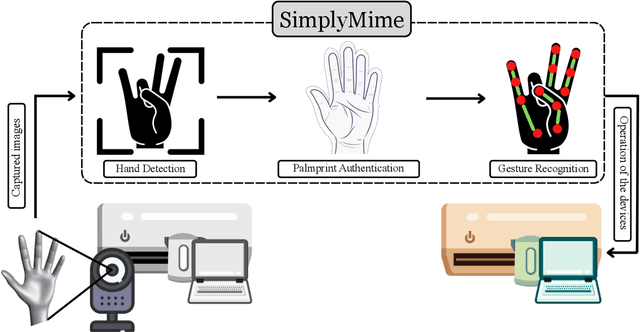
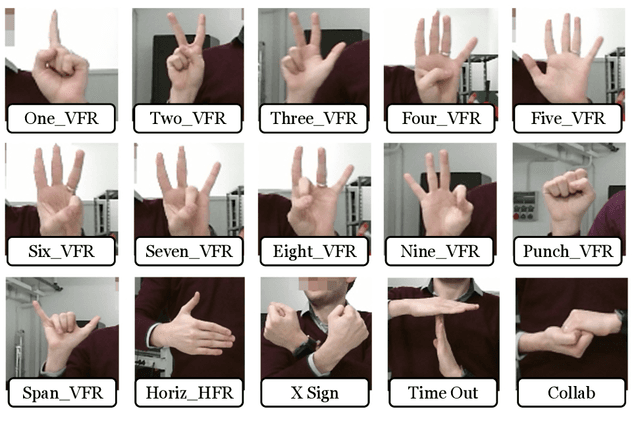
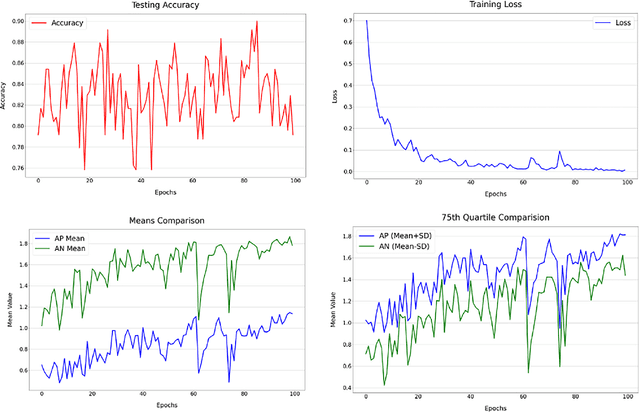
Abstract:The utilization of consumer electronics, such as televisions, set-top boxes, home theaters, and air conditioners, has become increasingly prevalent in modern society as technology continues to evolve. As new devices enter our homes each year, the accumulation of multiple infrared remote controls to operate them not only results in a waste of energy and resources, but also creates a cumbersome and cluttered environment for the user. This paper presents a novel system, named SimplyMime, which aims to eliminate the need for multiple remote controls for consumer electronics and provide the user with intuitive control without the need for additional devices. SimplyMime leverages a dynamic hand gesture recognition architecture, incorporating Artificial Intelligence and Human-Computer Interaction, to create a sophisticated system that enables users to interact with a vast majority of consumer electronics with ease. Additionally, SimplyMime has a security aspect where it can verify and authenticate the user utilising the palmprint, which ensures that only authorized users can control the devices. The performance of the proposed method for detecting and recognizing gestures in a stream of motion was thoroughly tested and validated using multiple benchmark datasets, resulting in commendable accuracy levels. One of the distinct advantages of the proposed method is its minimal computational power requirements, making it highly adaptable and reliable in a wide range of circumstances. The paper proposes incorporating this technology into all consumer electronic devices that currently require a secondary remote for operation, thus promoting a more efficient and sustainable living environment.
EfficientWord-Net: An Open Source Hotword Detection Engine based on One-shot Learning
Oct 31, 2021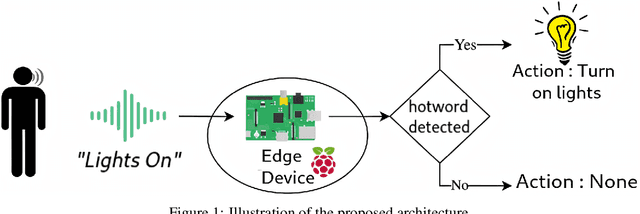
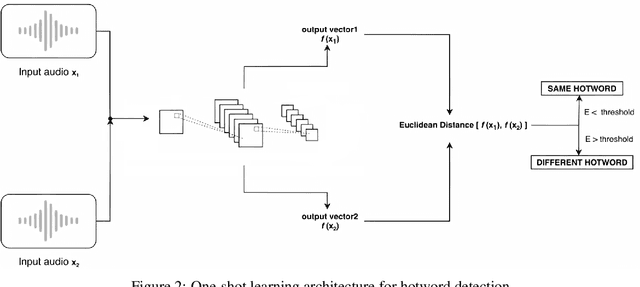
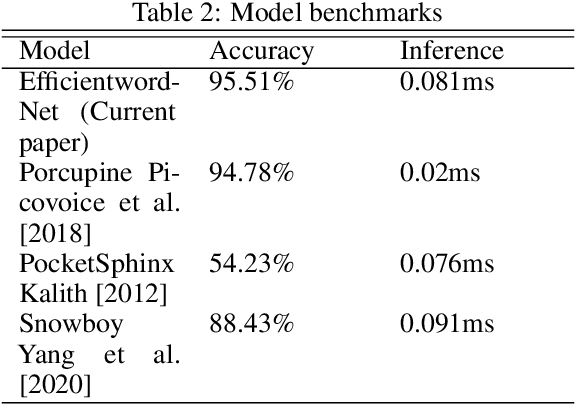
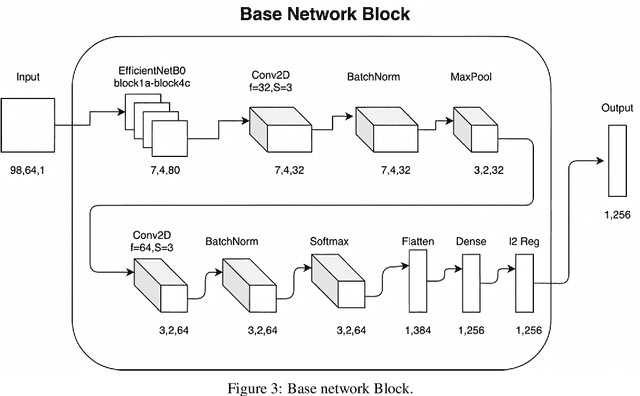
Abstract:Voice assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa etc. are used widely across the globe for home automation, these require the use of special phrases also known as hotwords to wake it up and perform an action like "Hey Alexa!", "Ok Google!" and "Hey Siri!" etc. These hotwords are detected with lightweight real-time engines whose purpose is to detect the hotwords uttered by the user. This paper presents the design and implementation of a hotword detection engine based on one-shot learning which detects the hotword uttered by the user in real-time with just one or few training samples of the hotword. This approach is efficient when compared to existing implementations because the process of adding a new hotword in the existing systems requires enormous amounts of positive and negative training samples and the model needs to retrain for every hotword. This makes the existing implementations inefficient in terms of computation and cost. The architecture proposed in this paper has achieved an accuracy of 94.51%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge