Shounak Ghatak
DPHGNN: A Dual Perspective Hypergraph Neural Networks
May 26, 2024
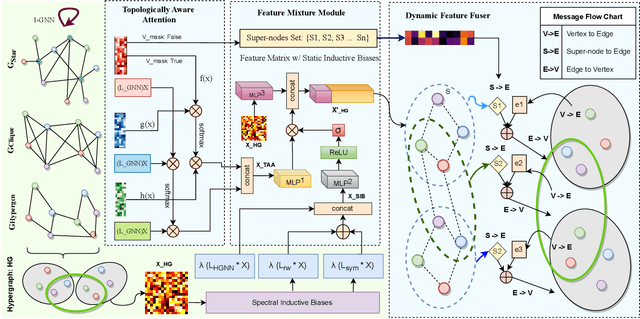

Abstract:Message passing on hypergraphs has been a standard framework for learning higher-order correlations between hypernodes. Recently-proposed hypergraph neural networks (HGNNs) can be categorized into spatial and spectral methods based on their design choices. In this work, we analyze the impact of change in hypergraph topology on the suboptimal performance of HGNNs and propose DPHGNN, a novel dual-perspective HGNN that introduces equivariant operator learning to capture lower-order semantics by inducing topology-aware spatial and spectral inductive biases. DPHGNN employs a unified framework to dynamically fuse lower-order explicit feature representations from the underlying graph into the super-imposed hypergraph structure. We benchmark DPHGNN over eight benchmark hypergraph datasets for the semi-supervised hypernode classification task and obtain superior performance compared to seven state-of-the-art baselines. We also provide a theoretical framework and a synthetic hypergraph isomorphism test to express the power of spatial HGNNs and quantify the expressivity of DPHGNN beyond the Generalized Weisfeiler Leman (1-GWL) test. Finally, DPHGNN was deployed by our partner e-commerce company for the Return-to-Origin (RTO) prediction task, which shows ~7% higher macro F1-Score than the best baseline.
Dish detection in food platters: A framework for automated diet logging and nutrition management
May 12, 2023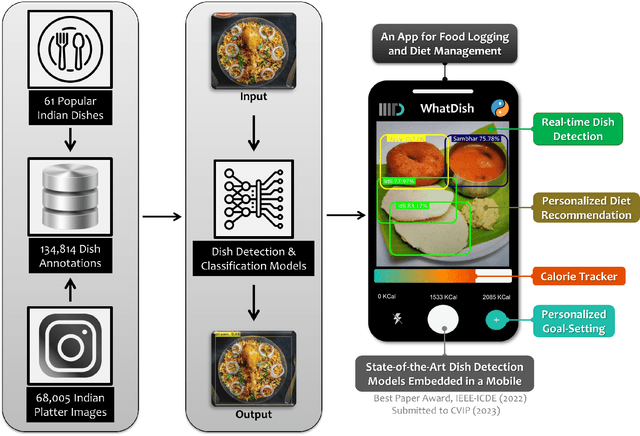

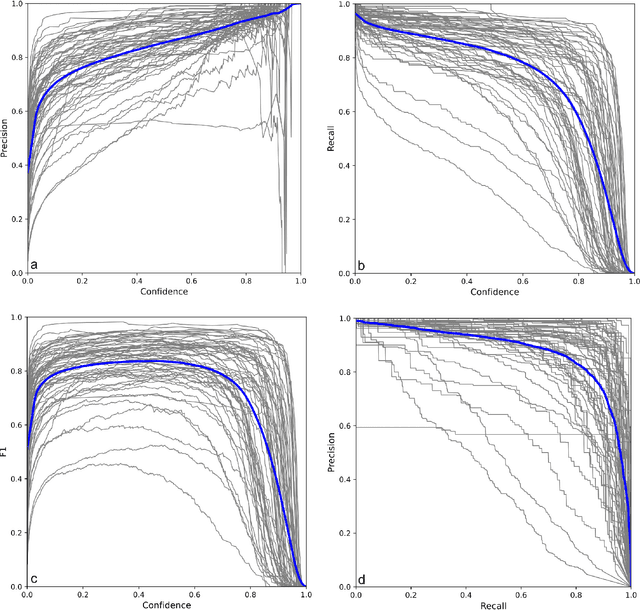
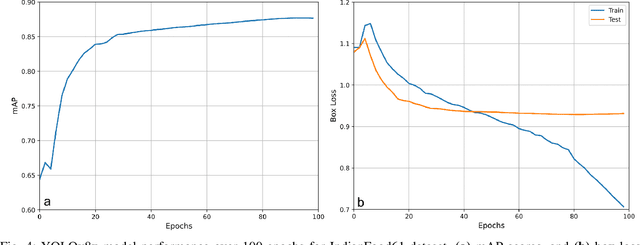
Abstract:Diet is central to the epidemic of lifestyle disorders. Accurate and effortless diet logging is one of the significant bottlenecks for effective diet management and calorie restriction. Dish detection from food platters is a challenging problem due to a visually complex food layout. We present an end-to-end computational framework for diet management, from data compilation, annotation, and state-of-the-art model identification to its mobile app implementation. As a case study, we implement the framework in the context of Indian food platters known for their complex presentation that poses a challenge for the automated detection of dishes. Starting with the 61 most popular Indian dishes, we identify the state-of-the-art model through a comparative analysis of deep-learning-based object detection architectures. Rooted in a meticulous compilation of 68,005 platter images with 134,814 manual dish annotations, we first compare ten architectures for multi-label classification to identify ResNet152 (mAP=84.51%) as the best model. YOLOv8x (mAP=87.70%) emerged as the best model architecture for dish detection among the eight deep-learning models implemented after a thorough performance evaluation. By comparing with the state-of-the-art model for the IndianFood10 dataset, we demonstrate the superior object detection performance of YOLOv8x for this subset and establish Resnet152 as the best architecture for multi-label classification. The models thus trained on richly annotated data can be extended to include dishes from across global cuisines. The proposed framework is demonstrated through a proof-of-concept mobile application with diverse applications for diet logging, food recommendation systems, nutritional interventions, and mitigation of lifestyle disorders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge