Shoko Niwa
Speech privacy-preserving methods using secret key for convolutional neural network models and their robustness evaluation
Aug 07, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose privacy-preserving methods with a secret key for convolutional neural network (CNN)-based models in speech processing tasks. In environments where untrusted third parties, like cloud servers, provide CNN-based systems, ensuring the privacy of speech queries becomes essential. This paper proposes encryption methods for speech queries using secret keys and a model structure that allows for encrypted queries to be accepted without decryption. Our approach introduces three types of secret keys: Shuffling, Flipping, and random orthogonal matrix (ROM). In experiments, we demonstrate that when the proposed methods are used with the correct key, identification performance did not degrade. Conversely, when an incorrect key is used, the performance significantly decreased. Particularly, with the use of ROM, we show that even with a relatively small key space, high privacy-preserving performance can be maintained many speech processing tasks. Furthermore, we also demonstrate the difficulty of recovering original speech from encrypted queries in various robustness evaluations.
A privacy-preserving method using secret key for convolutional neural network-based speech classification
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we propose a privacy-preserving method with a secret key for convolutional neural network (CNN)-based speech classification tasks. Recently, many methods related to privacy preservation have been developed in image classification research fields. In contrast, in speech classification research fields, little research has considered these risks. To promote research on privacy preservation for speech classification, we provide an encryption method with a secret key in CNN-based speech classification systems. The encryption method is based on a random matrix with an invertible inverse. The encrypted speech data with a correct key can be accepted by a model with an encrypted kernel generated using an inverse matrix of a random matrix. Whereas the encrypted speech data is strongly distorted, the classification tasks can be correctly performed when a correct key is provided. Additionally, in this paper, we evaluate the difficulty of reconstructing the original information from the encrypted spectrograms and waveforms. In our experiments, the proposed encryption methods are performed in automatic speech recognition~(ASR) and automatic speaker verification~(ASV) tasks. The results show that the encrypted data can be used completely the same as the original data when a correct secret key is provided in the transformer-based ASR and x-vector-based ASV with self-supervised front-end systems. The robustness of the encrypted data against reconstruction attacks is also illustrated.
A Detection Method of Temporally Operated Videos Using Robust Hashing
Aug 11, 2022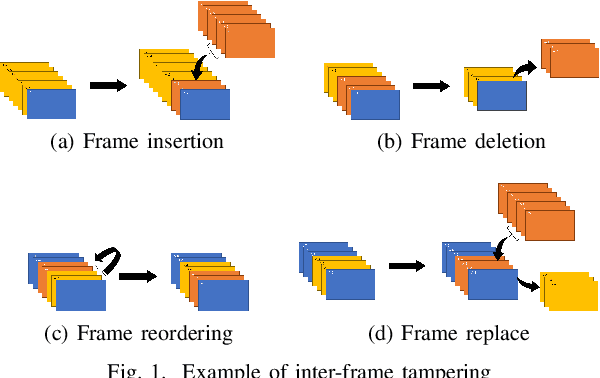
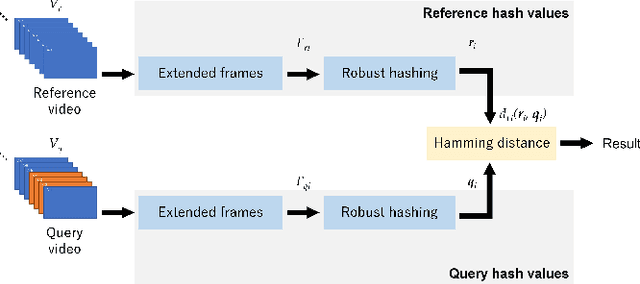


Abstract:SNS providers are known to carry out the recompression and resizing of uploaded videos/images, but most conventional methods for detecting tampered videos/images are not robust enough against such operations. In addition, videos are temporally operated such as the insertion of new frames and the permutation of frames, of which operations are difficult to be detected by using conventional methods. Accordingly, in this paper, we propose a novel method with a robust hashing algorithm for detecting temporally operated videos even when applying resizing and compression to the videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge