Shi-Xuan Zhao
Learning to Adapt to Light
Feb 16, 2022
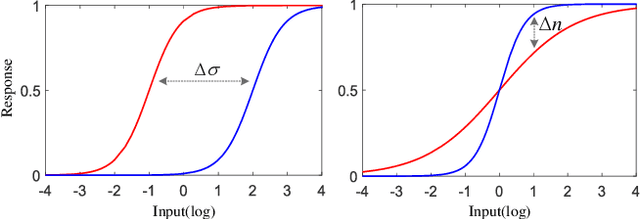
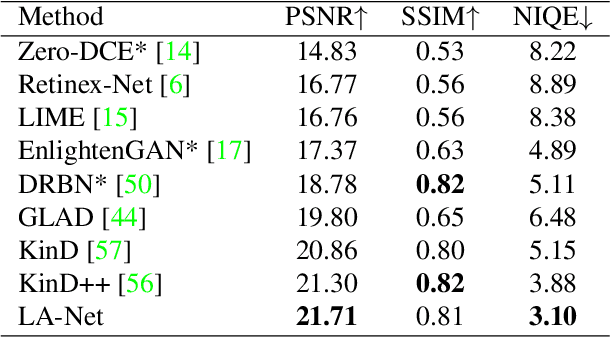
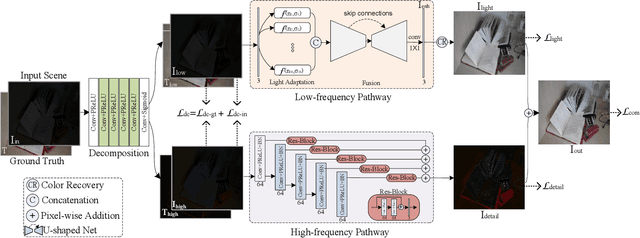
Abstract:Light adaptation or brightness correction is a key step in improving the contrast and visual appeal of an image. There are multiple light-related tasks (for example, low-light enhancement and exposure correction) and previous studies have mainly investigated these tasks individually. However, it is interesting to consider whether these light-related tasks can be executed by a unified model, especially considering that our visual system adapts to external light in such way. In this study, we propose a biologically inspired method to handle light-related image-enhancement tasks with a unified network (called LA-Net). First, a frequency-based decomposition module is designed to decouple the common and characteristic sub-problems of light-related tasks into two pathways. Then, a new module is built inspired by biological visual adaptation to achieve unified light adaptation in the low-frequency pathway. In addition, noise suppression or detail enhancement is achieved effectively in the high-frequency pathway regardless of the light levels. Extensive experiments on three tasks -- low-light enhancement, exposure correction, and tone mapping -- demonstrate that the proposed method almost obtains state-of-the-art performance compared with recent methods designed for these individual tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge