Sharath Srivatsa
Characterizing Latent Perspectives of Media Houses Towards Public Figures
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:Media houses reporting on public figures, often come with their own biases stemming from their respective worldviews. A characterization of these underlying patterns helps us in better understanding and interpreting news stories. For this, we need diverse or subjective summarizations, which may not be amenable for classifying into predefined class labels. This work proposes a zero-shot approach for non-extractive or generative characterizations of person entities from a corpus using GPT-2. We use well-articulated articles from several well-known news media houses as a corpus to build a sound argument for this approach. First, we fine-tune a GPT-2 pre-trained language model with a corpus where specific person entities are characterized. Second, we further fine-tune this with demonstrations of person entity characterizations, created from a corpus of programmatically constructed characterizations. This twice fine-tuned model is primed with manual prompts consisting of entity names that were not previously encountered in the second fine-tuning, to generate a simple sentence about the entity. The results were encouraging, when compared against actual characterizations from the corpus.
Zero-shot Entity and Tweet Characterization with Designed Conditional Prompts and Contexts
Apr 18, 2022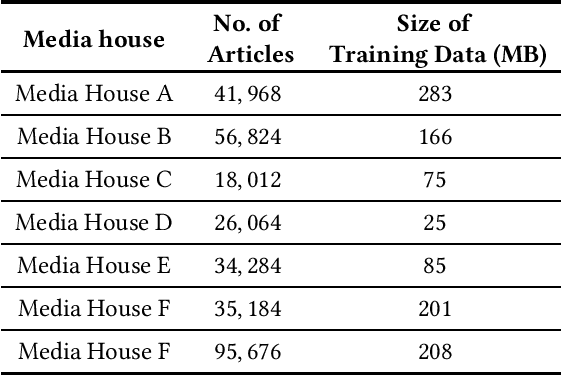

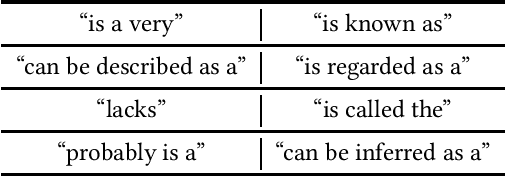
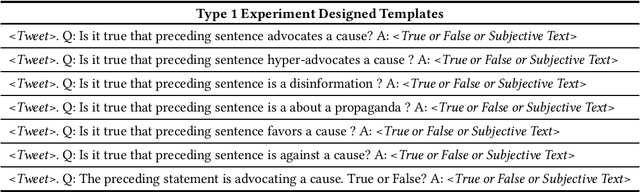
Abstract:Online news and social media have been the de facto mediums to disseminate information globally from the beginning of the last decade. However, bias in content and purpose of intentions are not regulated, and managing bias is the responsibility of content consumers. In this regard, understanding the stances and biases of news sources towards specific entities becomes important. To address this problem, we use pretrained language models, which have been shown to bring about good results with no task-specific training or few-shot training. In this work, we approach the problem of characterizing Named Entities and Tweets as an open-ended text classification and open-ended fact probing problem.We evaluate the zero-shot language model capabilities of Generative Pretrained Transformer 2 (GPT-2) to characterize Entities and Tweets subjectively with human psychology-inspired and logical conditional prefixes and contexts. First, we fine-tune the GPT-2 model on a sufficiently large news corpus and evaluate subjective characterization of popular entities in the corpus by priming with prefixes. Second, we fine-tune GPT-2 with a Tweets corpus from a few popular hashtags and evaluate characterizing tweets by priming the language model with prefixes, questions, and contextual synopsis prompts. Entity characterization results were positive across measures and human evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge