Shamin Achari
Watermark-Based Code Construction for Finite-State Markov Channel with Synchronisation Errors
Jul 20, 2022



Abstract:With advancements in telecommunications, data transmission over increasingly harsher channels that produce synchronisation errors is inevitable. Coding schemes for such channels are available through techniques such as the Davey-MacKay watermark coding; however, this is limited to memoryless channel estimates. Memory must be accounted for to ensure a realistic channel approximation - similar to a Finite State Markov Chain or Fritchman Model. A novel code construction and decoder are developed to correct synchronisation errors while considering the channel's correlated memory effects by incorporating ideas from the watermark scheme and memory modelling. Simulation results show that the proposed code construction and decoder rival the first and second-order Davey-MacKay type watermark decoder and even perform slightly better when the inner-channel capacity is higher than 0.9. The proposed system and decoder may prove helpful in fields such as free-space optics and possibly molecular communication, where harsh channels are used for communication.
Self-Synchronising On-Off-Keying Visible Light Communication System For Intra and Inter-Vehicle Data Transmission
Jan 13, 2021


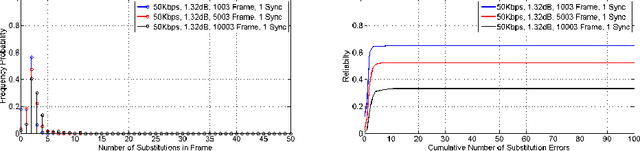
Abstract:Visible Light Communication (VLC) is a current technology which allows data to be transmitted by modulating information onto a light source. It has many advantages over traditional radio frequency communication and up to 10,000 times larger bandwidth. Existing research in visible light communication assumes a synchronised channel, however, this is not always easily achieved. In this paper, a novel synchronised intra and inter-vehicle VLC system is proposed to ensure reliable communication in both inter and intra-vehicle communication for Infotainment Systems (IS). The protocol achieves synchronisation at the symbol level using the transistor-transistor logic protocol and achieves frame synchronisations with markers. Consequently, the deployment of the protocol in both inter and intra-vehicle communication presents numerous advantages over existing data transmission processes. A practical application, where VLC is used for media streaming is also previewed. In addition, various regions of possible data transmission are determined with the intention to infer forward error correction schemes to ensure reliable communication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge