Shagun Sinha
Abstractive Text Summarization for Contemporary Sanskrit Prose: Issues and Challenges
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:This thesis presents Abstractive Text Summarization models for contemporary Sanskrit prose. The first chapter, titled Introduction, presents the motivation behind this work, the research questions, and the conceptual framework. Sanskrit is a low-resource inflectional language. The key research question that this thesis investigates is what the challenges in developing an abstractive TS for Sanskrit. To answer the key research questions, sub-questions based on four different themes have been posed in this work. The second chapter, Literature Review, surveys the previous works done. The third chapter, data preparation, answers the remaining three questions from the third theme. It reports the data collection and preprocessing challenges for both language model and summarization model trainings. The fourth chapter reports the training and inference of models and the results obtained therein. This research has initiated a pipeline for Sanskrit abstractive text summarization and has reported the challenges faced at every stage of the development. The research questions based on every theme have been answered to answer the key research question.
An Overview of Indian Language Datasets used for Text Summarization
Apr 01, 2022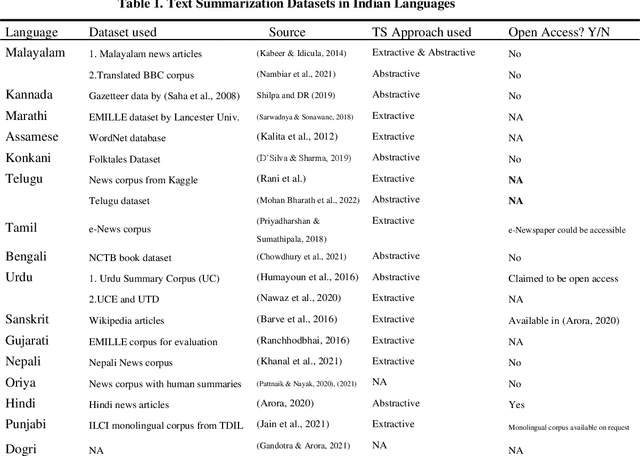
Abstract:In this paper, we survey Text Summarization (TS) datasets in Indian Languages (ILs), which are also low-resource languages (LRLs). We seek to answer one primary question: is the pool of Indian Language Text Summarization (ILTS) dataset growing or is there a resource poverty? To an-swer the primary question, we pose two sub-questions that we seek about ILTS datasets: first, what characteristics: format and domain do ILTS datasets have? Second, how different are those characteristics of ILTS datasets from high-resource languages (HRLs) particularly English. We focus on datasets reported in published ILTS research works during 2012-2022. The survey of ILTS and English datasets reveals two similarities and one contrast. The two similarities are: first, the domain of dataset commonly is news (Hermann et al., 2015). The second similarity is the format of the dataset which is both extractive and abstractive. The contrast is in how the research in dataset development has progressed. ILs face a slow speed of development and public release of datasets as compared with English. We argue that the relatively lower number of ILTS datasets is because of two reasons: first, absence of a dedicated forum for developing TS tools and resources; and second, lack of shareable standard datasets in the public domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge