Sevda Molani
Evolving Tsukamoto Neuro Fuzzy Model for Multiclass Covid 19 Classification with Chest X Ray Images
May 17, 2023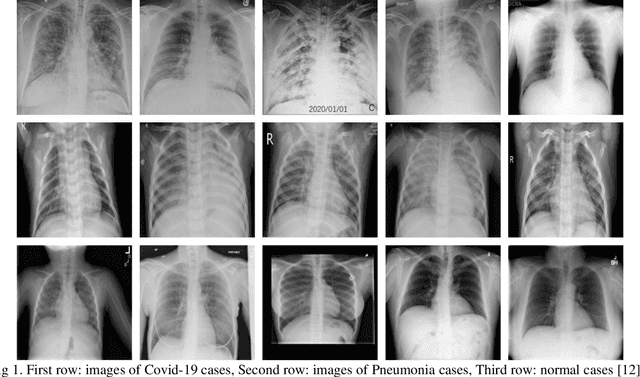
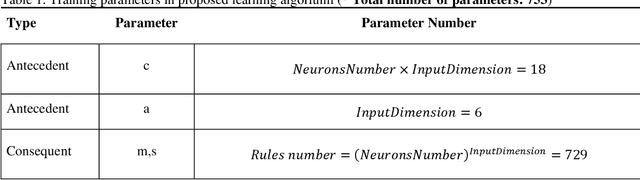
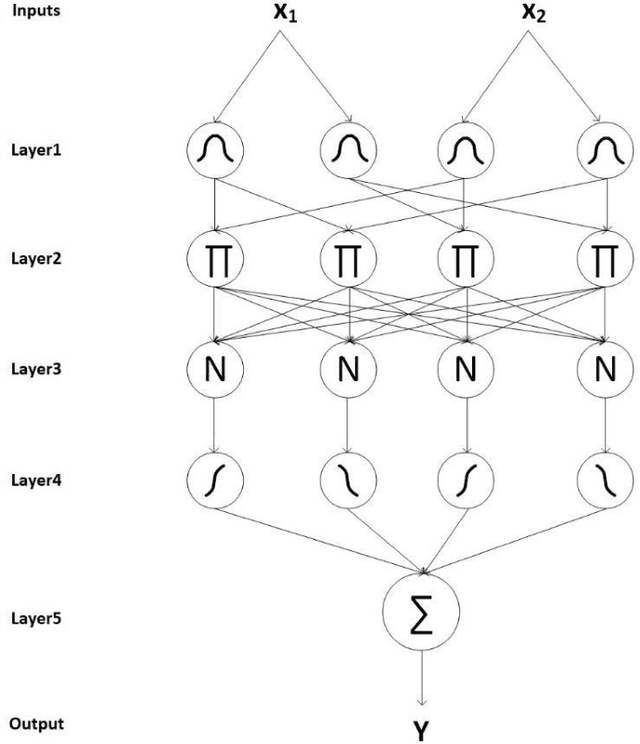
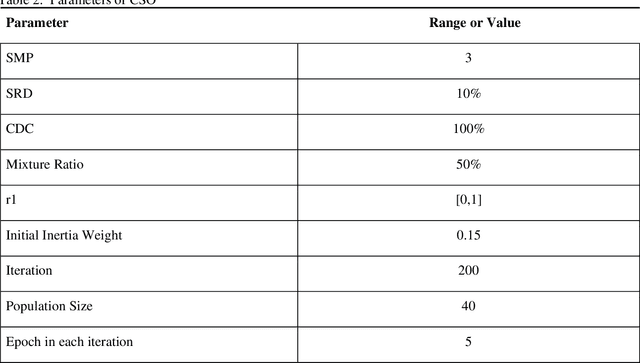
Abstract:Du e to rapid population growth and the need to use artificial intelligence to make quick decisions, developing a machine learning-based disease detection model and abnormality identification system has greatly improved the level of medical diagnosis Since COVID-19 has become one of the most severe diseases in the world, developing an automatic COVID-19 detection framework helps medical doctors in the diagnostic process of disease and provides correct and fast results. In this paper, we propose a machine lear ning based framework for the detection of Covid 19. The proposed model employs a Tsukamoto Neuro Fuzzy Inference network to identify and distinguish Covid 19 disease from normal and pneumonia cases. While the traditional training methods tune the parameters of the neuro-fuzzy model by gradient-based algorithms and recursive least square method, we use an evolutionary-based optimization, the Cat swarm algorithm to update the parameters. In addition, six texture features extracted from chest X-ray images are give n as input to the model. Finally, the proposed model is conducted on the chest X-ray dataset to detect Covid 19. The simulation results indicate that the proposed model achieves an accuracy of 98.51%, sensitivity of 98.35%, specificity of 98.08%, and F1 score of 98.17%.
Generative Adversarial Networks for Brain Images Synthesis: A Review
May 16, 2023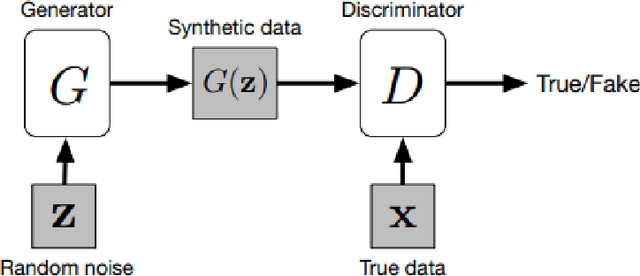
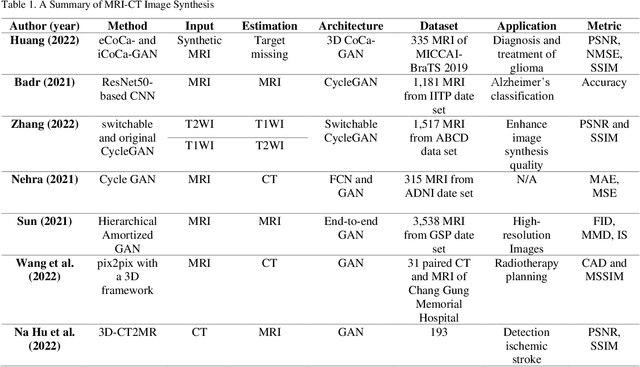
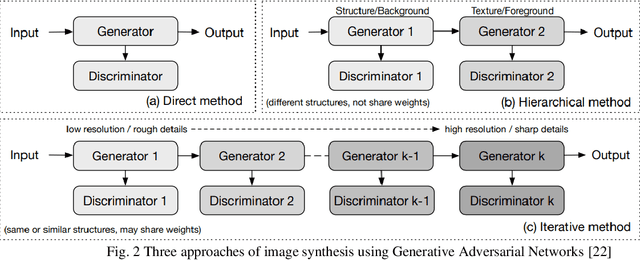
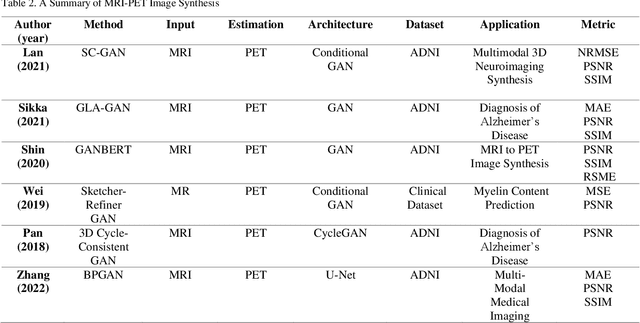
Abstract:In medical imaging, image synthesis is the estimation process of one image (sequence, modality) from another image (sequence, modality). Since images with different modalities provide diverse biomarkers and capture various features, multi-modality imaging is crucial in medicine. While multi-screening is expensive, costly, and time-consuming to report by radiologists, image synthesis methods are capable of artificially generating missing modalities. Deep learning models can automatically capture and extract the high dimensional features. Especially, generative adversarial network (GAN) as one of the most popular generative-based deep learning methods, uses convolutional networks as generators, and estimated images are discriminated as true or false based on a discriminator network. This review provides brain image synthesis via GANs. We summarized the recent developments of GANs for cross-modality brain image synthesis including CT to PET, CT to MRI, MRI to PET, and vice versa.
Imputing Missing Observations with Time Sliced Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique
Jan 14, 2022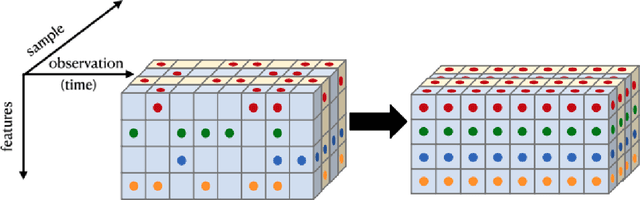
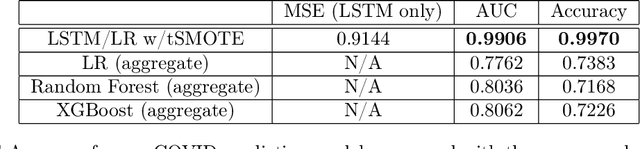
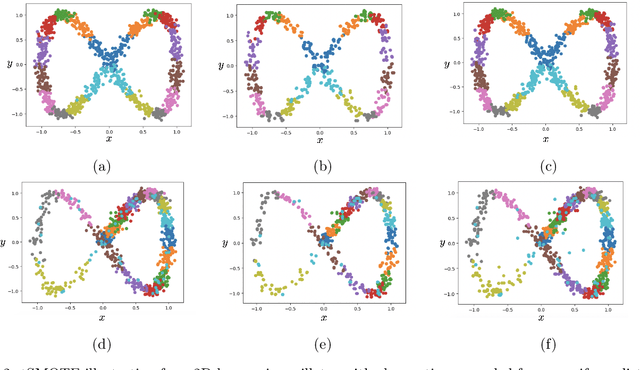
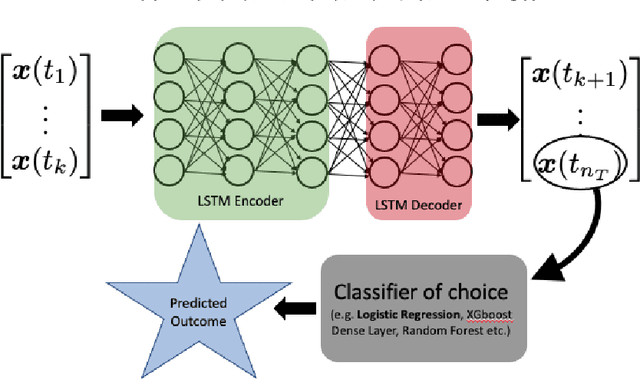
Abstract:We present a simple yet novel time series imputation technique with the goal of constructing an irregular time series that is uniform across every sample in a data set. Specifically, we fix a grid defined by the midpoints of non-overlapping bins (dubbed "slices") of observation times and ensure that each sample has values for all of the features at that given time. This allows one to both impute fully missing observations to allow uniform time series classification across the entire data and, in special cases, to impute individually missing features. To do so, we slightly generalize the well-known class imbalance algorithm SMOTE \cite{smote} to allow component wise nearest neighbor interpolation that preserves correlations when there are no missing features. We visualize the method in the simplified setting of 2-dimensional uncoupled harmonic oscillators. Next, we use tSMOTE to train an Encoder/Decoder long-short term memory (LSTM) model with Logistic Regression for predicting and classifying distinct trajectories of different 2D oscillators. After illustrating the the utility of tSMOTE in this context, we use the same architecture to train a clinical model for COVID-19 disease severity on an imputed data set. Our experiments show an improvement over standard mean and median imputation techniques by allowing a wider class of patient trajectories to be recognized by the model, as well as improvement over aggregated classification models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge