Seung-Bin Kim
Spotlight-TTS: Spotlighting the Style via Voiced-Aware Style Extraction and Style Direction Adjustment for Expressive Text-to-Speech
May 27, 2025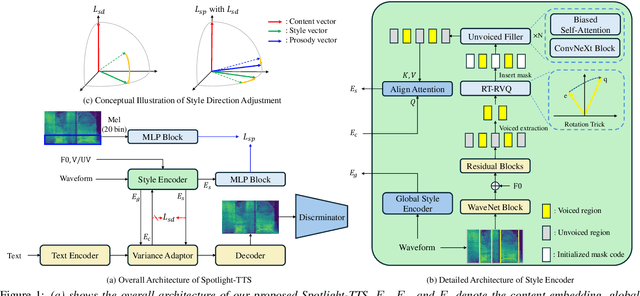
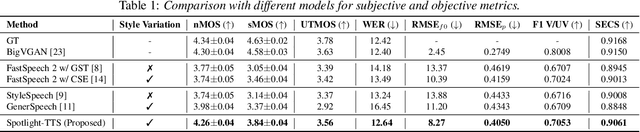
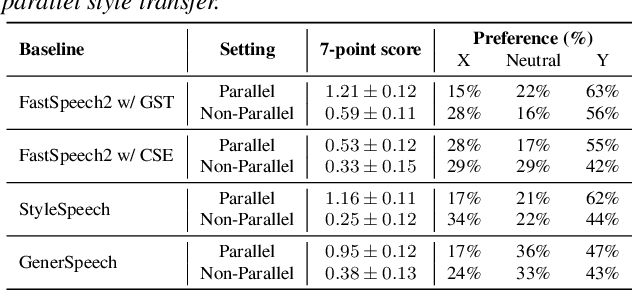
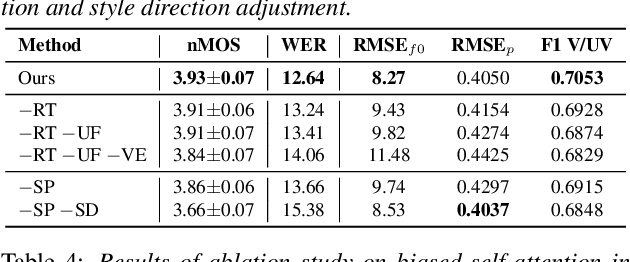
Abstract:Recent advances in expressive text-to-speech (TTS) have introduced diverse methods based on style embedding extracted from reference speech. However, synthesizing high-quality expressive speech remains challenging. We propose Spotlight-TTS, which exclusively emphasizes style via voiced-aware style extraction and style direction adjustment. Voiced-aware style extraction focuses on voiced regions highly related to style while maintaining continuity across different speech regions to improve expressiveness. We adjust the direction of the extracted style for optimal integration into the TTS model, which improves speech quality. Experimental results demonstrate that Spotlight-TTS achieves superior performance compared to baseline models in terms of expressiveness, overall speech quality, and style transfer capability. Our audio samples are publicly available.
EmoSphere-SER: Enhancing Speech Emotion Recognition Through Spherical Representation with Auxiliary Classification
May 26, 2025Abstract:Speech emotion recognition predicts a speaker's emotional state from speech signals using discrete labels or continuous dimensions such as arousal, valence, and dominance (VAD). We propose EmoSphere-SER, a joint model that integrates spherical VAD region classification to guide VAD regression for improved emotion prediction. In our framework, VAD values are transformed into spherical coordinates that are divided into multiple spherical regions, and an auxiliary classification task predicts which spherical region each point belongs to, guiding the regression process. Additionally, we incorporate a dynamic weighting scheme and a style pooling layer with multi-head self-attention to capture spectral and temporal dynamics, further boosting performance. This combined training strategy reinforces structured learning and improves prediction consistency. Experimental results show that our approach exceeds baseline methods, confirming the validity of the proposed framework.
DiEmo-TTS: Disentangled Emotion Representations via Self-Supervised Distillation for Cross-Speaker Emotion Transfer in Text-to-Speech
May 26, 2025Abstract:Cross-speaker emotion transfer in speech synthesis relies on extracting speaker-independent emotion embeddings for accurate emotion modeling without retaining speaker traits. However, existing timbre compression methods fail to fully separate speaker and emotion characteristics, causing speaker leakage and degraded synthesis quality. To address this, we propose DiEmo-TTS, a self-supervised distillation method to minimize emotional information loss and preserve speaker identity. We introduce cluster-driven sampling and information perturbation to preserve emotion while removing irrelevant factors. To facilitate this process, we propose an emotion clustering and matching approach using emotional attribute prediction and speaker embeddings, enabling generalization to unlabeled data. Additionally, we designed a dual conditioning transformer to integrate style features better. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of our method in learning speaker-irrelevant emotion embeddings.
FLowHigh: Towards Efficient and High-Quality Audio Super-Resolution with Single-Step Flow Matching
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Audio super-resolution is challenging owing to its ill-posed nature. Recently, the application of diffusion models in audio super-resolution has shown promising results in alleviating this challenge. However, diffusion-based models have limitations, primarily the necessity for numerous sampling steps, which causes significantly increased latency when synthesizing high-quality audio samples. In this paper, we propose FLowHigh, a novel approach that integrates flow matching, a highly efficient generative model, into audio super-resolution. We also explore probability paths specially tailored for audio super-resolution, which effectively capture high-resolution audio distributions, thereby enhancing reconstruction quality. The proposed method generates high-fidelity, high-resolution audio through a single-step sampling process across various input sampling rates. The experimental results on the VCTK benchmark dataset demonstrate that FLowHigh achieves state-of-the-art performance in audio super-resolution, as evaluated by log-spectral distance and ViSQOL while maintaining computational efficiency with only a single-step sampling process.
JELLY: Joint Emotion Recognition and Context Reasoning with LLMs for Conversational Speech Synthesis
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Recently, there has been a growing demand for conversational speech synthesis (CSS) that generates more natural speech by considering the conversational context. To address this, we introduce JELLY, a novel CSS framework that integrates emotion recognition and context reasoning for generating appropriate speech in conversation by fine-tuning a large language model (LLM) with multiple partial LoRA modules. We propose an Emotion-aware Q-former encoder, which enables the LLM to perceive emotions in speech. The encoder is trained to align speech emotions with text, utilizing datasets of emotional speech. The entire model is then fine-tuned with conversational speech data to infer emotional context for generating emotionally appropriate speech in conversation. Our experimental results demonstrate that JELLY excels in emotional context modeling, synthesizing speech that naturally aligns with conversation, while mitigating the scarcity of emotional conversational speech datasets.
EmoSphere++: Emotion-Controllable Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech via Emotion-Adaptive Spherical Vector
Nov 04, 2024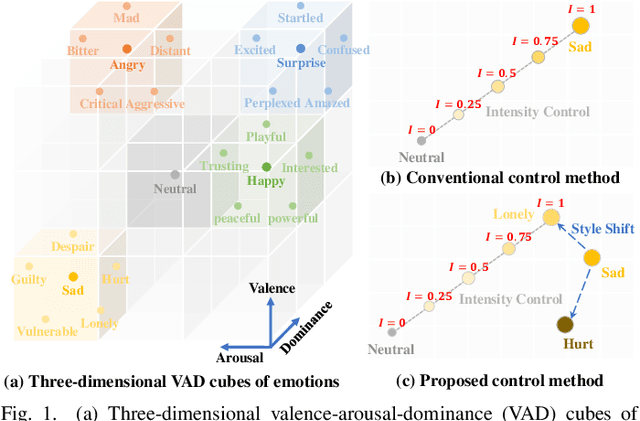
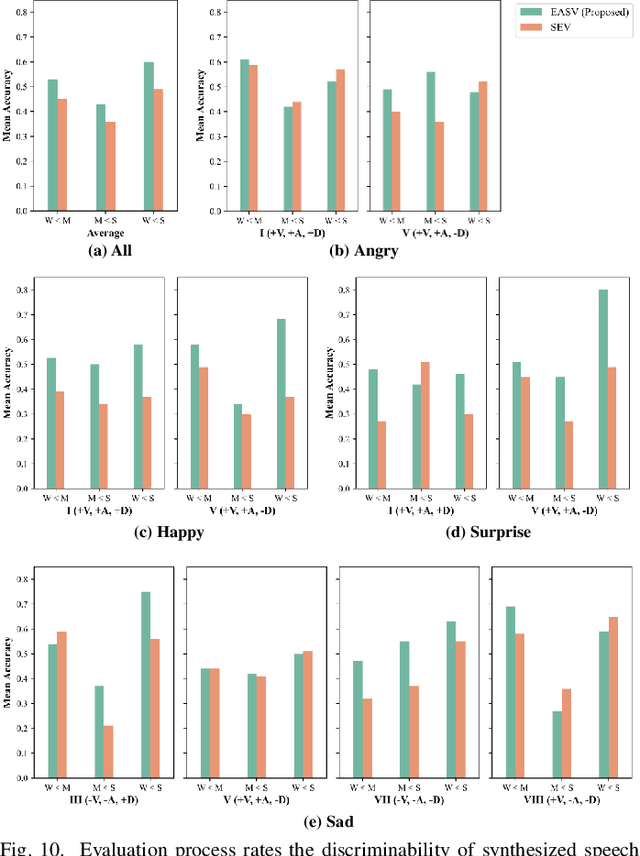
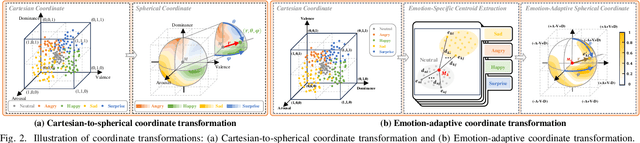
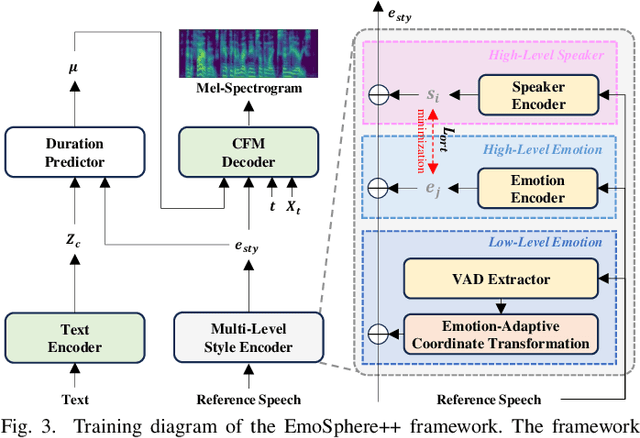
Abstract:Emotional text-to-speech (TTS) technology has achieved significant progress in recent years; however, challenges remain owing to the inherent complexity of emotions and limitations of the available emotional speech datasets and models. Previous studies typically relied on limited emotional speech datasets or required extensive manual annotations, restricting their ability to generalize across different speakers and emotional styles. In this paper, we present EmoSphere++, an emotion-controllable zero-shot TTS model that can control emotional style and intensity to resemble natural human speech. We introduce a novel emotion-adaptive spherical vector that models emotional style and intensity without human annotation. Moreover, we propose a multi-level style encoder that can ensure effective generalization for both seen and unseen speakers. We also introduce additional loss functions to enhance the emotion transfer performance for zero-shot scenarios. We employ a conditional flow matching-based decoder to achieve high-quality and expressive emotional TTS in a few sampling steps. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
EmoSphere-TTS: Emotional Style and Intensity Modeling via Spherical Emotion Vector for Controllable Emotional Text-to-Speech
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:Despite rapid advances in the field of emotional text-to-speech (TTS), recent studies primarily focus on mimicking the average style of a particular emotion. As a result, the ability to manipulate speech emotion remains constrained to several predefined labels, compromising the ability to reflect the nuanced variations of emotion. In this paper, we propose EmoSphere-TTS, which synthesizes expressive emotional speech by using a spherical emotion vector to control the emotional style and intensity of the synthetic speech. Without any human annotation, we use the arousal, valence, and dominance pseudo-labels to model the complex nature of emotion via a Cartesian-spherical transformation. Furthermore, we propose a dual conditional adversarial network to improve the quality of generated speech by reflecting the multi-aspect characteristics. The experimental results demonstrate the model ability to control emotional style and intensity with high-quality expressive speech.
TranSentence: Speech-to-speech Translation via Language-agnostic Sentence-level Speech Encoding without Language-parallel Data
Jan 17, 2024Abstract:Although there has been significant advancement in the field of speech-to-speech translation, conventional models still require language-parallel speech data between the source and target languages for training. In this paper, we introduce TranSentence, a novel speech-to-speech translation without language-parallel speech data. To achieve this, we first adopt a language-agnostic sentence-level speech encoding that captures the semantic information of speech, irrespective of language. We then train our model to generate speech based on the encoded embedding obtained from a language-agnostic sentence-level speech encoder that is pre-trained with various languages. With this method, despite training exclusively on the target language's monolingual data, we can generate target language speech in the inference stage using language-agnostic speech embedding from the source language speech. Furthermore, we extend TranSentence to multilingual speech-to-speech translation. The experimental results demonstrate that TranSentence is superior to other models.
HierSpeech++: Bridging the Gap between Semantic and Acoustic Representation of Speech by Hierarchical Variational Inference for Zero-shot Speech Synthesis
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLM)-based speech synthesis has been widely adopted in zero-shot speech synthesis. However, they require a large-scale data and possess the same limitations as previous autoregressive speech models, including slow inference speed and lack of robustness. This paper proposes HierSpeech++, a fast and strong zero-shot speech synthesizer for text-to-speech (TTS) and voice conversion (VC). We verified that hierarchical speech synthesis frameworks could significantly improve the robustness and expressiveness of the synthetic speech. Furthermore, we significantly improve the naturalness and speaker similarity of synthetic speech even in zero-shot speech synthesis scenarios. For text-to-speech, we adopt the text-to-vec framework, which generates a self-supervised speech representation and an F0 representation based on text representations and prosody prompts. Then, HierSpeech++ generates speech from the generated vector, F0, and voice prompt. We further introduce a high-efficient speech super-resolution framework from 16 kHz to 48 kHz. The experimental results demonstrated that the hierarchical variational autoencoder could be a strong zero-shot speech synthesizer given that it outperforms LLM-based and diffusion-based models. Moreover, we achieved the first human-level quality zero-shot speech synthesis. Audio samples and source code are available at https://github.com/sh-lee-prml/HierSpeechpp.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge