Seongeun Ryu
HearHere: Mitigating Echo Chambers in News Consumption through an AI-based Web System
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Considerable efforts are currently underway to mitigate the negative impacts of echo chambers, such as increased susceptibility to fake news and resistance towards accepting scientific evidence. Prior research has presented the development of computer systems that support the consumption of news information from diverse political perspectives to mitigate the echo chamber effect. However, existing studies still lack the ability to effectively support the key processes of news information consumption and quantitatively identify a political stance towards the information. In this paper, we present HearHere, an AI-based web system designed to help users accommodate information and opinions from diverse perspectives. HearHere facilitates the key processes of news information consumption through two visualizations. Visualization 1 provides political news with quantitative political stance information, derived from our graph-based political classification model, and users can experience diverse perspectives (Hear). Visualization 2 allows users to express their opinions on specific political issues in a comment form and observe the position of their own opinions relative to pro-liberal and pro-conservative comments presented on a map interface (Here). Through a user study with 94 participants, we demonstrate the feasibility of HearHere in supporting the consumption of information from various perspectives. Our findings highlight the importance of providing political stance information and quantifying users' political status as a means to mitigate political polarization. In addition, we propose design implications for system development, including the consideration of demographics such as political interest and providing users with initiatives.
CIDER: Category-Guided Intent Disentanglement for Accurate Personalized News Recommendation
Oct 13, 2023
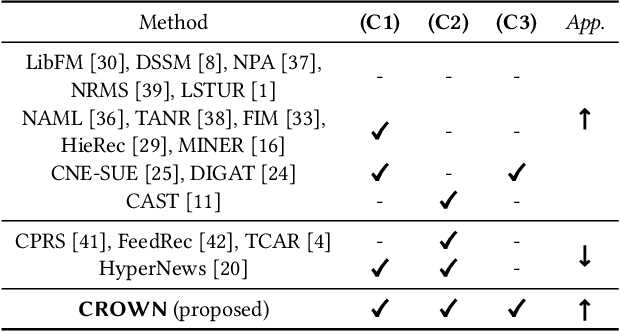

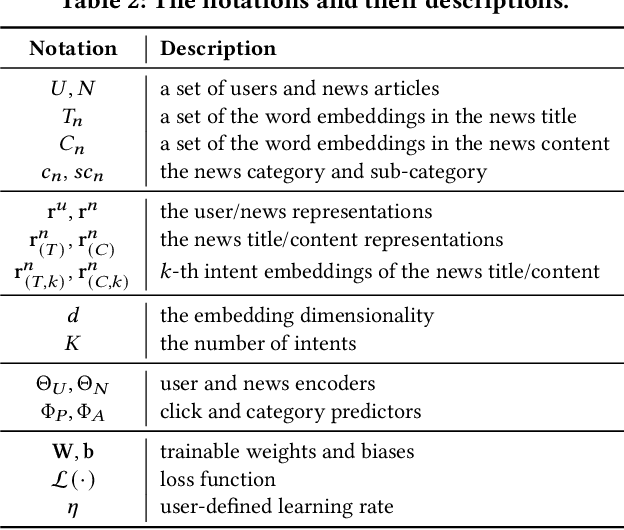
Abstract:Personalized news recommendation aims to assist users in finding news articles that align with their interests, which plays a pivotal role in mitigating users' information overload problem. Although many recent works have been studied for better user and news representations, the following challenges have been rarely studied: (C1) How to precisely comprehend a range of intents coupled within a news article? and (C2) How to differentiate news articles with varying post-read preferences in users' click history? To tackle both challenges together, in this paper, we propose a novel personalized news recommendation framework (CIDER) that employs (1) category-guided intent disentanglement for (C1) and (2) consistency-based news representation for (C2). Furthermore, we incorporate a category prediction into the training process of CIDER as an auxiliary task, which provides supplementary supervisory signals to enhance intent disentanglement. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets reveal that (1) CIDER provides consistent performance improvements over seven state-of-the-art news recommendation methods and (2) the proposed strategies significantly improve the model accuracy of CIDER.
KHAN: Knowledge-Aware Hierarchical Attention Networks for Accurate Political Stance Prediction
Mar 01, 2023



Abstract:The political stance prediction for news articles has been widely studied to mitigate the echo chamber effect -- people fall into their thoughts and reinforce their pre-existing beliefs. The previous works for the political stance problem focus on (1) identifying political factors that could reflect the political stance of a news article and (2) capturing those factors effectively. Despite their empirical successes, they are not sufficiently justified in terms of how effective their identified factors are in the political stance prediction. Motivated by this, in this work, we conduct a user study to investigate important factors in political stance prediction, and observe that the context and tone of a news article (implicit) and external knowledge for real-world entities appearing in the article (explicit) are important in determining its political stance. Based on this observation, we propose a novel knowledge-aware approach to political stance prediction (KHAN), employing (1) hierarchical attention networks (HAN) to learn the relationships among words and sentences in three different levels and (2) knowledge encoding (KE) to incorporate external knowledge for real-world entities into the process of political stance prediction. Also, to take into account the subtle and important difference between opposite political stances, we build two independent political knowledge graphs (KG) (i.e., KG-lib and KG-con) by ourselves and learn to fuse the different political knowledge. Through extensive evaluations on three real-world datasets, we demonstrate the superiority of DASH in terms of (1) accuracy, (2) efficiency, and (3) effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge