Senmao Ye
Data Extrapolation for Text-to-image Generation on Small Datasets
Oct 02, 2024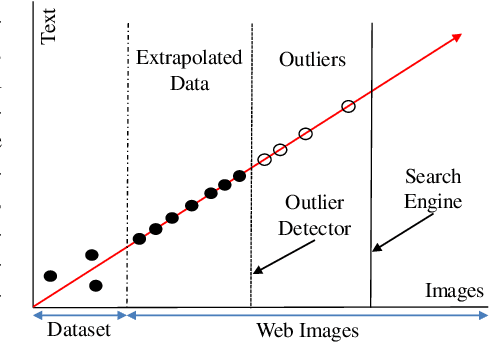
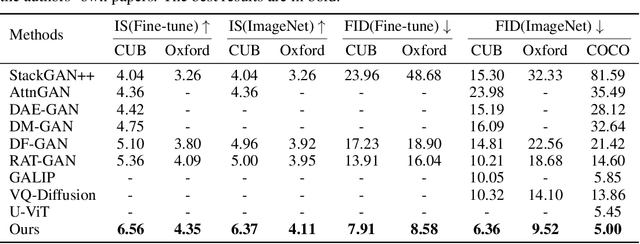
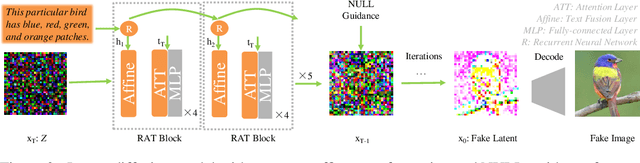
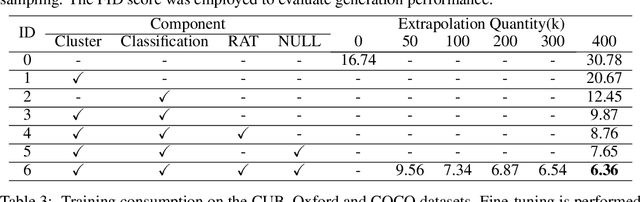
Abstract:Text-to-image generation requires large amount of training data to synthesizing high-quality images. For augmenting training data, previous methods rely on data interpolations like cropping, flipping, and mixing up, which fail to introduce new information and yield only marginal improvements. In this paper, we propose a new data augmentation method for text-to-image generation using linear extrapolation. Specifically, we apply linear extrapolation only on text feature, and new image data are retrieved from the internet by search engines. For the reliability of new text-image pairs, we design two outlier detectors to purify retrieved images. Based on extrapolation, we construct training samples dozens of times larger than the original dataset, resulting in a significant improvement in text-to-image performance. Moreover, we propose a NULL-guidance to refine score estimation, and apply recurrent affine transformation to fuse text information. Our model achieves FID scores of 7.91, 9.52 and 5.00 on the CUB, Oxford and COCO datasets. The code and data will be available on GitHub (https://github.com/senmaoy/RAT-Diffusion).
Score Mismatching for Generative Modeling
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:We propose a new score-based model with one-step sampling. Previously, score-based models were burdened with heavy computations due to iterative sampling. For substituting the iterative process, we train a standalone generator to compress all the time steps with the gradient backpropagated from the score network. In order to produce meaningful gradients for the generator, the score network is trained to simultaneously match the real data distribution and mismatch the fake data distribution. This model has the following advantages: 1) For sampling, it generates a fake image with only one step forward. 2) For training, it only needs 10 diffusion steps.3) Compared with consistency model, it is free of the ill-posed problem caused by consistency loss. On the popular CIFAR-10 dataset, our model outperforms Consistency Model and Denoising Score Matching, which demonstrates the potential of the framework. We further provide more examples on the MINIST and LSUN datasets. The code is available on GitHub.
Recurrent Affine Transformation for Text-to-image Synthesis
Apr 22, 2022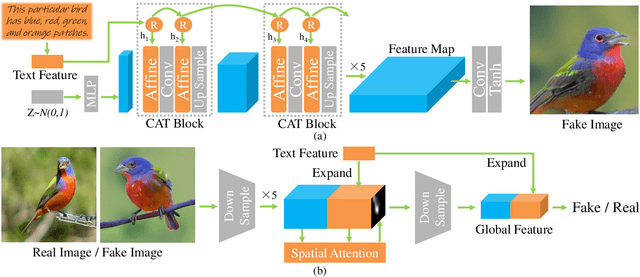
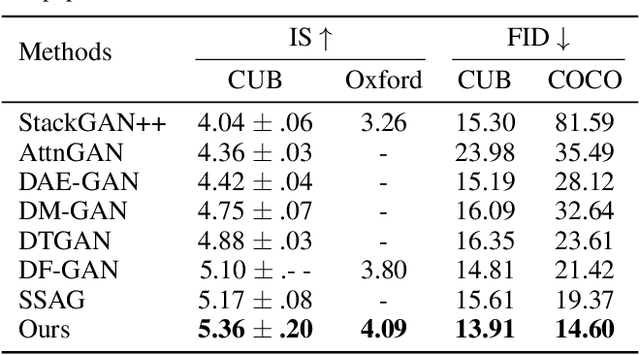

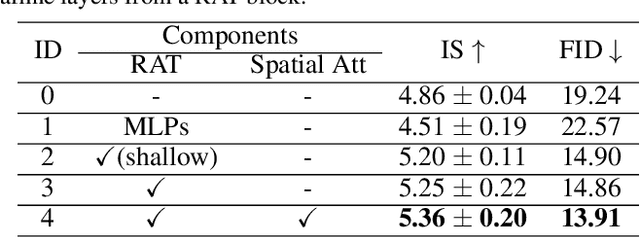
Abstract:Text-to-image synthesis aims to generate natural images conditioned on text descriptions. The main difficulty of this task lies in effectively fusing text information into the image synthesis process. Existing methods usually adaptively fuse suitable text information into the synthesis process with multiple isolated fusion blocks (e.g., Conditional Batch Normalization and Instance Normalization). However, isolated fusion blocks not only conflict with each other but also increase the difficulty of training (see first page of the supplementary). To address these issues, we propose a Recurrent Affine Transformation (RAT) for Generative Adversarial Networks that connects all the fusion blocks with a recurrent neural network to model their long-term dependency. Besides, to improve semantic consistency between texts and synthesized images, we incorporate a spatial attention model in the discriminator. Being aware of matching image regions, text descriptions supervise the generator to synthesize more relevant image contents. Extensive experiments on the CUB, Oxford-102 and COCO datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model in comparison to state-of-the-art models \footnote{https://github.com/senmaoy/Recurrent-Affine-Transformation-for-Text-to-image-Synthesis.git}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge