Semion Saikin
Text to Insight: Accelerating Organic Materials Knowledge Extraction via Deep Learning
Sep 27, 2021
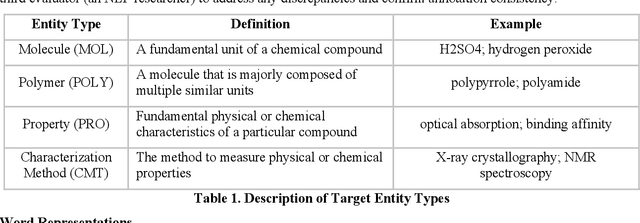

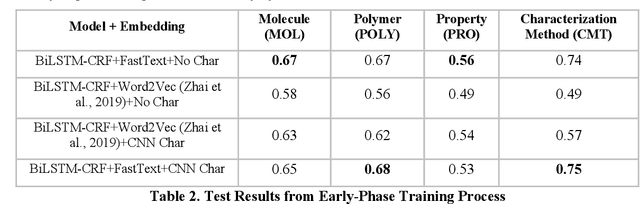
Abstract:Scientific literature is one of the most significant resources for sharing knowledge. Researchers turn to scientific literature as a first step in designing an experiment. Given the extensive and growing volume of literature, the common approach of reading and manually extracting knowledge is too time consuming, creating a bottleneck in the research cycle. This challenge spans nearly every scientific domain. For the materials science, experimental data distributed across millions of publications are extremely helpful for predicting materials properties and the design of novel materials. However, only recently researchers have explored computational approaches for knowledge extraction primarily for inorganic materials. This study aims to explore knowledge extraction for organic materials. We built a research dataset composed of 855 annotated and 708,376 unannotated sentences drawn from 92,667 abstracts. We used named-entity-recognition (NER) with BiLSTM-CNN-CRF deep learning model to automatically extract key knowledge from literature. Early-phase results show a high potential for automated knowledge extraction. The paper presents our findings and a framework for supervised knowledge extraction that can be adapted to other scientific domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge