Sebastian Vizcay
Electrotactile feedback for hand interactions:A systematic review, meta-analysis,and future directions
May 11, 2021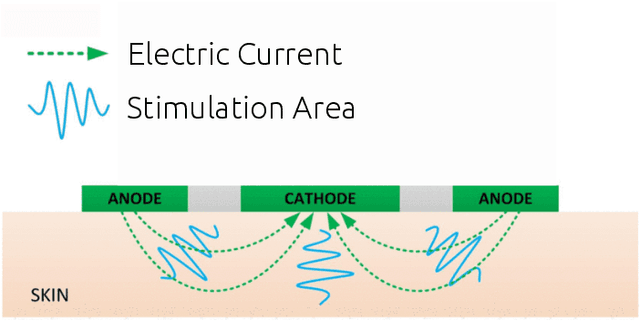
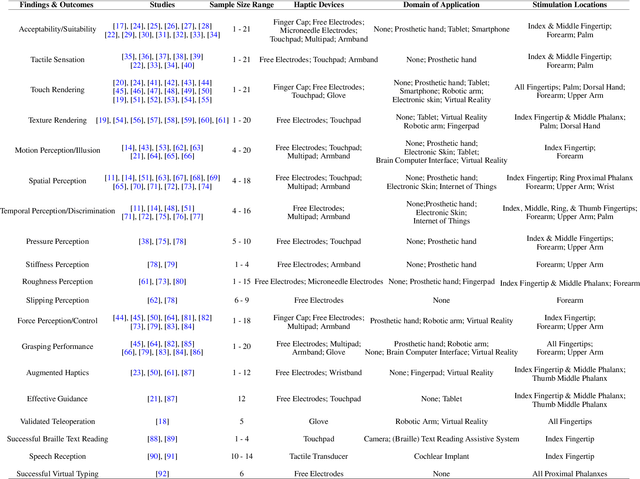
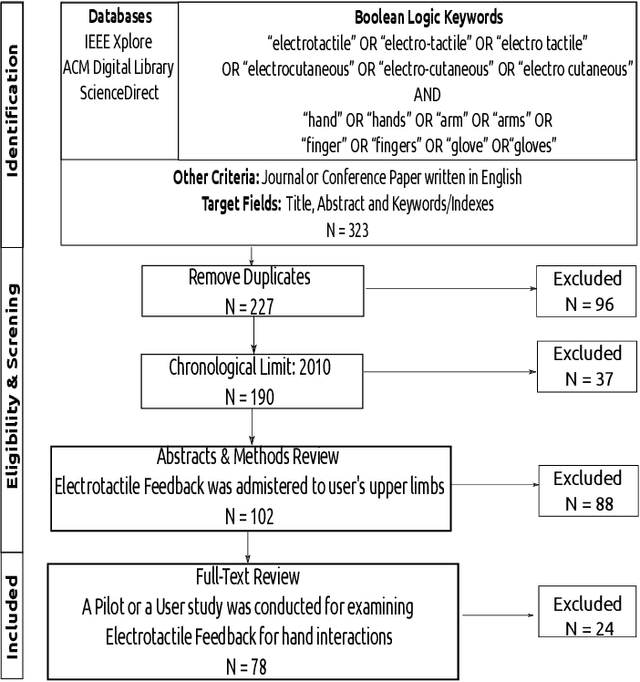
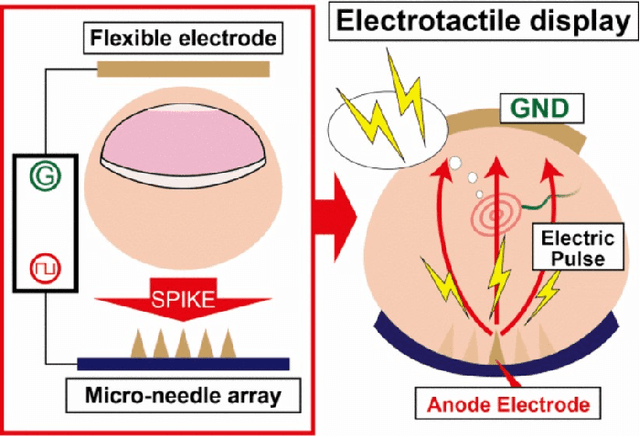
Abstract:Haptic feedback is critical in a broad range of human-machine/computer-interaction applications. However, the high cost and low portability/wearability of haptic devices remains an unresolved issue, severely limiting the adoption of this otherwise promising technology. Electrotactile interfaces have the advantage of being more portable and wearable due to its reduced actuators' size, as well as benefiting from lower power consumption and manufacturing cost. The usages of electrotactile feedback have been explored in human-computer interaction and human-machine-interaction for facilitating hand-based interactions in applications such as prosthetics, virtual reality, robotic teleoperation, surface haptics, portable devices, and rehabilitation. This paper presents a systematic review and meta-analysis of electrotactile feedback systems for hand-based interactions in the last decade. We categorize the different electrotactile systems according to their type of stimulation and implementation/application. We also present and discuss a quantitative congregation of the findings, so as to offer a high-level overview into the state-of-art and suggest future directions. Electrotactile feedback was successful in rendering and/or augmenting most tactile sensations, eliciting perceptual processes, and improving performance in many scenarios, especially in those where the wearability/portability of the system is important. However, knowledge gaps, technical drawbacks, and methodological limitations were detected, which should be addressed in future studies.
Electrotactile Feedback in Virtual Reality For Precise and Accurate Contact Rendering
Jan 30, 2021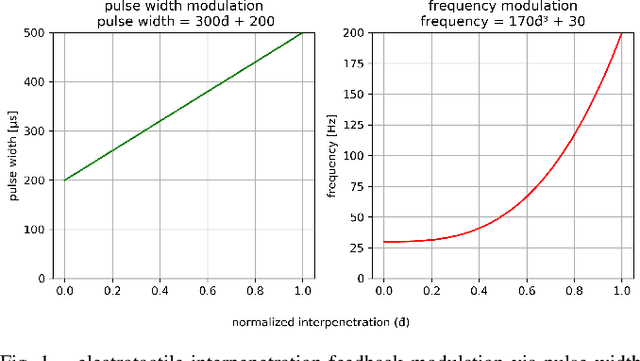

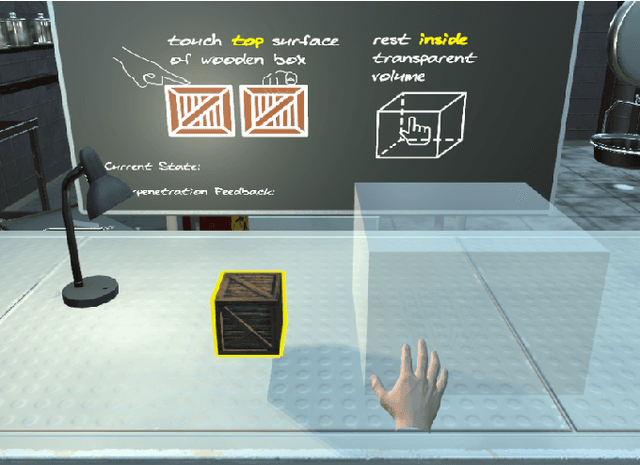
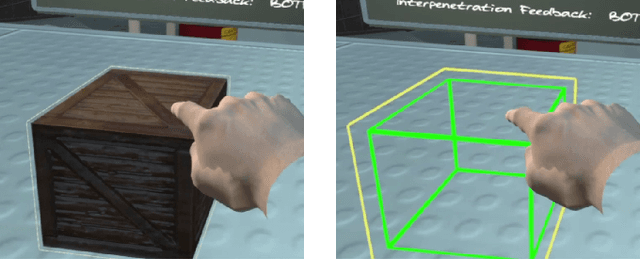
Abstract:This paper presents a wearable electrotactile feedback system to enable precise and accurate contact rendering with virtual objects for mid-air interactions. In particular, we propose the use of electrotactile feedback to render the interpenetration distance between the user's finger and the virtual content is touched. Our approach consists of modulating the perceived intensity (frequency and pulse width modulation) of the electrotactile stimuli according to the registered interpenetration distance. In a user study (N=21), we assessed the performance of four different interpenetration feedback approaches: electrotactile-only, visual-only, electrotactile and visual, and no interpenetration feedback. First, the results showed that contact precision and accuracy were significantly improved when using interpenetration feedback. Second, and more interestingly, there were no significant differences between visual and electrotactile feedback when the calibration was optimized and the user was familiarized with electrotactile feedback. Taken together, these results suggest that electrotactile feedback could be an efficient replacement of visual feedback for accurate and precise contact rendering in virtual reality avoiding the need of active visual focus and the rendering of additional visual artefacts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge