Sandipan Dhar
Generative Adversarial Network based Voice Conversion: Techniques, Challenges, and Recent Advancements
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Voice conversion (VC) stands as a crucial research area in speech synthesis, enabling the transformation of a speaker's vocal characteristics to resemble another while preserving the linguistic content. This technology has broad applications, including automated movie dubbing, speech-to-singing conversion, and assistive devices for pathological speech rehabilitation. With the increasing demand for high-quality and natural-sounding synthetic voices, researchers have developed a wide range of VC techniques. Among these, generative adversarial network (GAN)-based approaches have drawn considerable attention for their powerful feature-mapping capabilities and potential to produce highly realistic speech. Despite notable advancements, challenges such as ensuring training stability, maintaining linguistic consistency, and achieving perceptual naturalness continue to hinder progress in GAN-based VC systems. This systematic review presents a comprehensive analysis of the voice conversion landscape, highlighting key techniques, key challenges, and the transformative impact of GANs in the field. The survey categorizes existing methods, examines technical obstacles, and critically evaluates recent developments in GAN-based VC. By consolidating and synthesizing research findings scattered across the literature, this review provides a structured understanding of the strengths and limitations of different approaches. The significance of this survey lies in its ability to guide future research by identifying existing gaps, proposing potential directions, and offering insights for building more robust and efficient VC systems. Overall, this work serves as an essential resource for researchers, developers, and practitioners aiming to advance the state-of-the-art (SOTA) in voice conversion technology.
Collective Learning Mechanism based Optimal Transport Generative Adversarial Network for Non-parallel Voice Conversion
Apr 18, 2025


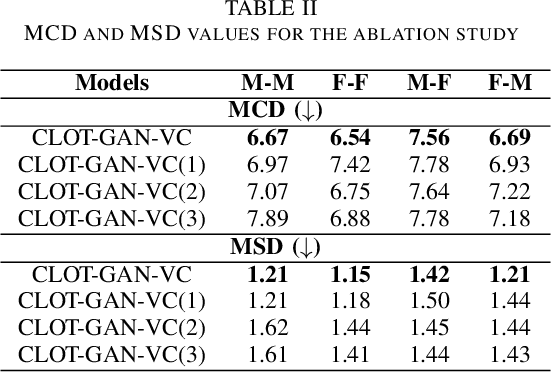
Abstract:After demonstrating significant success in image synthesis, Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) models have likewise made significant progress in the field of speech synthesis, leveraging their capacity to adapt the precise distribution of target data through adversarial learning processes. Notably, in the realm of State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) GAN-based Voice Conversion (VC) models, there exists a substantial disparity in naturalness between real and GAN-generated speech samples. Furthermore, while many GAN models currently operate on a single generator discriminator learning approach, optimizing target data distribution is more effectively achievable through a single generator multi-discriminator learning scheme. Hence, this study introduces a novel GAN model named Collective Learning Mechanism-based Optimal Transport GAN (CLOT-GAN) model, incorporating multiple discriminators, including the Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) model, Vision Transformer (ViT), and conformer. The objective of integrating various discriminators lies in their ability to comprehend the formant distribution of mel-spectrograms, facilitated by a collective learning mechanism. Simultaneously, the inclusion of Optimal Transport (OT) loss aims to precisely bridge the gap between the source and target data distribution, employing the principles of OT theory. The experimental validation on VCC 2018, VCTK, and CMU-Arctic datasets confirms that the CLOT-GAN-VC model outperforms existing VC models in objective and subjective assessments.
Differential Evolution Algorithm based Hyper-Parameters Selection of Convolutional Neural Network for Speech Command Recognition
Oct 13, 2023Abstract:Speech Command Recognition (SCR), which deals with identification of short uttered speech commands, is crucial for various applications, including IoT devices and assistive technology. Despite the promise shown by Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in SCR tasks, their efficacy relies heavily on hyper-parameter selection, which is typically laborious and time-consuming when done manually. This paper introduces a hyper-parameter selection method for CNNs based on the Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm, aiming to enhance performance in SCR tasks. Training and testing with the Google Speech Command (GSC) dataset, the proposed approach showed effectiveness in classifying speech commands. Moreover, a comparative analysis with Genetic Algorithm based selections and other deep CNN (DCNN) models highlighted the efficiency of the proposed DE algorithm in hyper-parameter selection for CNNs in SCR tasks.
Comparative Evaluation of Metaheuristic Algorithms for Hyperparameter Selection in Short-Term Weather Forecasting
Sep 05, 2023Abstract:Weather forecasting plays a vital role in numerous sectors, but accurately capturing the complex dynamics of weather systems remains a challenge for traditional statistical models. Apart from Auto Regressive time forecasting models like ARIMA, deep learning techniques (Vanilla ANNs, LSTM and GRU networks), have shown promise in improving forecasting accuracy by capturing temporal dependencies. This paper explores the application of metaheuristic algorithms, namely Genetic Algorithm (GA), Differential Evolution (DE), and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), to automate the search for optimal hyperparameters in these model architectures. Metaheuristic algorithms excel in global optimization, offering robustness, versatility, and scalability in handling non-linear problems. We present a comparative analysis of different model architectures integrated with metaheuristic optimization, evaluating their performance in weather forecasting based on metrics such as Mean Squared Error (MSE) and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE). The results demonstrate the potential of metaheuristic algorithms in enhancing weather forecasting accuracy \& helps in determining the optimal set of hyper-parameters for each model. The paper underscores the importance of harnessing advanced optimization techniques to select the most suitable metaheuristic algorithm for the given weather forecasting task.
An Adaptive Learning based Generative Adversarial Network for One-To-One Voice Conversion
Apr 25, 2021



Abstract:Voice Conversion (VC) emerged as a significant domain of research in the field of speech synthesis in recent years due to its emerging application in voice-assisting technology, automated movie dubbing, and speech-to-singing conversion to name a few. VC basically deals with the conversion of vocal style of one speaker to another speaker while keeping the linguistic contents unchanged. VC task is performed through a three-stage pipeline consisting of speech analysis, speech feature mapping, and speech reconstruction. Nowadays the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) models are widely in use for speech feature mapping from source to target speaker. In this paper, we propose an adaptive learning-based GAN model called ALGAN-VC for an efficient one-to-one VC of speakers. Our ALGAN-VC framework consists of some approaches to improve the speech quality and voice similarity between source and target speakers. The model incorporates a Dense Residual Network (DRN) like architecture to the generator network for efficient speech feature learning, for source to target speech feature conversion. We also integrate an adaptive learning mechanism to compute the loss function for the proposed model. Moreover, we use a boosted learning rate approach to enhance the learning capability of the proposed model. The model is trained by using both forward and inverse mapping simultaneously for a one-to-one VC. The proposed model is tested on Voice Conversion Challenge (VCC) 2016, 2018, and 2020 datasets as well as on our self-prepared speech dataset, which has been recorded in Indian regional languages and in English. A subjective and objective evaluation of the generated speech samples indicated that the proposed model elegantly performed the voice conversion task by achieving high speaker similarity and adequate speech quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge