Samuel Holtzman
Exact Reasoning Under Uncertainty
Mar 27, 2013Abstract:This paper focuses on designing expert systems to support decision making in complex, uncertain environments. In this context, our research indicates that strictly probabilistic representations, which enable the use of decision-theoretic reasoning, are highly preferable to recently proposed alternatives (e.g., fuzzy set theory and Dempster-Shafer theory). Furthermore, we discuss the language of influence diagrams and a corresponding methodology -decision analysis -- that allows decision theory to be used effectively and efficiently as a decision-making aid. Finally, we use RACHEL, a system that helps infertile couples select medical treatments, to illustrate the methodology of decision analysis as basis for expert decision systems.
R&D Analyst: An Interactive Approach to Normative Decision System Model Construction
Mar 13, 2013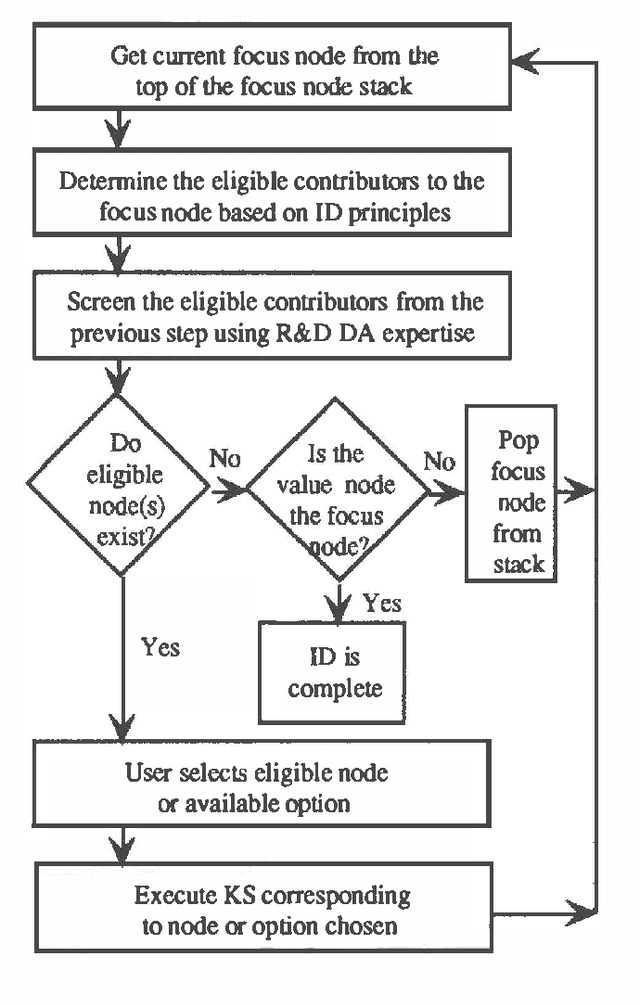
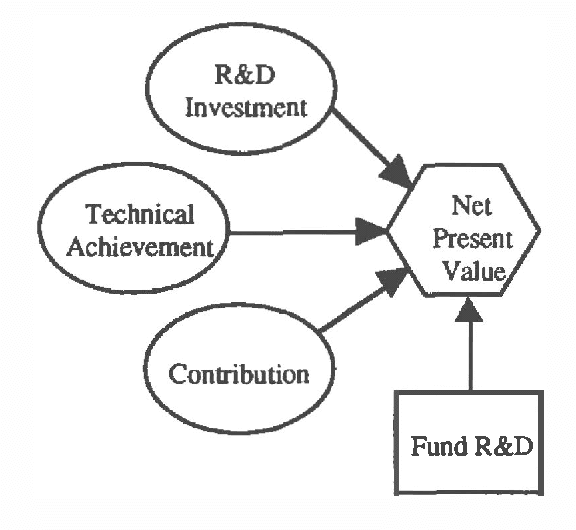

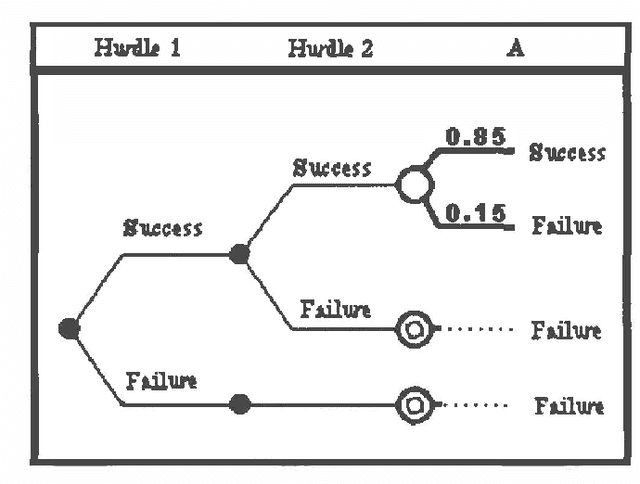
Abstract:This paper describes the architecture of R&D Analyst, a commercial intelligent decision system for evaluating corporate research and development projects and portfolios. In analyzing projects, R&D Analyst interactively guides a user in constructing an influence diagram model for an individual research project. The system's interactive approach can be clearly explained from a blackboard system perspective. The opportunistic reasoning emphasis of blackboard systems satisfies the flexibility requirements of model construction, thereby suggesting that a similar architecture would be valuable for developing normative decision systems in other domains. Current research is aimed at extending the system architecture to explicitly consider of sequential decisions involving limited temporal, financial, and physical resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge