Samuel Aeschbach
Measuring individual semantic networks: A simulation study
Oct 23, 2024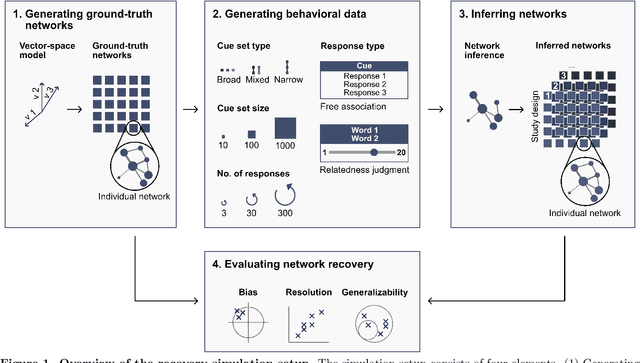
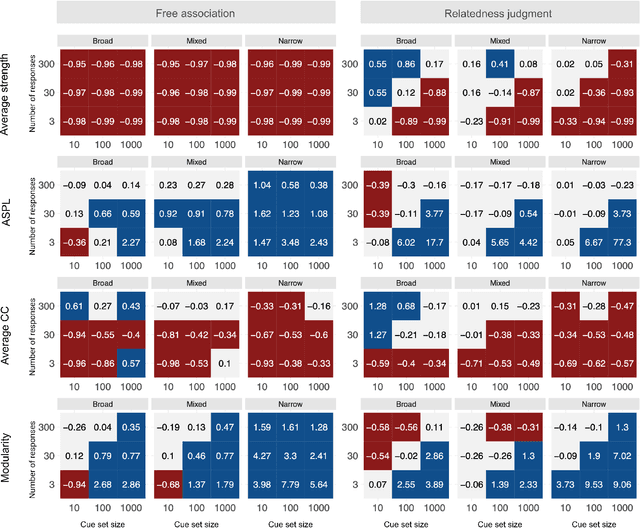
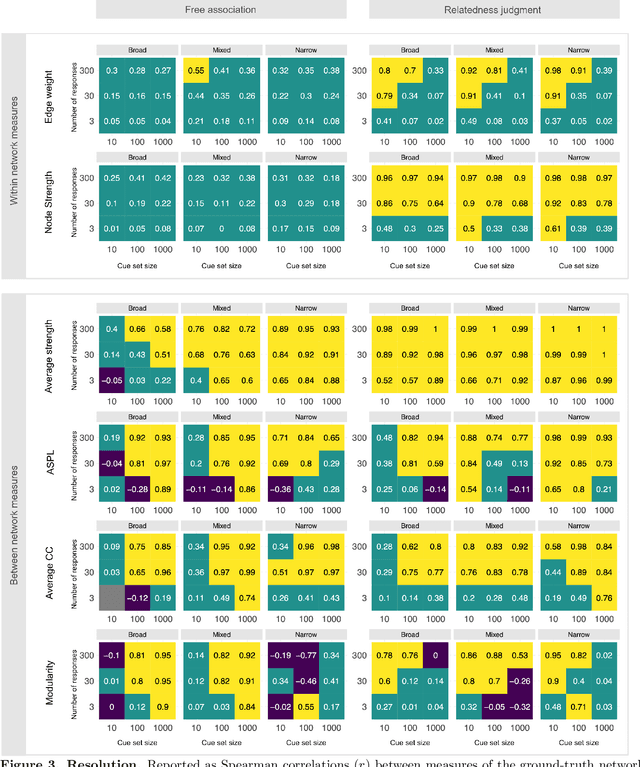
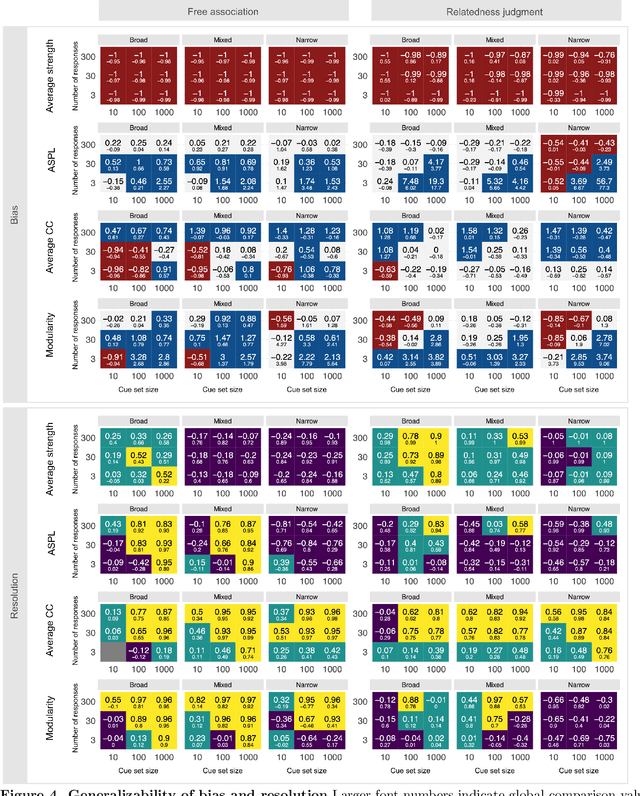
Abstract:Accurately capturing individual differences in semantic networks is fundamental to advancing our mechanistic understanding of semantic memory. Past empirical attempts to construct individual-level semantic networks from behavioral paradigms may be limited by data constraints. To assess these limitations and propose improved designs for the measurement of individual semantic networks, we conducted a recovery simulation investigating the psychometric properties underlying estimates of individual semantic networks obtained from two different behavioral paradigms: free associations and relatedness judgment tasks. Our results show that successful inference of semantic networks is achievable, but they also highlight critical challenges. Estimates of absolute network characteristics are severely biased, such that comparisons between behavioral paradigms and different design configurations are often not meaningful. However, comparisons within a given paradigm and design configuration can be accurate and generalizable when based on designs with moderate numbers of cues, moderate numbers of responses, and cue sets including diverse words. Ultimately, our results provide insights that help evaluate past findings on the structure of semantic networks and design new studies capable of more reliably revealing individual differences in semantic networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge