Samia Sultana
Detection and Segmentation of Cosmic Objects Based on Adaptive Thresholding and Back Propagation Neural Network
Aug 02, 2023



Abstract:Astronomical images provide information about the great variety of cosmic objects in the Universe. Due to the large volumes of data, the presence of innumerable bright point sources as well as noise within the frame and the spatial gap between objects and satellite cameras, it is a challenging task to classify and detect the celestial objects. We propose an Adaptive Thresholding Method (ATM) based segmentation and Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) based cosmic object detection including a well-structured series of pre-processing steps designed to enhance segmentation and detection.
Vision-Based Lane Detection and Tracking under Different Challenging Environmental Conditions
Oct 19, 2022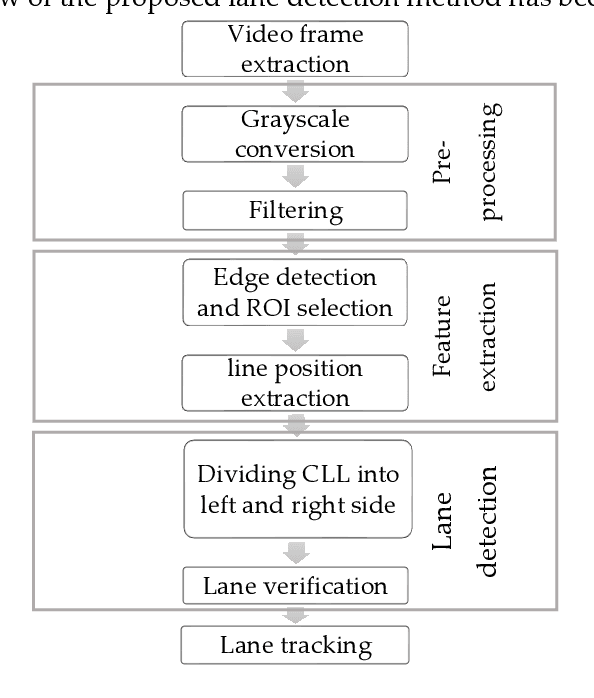



Abstract:Driving is very challenging when the visibility of a road lane marking is low, obscured or often invisible due to abrupt environmental change which may lead to severe vehicle clash. A large volume of research has been done on lane marking detection. Most of the lane detection methods suffer from four types of major problems: (i) abrupt illumination change due to change in time (day, night), weather, road, etc.; (ii) lane markings get obscured partially or fully when they are colored, eroded or occluded; (iii) blurred view created by adverse weather like rain or snow; and (iv) incorrect lane detection due to presence of other lookalike lines e.g. guardrails, pavement marking, road divider, vehicle lines, the shadow of trees, etc. In this paper, we proposed a robust lane detection and tracking method to detect lane marking considering the abovementioned challenging conditions. In this method, we introduced three key technologies. First, the bilateral filter is applied to smooth and preserve the edges and we introduced an optimized intensity threshold range (OITR) to improve the performance of the canny operator which detects the edges of low intensity (colored, eroded, or blurred) lane markings. Second, we proposed a robust lane verification technique, the angle and length-based geometric constraint (ALGC) algorithm followed by Hough Transform, to verify the characteristics of lane marking and to prevent incorrect lane detection. Finally, a novel lane tracking technique, the horizontally adjustable lane repositioning range (HALRR) algorithm is proposed, which can keep track of the lane position. To evaluate the performance of the proposed method we used the DSDLDE dataset with 1080x1920 resolutions at 24 frames/sec. Experimental results show that the average detection rate is 97.36%, and the average detection time is 29.06msec per frame, which outperformed the state-of-the-art method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge