Sajid Mahmud
HalluMat: Detecting Hallucinations in LLM-Generated Materials Science Content Through Multi-Stage Verification
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly Large Language Models (LLMs), is transforming scientific discovery, enabling rapid knowledge generation and hypothesis formulation. However, a critical challenge is hallucination, where LLMs generate factually incorrect or misleading information, compromising research integrity. To address this, we introduce HalluMatData, a benchmark dataset for evaluating hallucination detection methods, factual consistency, and response robustness in AI-generated materials science content. Alongside this, we propose HalluMatDetector, a multi-stage hallucination detection framework that integrates intrinsic verification, multi-source retrieval, contradiction graph analysis, and metric-based assessment to detect and mitigate LLM hallucinations. Our findings reveal that hallucination levels vary significantly across materials science subdomains, with high-entropy queries exhibiting greater factual inconsistencies. By utilizing HalluMatDetector verification pipeline, we reduce hallucination rates by 30% compared to standard LLM outputs. Furthermore, we introduce the Paraphrased Hallucination Consistency Score (PHCS) to quantify inconsistencies in LLM responses across semantically equivalent queries, offering deeper insights into model reliability.
Deep Learning Prediction of Severe Health Risks for Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with a Large Feature Set in 2021 BARDA Data Challenge
Jun 06, 2022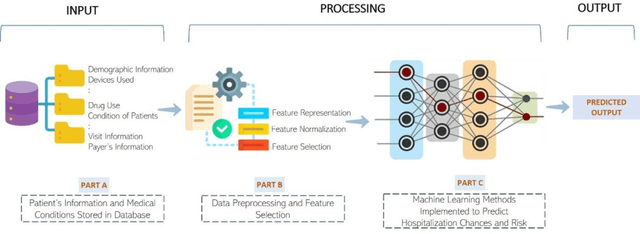
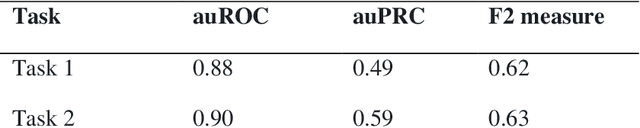
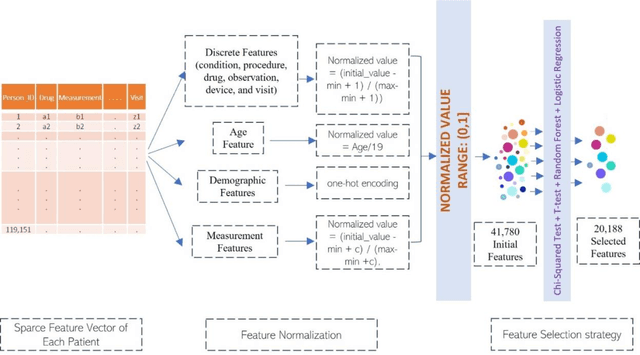
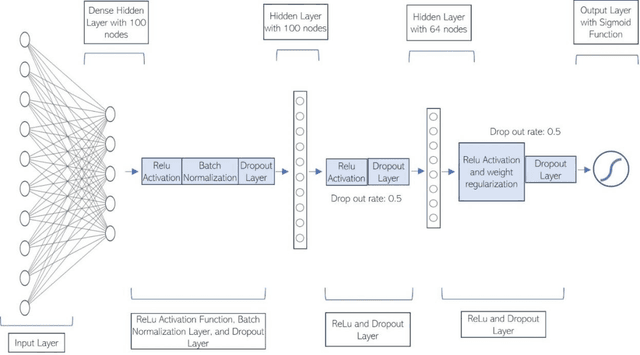
Abstract:Most children infected with COVID-19 have no or mild symptoms and can recover automatically by themselves, but some pediatric COVID-19 patients need to be hospitalized or even to receive intensive medical care (e.g., invasive mechanical ventilation or cardiovascular support) to recover from the illnesses. Therefore, it is critical to predict the severe health risk that COVID-19 infection poses to children to provide precise and timely medical care for vulnerable pediatric COVID-19 patients. However, predicting the severe health risk for COVID-19 patients including children remains a significant challenge because many underlying medical factors affecting the risk are still largely unknown. In this work, instead of searching for a small number of most useful features to make prediction, we design a novel large-scale bag-of-words like method to represent various medical conditions and measurements of COVID-19 patients. After some simple feature filtering based on logistical regression, the large set of features is used with a deep learning method to predict both the hospitalization risk for COVID-19 infected children and the severe complication risk for the hospitalized pediatric COVID-19 patients. The method was trained and tested the datasets of the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) Pediatric COVID-19 Data Challenge held from Sept. 15 to Dec. 17, 2021. The results show that the approach can rather accurately predict the risk of hospitalization and severe complication for pediatric COVID-19 patients and deep learning is more accurate than other machine learning methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge