Saif Sayed
Cross Your Body: A Cognitive Assessment System for Children
Nov 24, 2021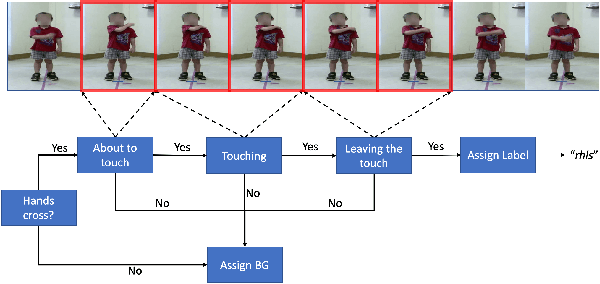
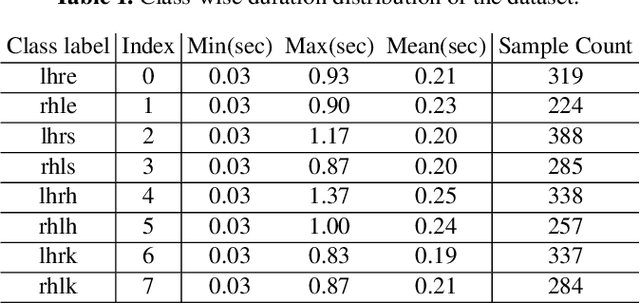

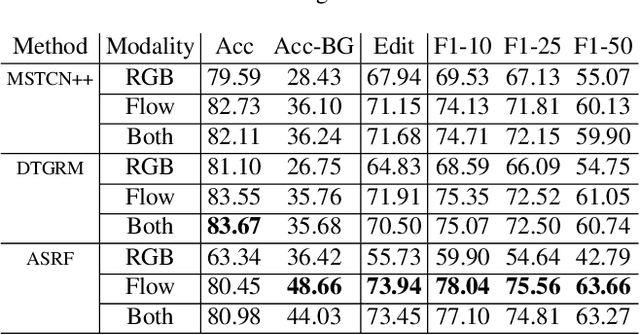
Abstract:While many action recognition techniques have great success on public benchmarks, such performance is not necessarily replicated in real-world scenarios, where the data comes from specific application requirements. The specific real-world application that we are focusing on in this paper is cognitive assessment in children using cognitively demanding physical tasks. We created a system called Cross-Your-Body and recorded data, which is unique in several aspects, including the fact that the tasks have been designed by psychologists, the subjects are children, and the videos capture real-world usage, as they record children performing tasks during real-world assessment by psychologists. Other distinguishing features of our system is that it's scores can directly be translated to measure executive functioning which is one of the key factor to distinguish onset of ADHD in adolescent kids. Due to imprecise execution of actions performed by children, and the presence of fine-grained motion patterns, we systematically investigate and evaluate relevant methods on the recorded data. It is our goal that this system will be useful in advancing research in cognitive assessment of kids.
Hierarchical Modeling for Task Recognition and Action Segmentation in Weakly-Labeled Instructional Videos
Oct 12, 2021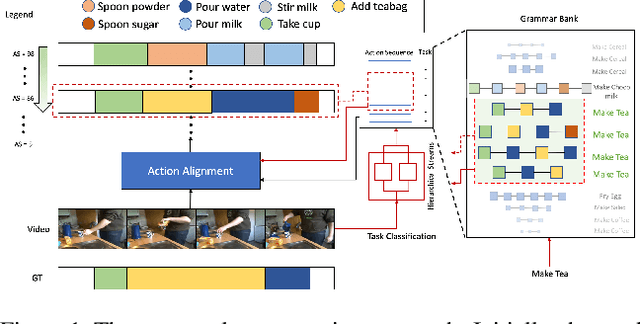
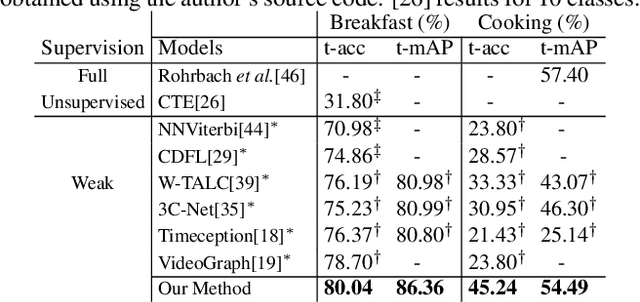
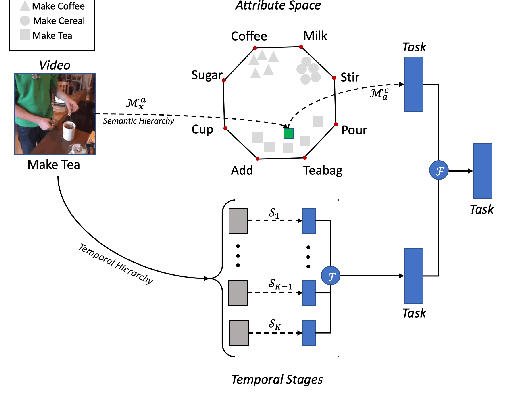
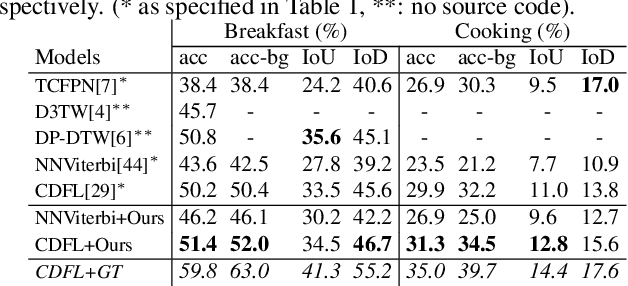
Abstract:This paper focuses on task recognition and action segmentation in weakly-labeled instructional videos, where only the ordered sequence of video-level actions is available during training. We propose a two-stream framework, which exploits semantic and temporal hierarchies to recognize top-level tasks in instructional videos. Further, we present a novel top-down weakly-supervised action segmentation approach, where the predicted task is used to constrain the inference of fine-grained action sequences. Experimental results on the popular Breakfast and Cooking 2 datasets show that our two-stream hierarchical task modeling significantly outperforms existing methods in top-level task recognition for all datasets and metrics. Additionally, using our task recognition framework in the proposed top-down action segmentation approach consistently improves the state of the art, while also reducing segmentation inference time by 80-90 percent.
Action Duration Prediction for Segment-Level Alignment of Weakly-Labeled Videos
Nov 20, 2020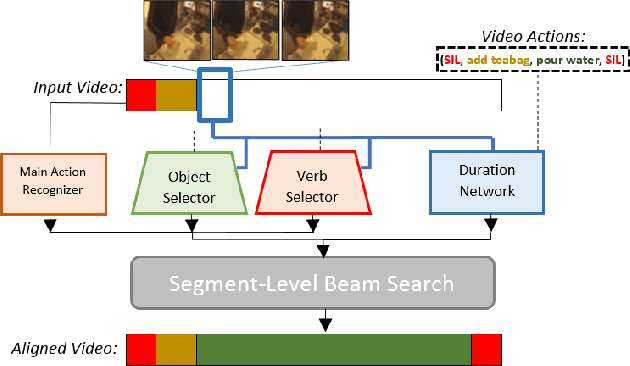
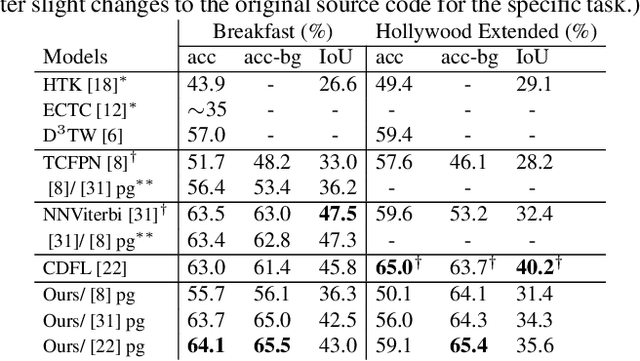
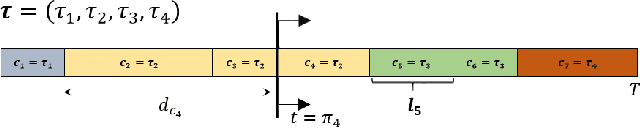
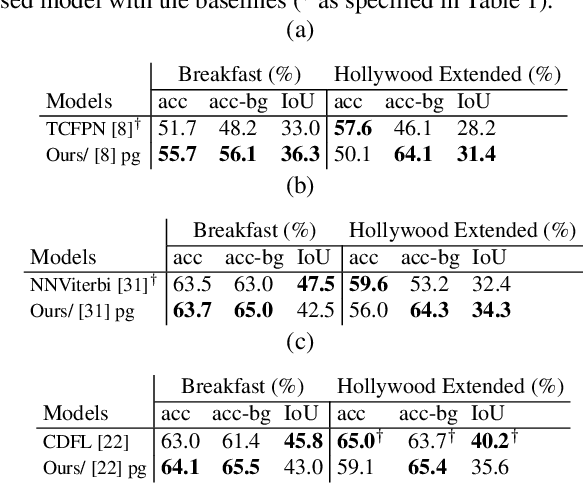
Abstract:This paper focuses on weakly-supervised action alignment, where only the ordered sequence of video-level actions is available for training. We propose a novel Duration Network, which captures a short temporal window of the video and learns to predict the remaining duration of a given action at any point in time with a level of granularity based on the type of that action. Further, we introduce a Segment-Level Beam Search to obtain the best alignment, that maximizes our posterior probability. Segment-Level Beam Search efficiently aligns actions by considering only a selected set of frames that have more confident predictions. The experimental results show that our alignments for long videos are more robust than existing models. Moreover, the proposed method achieves state of the art results in certain cases on the popular Breakfast and Hollywood Extended datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge