Said Fathalla
DISO: A Domain Ontology for Modeling Dislocations in Crystalline Materials
Jan 04, 2024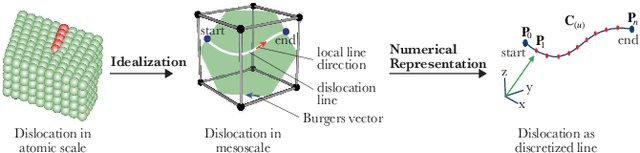
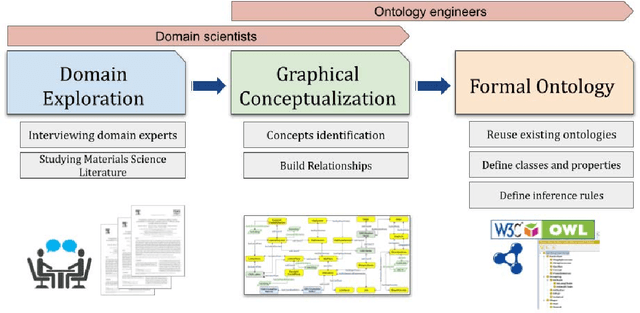

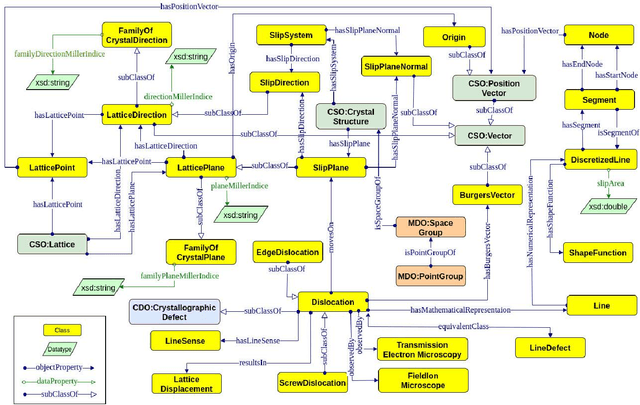
Abstract:Crystalline materials, such as metals and semiconductors, nearly always contain a special defect type called dislocation. This defect decisively determines many important material properties, e.g., strength, fracture toughness, or ductility. Over the past years, significant effort has been put into understanding dislocation behavior across different length scales via experimental characterization techniques and simulations. This paper introduces the dislocation ontology (DISO), which defines the concepts and relationships related to linear defects in crystalline materials. We developed DISO using a top-down approach in which we start defining the most general concepts in the dislocation domain and subsequent specialization of them. DISO is published through a persistent URL following W3C best practices for publishing Linked Data. Two potential use cases for DISO are presented to illustrate its usefulness in the dislocation dynamics domain. The evaluation of the ontology is performed in two directions, evaluating the success of the ontology in modeling a real-world domain and the richness of the ontology.
Modeling Dislocation Dynamics Data Using Semantic Web Technologies
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:Research in the field of Materials Science and Engineering focuses on the design, synthesis, properties, and performance of materials. An important class of materials that is widely investigated are crystalline materials, including metals and semiconductors. Crystalline material typically contains a distinct type of defect called "dislocation". This defect significantly affects various material properties, including strength, fracture toughness, and ductility. Researchers have devoted a significant effort in recent years to understanding dislocation behavior through experimental characterization techniques and simulations, e.g., dislocation dynamics simulations. This paper presents how data from dislocation dynamics simulations can be modeled using semantic web technologies through annotating data with ontologies. We extend the already existing Dislocation Ontology by adding missing concepts and aligning it with two other domain-related ontologies (i.e., the Elementary Multi-perspective Material Ontology and the Materials Design Ontology) allowing for representing the dislocation simulation data efficiently. Moreover, we show a real-world use case by representing the discrete dislocation dynamics data as a knowledge graph (DisLocKG) that illustrates the relationship between them. We also developed a SPARQL endpoint that brings extensive flexibility to query DisLocKG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge