Sahil Gupta
Knowing When to Abstain: Medical LLMs Under Clinical Uncertainty
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Current evaluation of large language models (LLMs) overwhelmingly prioritizes accuracy; however, in real-world and safety-critical applications, the ability to abstain when uncertain is equally vital for trustworthy deployment. We introduce MedAbstain, a unified benchmark and evaluation protocol for abstention in medical multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) -- a discrete-choice setting that generalizes to agentic action selection -- integrating conformal prediction, adversarial question perturbations, and explicit abstention options. Our systematic evaluation of both open- and closed-source LLMs reveals that even state-of-the-art, high-accuracy models often fail to abstain with uncertain. Notably, providing explicit abstention options consistently increases model uncertainty and safer abstention, far more than input perturbations, while scaling model size or advanced prompting brings little improvement. These findings highlight the central role of abstention mechanisms for trustworthy LLM deployment and offer practical guidance for improving safety in high-stakes applications.
Style is a Distribution of Features
Jul 25, 2020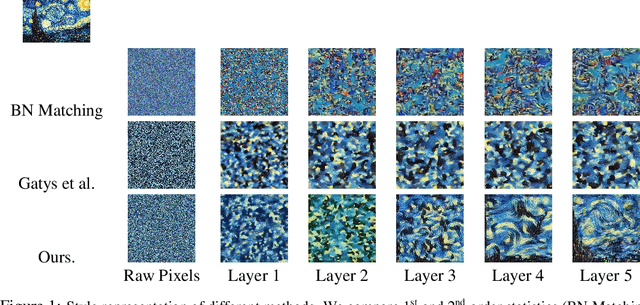
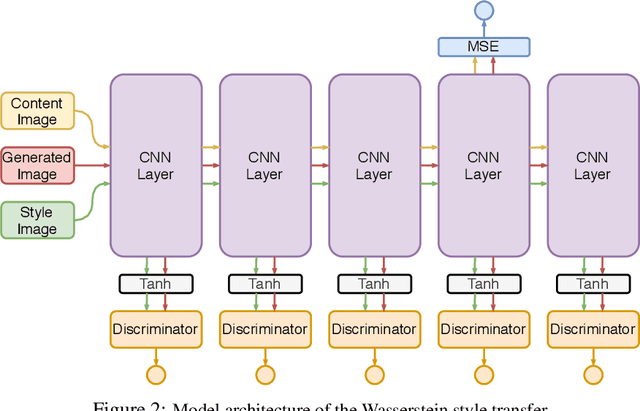
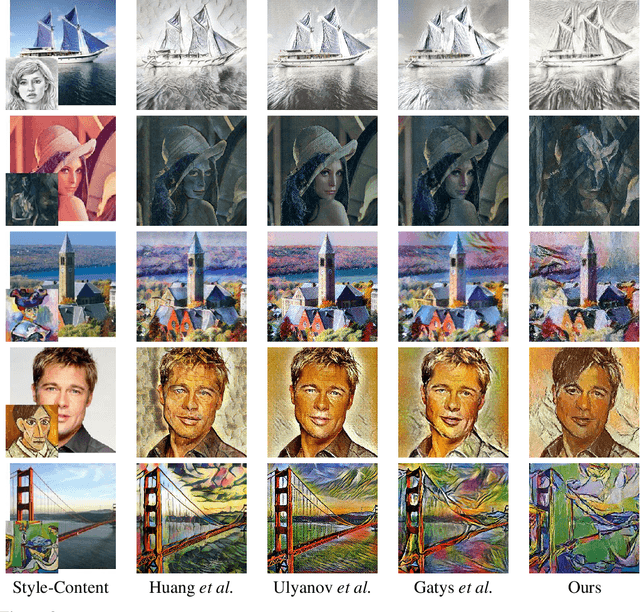
Abstract:Neural style transfer (NST) is a powerful image generation technique that uses a convolutional neural network (CNN) to merge the content of one image with the style of another. Contemporary methods of NST use first or second order statistics of the CNN's features to achieve transfers with relatively little computational cost. However, these methods cannot fully extract the style from the CNN's features. We present a new algorithm for style transfer that fully extracts the style from the features by redefining the style loss as the Wasserstein distance between the distribution of features. Thus, we set a new standard in style transfer quality. In addition, we state two important interpretations of NST. The first is a re-emphasis from Li et al., which states that style is simply the distribution of features. The second states that NST is a type of generative adversarial network (GAN) problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge