Sadegh Fadaei
Fluid segmentation in Neutrosophic domain
Dec 23, 2019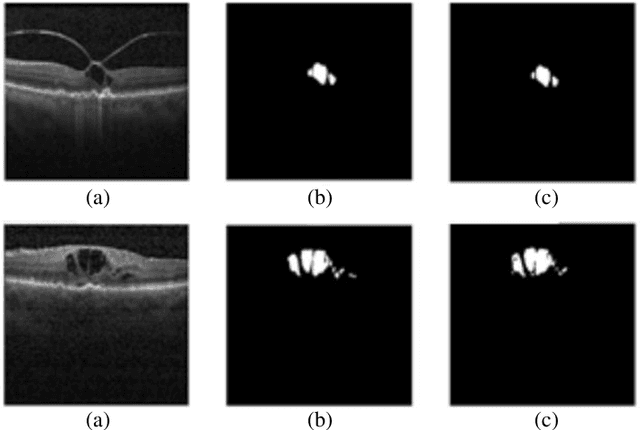
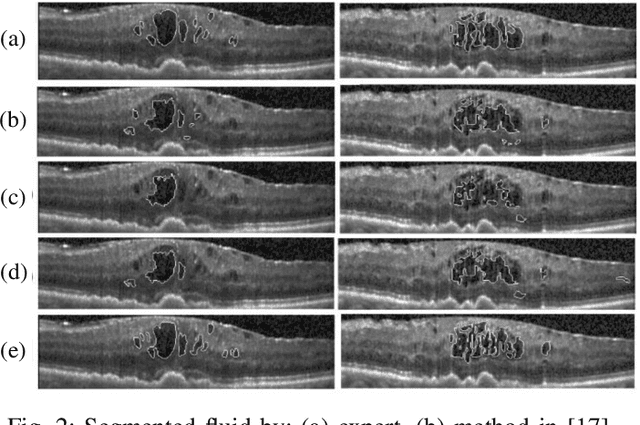
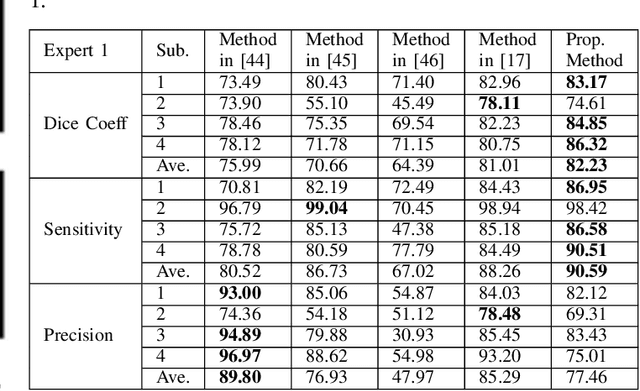
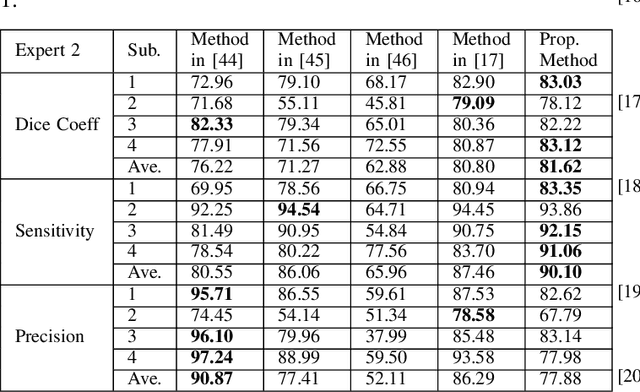
Abstract:Optical coherence tomography (OCT) as retina imaging technology is currently used by ophthalmologist as a non-invasive and non-contact method for diagnosis of agerelated degeneration (AMD) and diabetic macular edema (DME) diseases. Fluid regions in OCT images reveal the main signs of AMD and DME. In this paper, an efficient and fast clustering in neutrosophic (NS) domain referred as neutrosophic C-means is adapted for fluid segmentation. For this task, a NCM cost function in NS domain is adapted for fluid segmentation and then optimized by gradient descend methods which leads to binary segmentation of OCT Bscans to fluid and tissue regions. The proposed method is evaluated in OCT datasets of subjects with DME abnormalities. Results showed that the proposed method outperforms existing fluid segmentation methods by 6% in dice coefficient and sensitivity criteria.
Content-based image retrieval speedup
Dec 22, 2019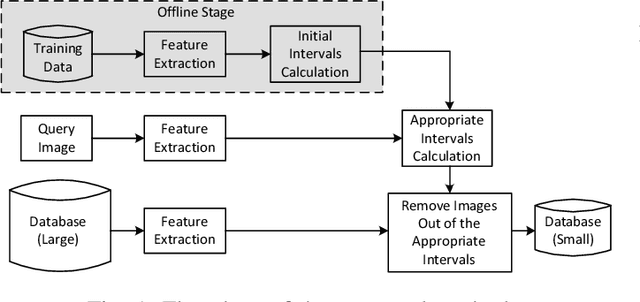
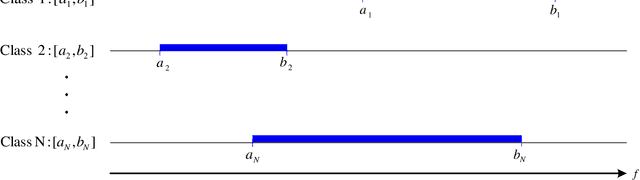
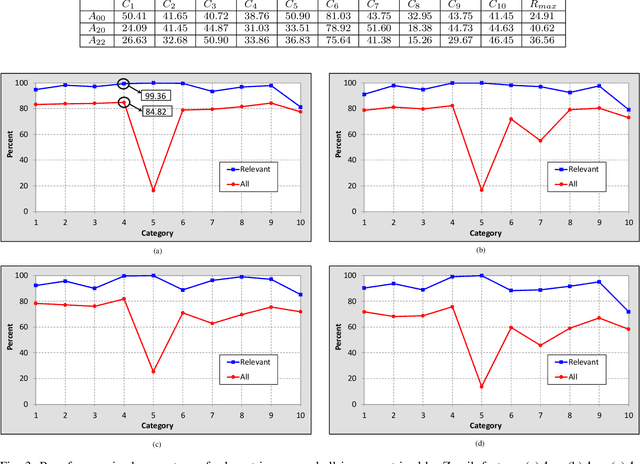
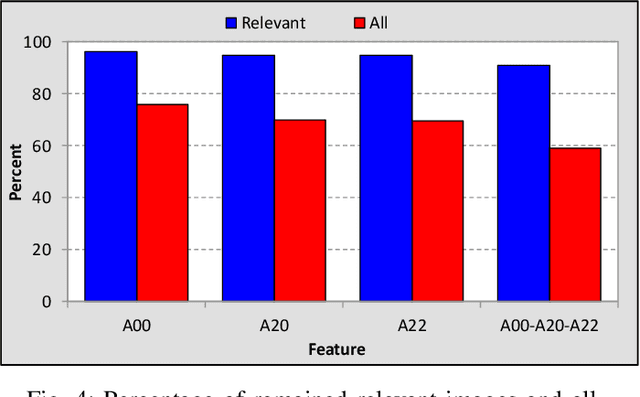
Abstract:Content-based image retrieval (CBIR) is a task of retrieving images from their contents. Since retrieval process is a time-consuming task in large image databases, acceleration methods can be very useful. This paper presents a novel method to speed up CBIR systems. In the proposed method, first Zernike moments are extracted from query image and an interval is calculated for that query. Images in database which are out of the interval are ignored in retrieval process. Therefore, a database reduction occurs before retrieval which leads to speed up. It is shown that in reduced database, relevant images to query image are preserved and irrelevant images are throwed away. Therefore, the proposed method speed up retrieval process and preserve CBIR accuracy, simultaneously.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge