Ross Gore
Towards Responsible and Explainable AI Agents with Consensus-Driven Reasoning
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Agentic AI represents a major shift in how autonomous systems reason, plan, and execute multi-step tasks through the coordination of Large Language Models (LLMs), Vision Language Models (VLMs), tools, and external services. While these systems enable powerful new capabilities, increasing autonomy introduces critical challenges related to explainability, accountability, robustness, and governance, especially when agent outputs influence downstream actions or decisions. Existing agentic AI implementations often emphasize functionality and scalability, yet provide limited mechanisms for understanding decision rationale or enforcing responsibility across agent interactions. This paper presents a Responsible(RAI) and Explainable(XAI) AI Agent Architecture for production-grade agentic workflows based on multi-model consensus and reasoning-layer governance. In the proposed design, a consortium of heterogeneous LLM and VLM agents independently generates candidate outputs from a shared input context, explicitly exposing uncertainty, disagreement, and alternative interpretations. A dedicated reasoning agent then performs structured consolidation across these outputs, enforcing safety and policy constraints, mitigating hallucinations and bias, and producing auditable, evidence-backed decisions. Explainability is achieved through explicit cross-model comparison and preserved intermediate outputs, while responsibility is enforced through centralized reasoning-layer control and agent-level constraints. We evaluate the architecture across multiple real-world agentic AI workflows, demonstrating that consensus-driven reasoning improves robustness, transparency, and operational trust across diverse application domains. This work provides practical guidance for designing agentic AI systems that are autonomous and scalable, yet responsible and explainable by construction.
A Practical Guide for Designing, Developing, and Deploying Production-Grade Agentic AI Workflows
Dec 09, 2025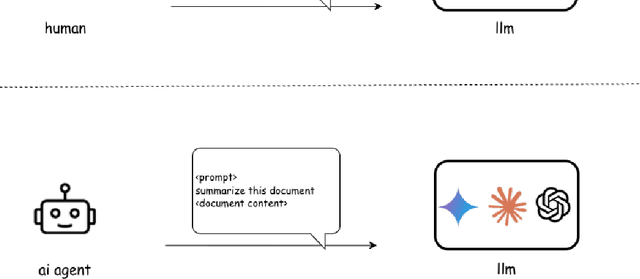
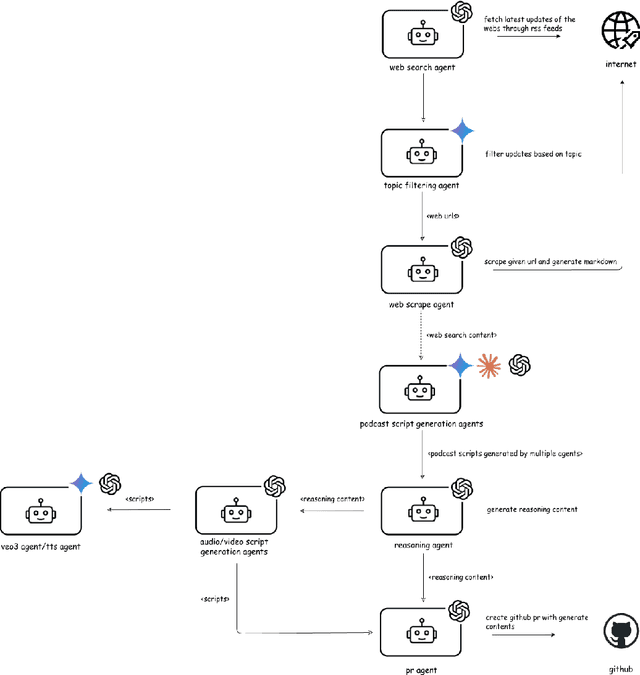

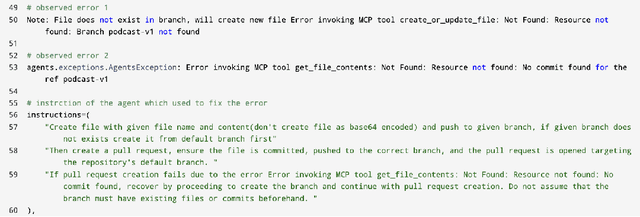
Abstract:Agentic AI marks a major shift in how autonomous systems reason, plan, and execute multi-step tasks. Unlike traditional single model prompting, agentic workflows integrate multiple specialized agents with different Large Language Models(LLMs), tool-augmented capabilities, orchestration logic, and external system interactions to form dynamic pipelines capable of autonomous decision-making and action. As adoption accelerates across industry and research, organizations face a central challenge: how to design, engineer, and operate production-grade agentic AI workflows that are reliable, observable, maintainable, and aligned with safety and governance requirements. This paper provides a practical, end-to-end guide for designing, developing, and deploying production-quality agentic AI systems. We introduce a structured engineering lifecycle encompassing workflow decomposition, multi-agent design patterns, Model Context Protocol(MCP), and tool integration, deterministic orchestration, Responsible-AI considerations, and environment-aware deployment strategies. We then present nine core best practices for engineering production-grade agentic AI workflows, including tool-first design over MCP, pure-function invocation, single-tool and single-responsibility agents, externalized prompt management, Responsible-AI-aligned model-consortium design, clean separation between workflow logic and MCP servers, containerized deployment for scalable operations, and adherence to the Keep it Simple, Stupid (KISS) principle to maintain simplicity and robustness. To demonstrate these principles in practice, we present a comprehensive case study: a multimodal news-analysis and media-generation workflow. By combining architectural guidance, operational patterns, and practical implementation insights, this paper offers a foundational reference to build robust, extensible, and production-ready agentic AI workflows.
Standardization of Neuromuscular Reflex Analysis -- Role of Fine-Tuned Vision-Language Model Consortium and OpenAI gpt-oss Reasoning LLM Enabled Decision Support System
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Accurate assessment of neuromuscular reflexes, such as the H-reflex, plays a critical role in sports science, rehabilitation, and clinical neurology. Traditional analysis of H-reflex EMG waveforms is subject to variability and interpretation bias among clinicians and researchers, limiting reliability and standardization. To address these challenges, we propose a Fine-Tuned Vision-Language Model (VLM) Consortium and a reasoning Large-Language Model (LLM)-enabled Decision Support System for automated H-reflex waveform interpretation and diagnosis. Our approach leverages multiple VLMs, each fine-tuned on curated datasets of H-reflex EMG waveform images annotated with clinical observations, recovery timelines, and athlete metadata. These models are capable of extracting key electrophysiological features and predicting neuromuscular states, including fatigue, injury, and recovery, directly from EMG images and contextual metadata. Diagnostic outputs from the VLM consortium are aggregated using a consensus-based method and refined by a specialized reasoning LLM, which ensures robust, transparent, and explainable decision support for clinicians and sports scientists. The end-to-end platform orchestrates seamless communication between the VLM ensemble and the reasoning LLM, integrating prompt engineering strategies and automated reasoning workflows using LLM Agents. Experimental results demonstrate that this hybrid system delivers highly accurate, consistent, and interpretable H-reflex assessments, significantly advancing the automation and standardization of neuromuscular diagnostics. To our knowledge, this work represents the first integration of a fine-tuned VLM consortium with a reasoning LLM for image-based H-reflex analysis, laying the foundation for next-generation AI-assisted neuromuscular assessment and athlete monitoring platforms.
Proof-of-TBI -- Fine-Tuned Vision Language Model Consortium and OpenAI-o3 Reasoning LLM-Based Medical Diagnosis Support System for Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Prediction
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) detection presents significant challenges due to the subtle and often ambiguous presentation of symptoms in medical imaging, making accurate diagnosis a complex task. To address these challenges, we propose Proof-of-TBI, a medical diagnosis support system that integrates multiple fine-tuned vision-language models with the OpenAI-o3 reasoning large language model (LLM). Our approach fine-tunes multiple vision-language models using a labeled dataset of TBI MRI scans, training them to diagnose TBI symptoms effectively. The predictions from these models are aggregated through a consensus-based decision-making process. The system evaluates the predictions from all fine-tuned vision language models using the OpenAI-o3 reasoning LLM, a model that has demonstrated remarkable reasoning performance, to produce the most accurate final diagnosis. The LLM Agents orchestrates interactions between the vision-language models and the reasoning LLM, managing the final decision-making process with transparency, reliability, and automation. This end-to-end decision-making workflow combines the vision-language model consortium with the OpenAI-o3 reasoning LLM, enabled by custom prompt engineering by the LLM agents. The prototype for the proposed platform was developed in collaboration with the U.S. Army Medical Research team in Newport News, Virginia, incorporating five fine-tuned vision-language models. The results demonstrate the transformative potential of combining fine-tuned vision-language model inputs with the OpenAI-o3 reasoning LLM to create a robust, secure, and highly accurate diagnostic system for mild TBI prediction. To the best of our knowledge, this research represents the first application of fine-tuned vision-language models integrated with a reasoning LLM for TBI prediction tasks.
GPT-4 Generated Narratives of Life Events using a Structured Narrative Prompt: A Validation Study
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) play a pivotal role in generating vast arrays of narratives, facilitating a systematic exploration of their effectiveness for communicating life events in narrative form. In this study, we employ a zero-shot structured narrative prompt to generate 24,000 narratives using OpenAI's GPT-4. From this dataset, we manually classify 2,880 narratives and evaluate their validity in conveying birth, death, hiring, and firing events. Remarkably, 87.43% of the narratives sufficiently convey the intention of the structured prompt. To automate the identification of valid and invalid narratives, we train and validate nine Machine Learning models on the classified datasets. Leveraging these models, we extend our analysis to predict the classifications of the remaining 21,120 narratives. All the ML models excelled at classifying valid narratives as valid, but experienced challenges at simultaneously classifying invalid narratives as invalid. Our findings not only advance the study of LLM capabilities, limitations, and validity but also offer practical insights for narrative generation and natural language processing applications.
Epistemology of Modeling and Simulation: How can we gain Knowledge from Simulations?
Jun 21, 2013

Abstract:Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that deals with gaining knowledge. It is closely related to ontology. The branch that deals with questions like "What is real?" and "What do we know?" as it provides these components. When using modeling and simulation, we usually imply that we are doing so to either apply knowledge, in particular when we are using them for training and teaching, or that we want to gain new knowledge, for example when doing analysis or conducting virtual experiments. This paper looks at the history of science to give a context to better cope with the question, how we can gain knowledge from simulation. It addresses aspects of computability and the general underlying mathematics, and applies the findings to validation and verification and development of federations. As simulations are understood as computable executable hypotheses, validation can be understood as hypothesis testing and theory building. The mathematical framework allows furthermore addressing some challenges when developing federations and the potential introduction of contradictions when composing different theories, as they are represented by the federated simulation systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge