Roey Regev
A Step Towards Interpretable Authorship Verification
Jul 07, 2020
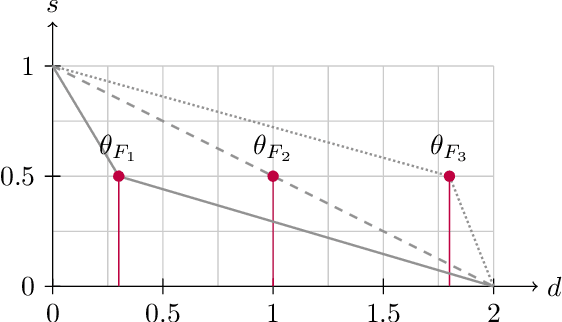

Abstract:A central problem that has been researched for many years in the field of digital text forensics is the question whether two documents were written by the same author. Authorship verification (AV) is a research branch in this field that deals with this question. Over the years, research activities in the context of AV have steadily increased, which has led to a variety of approaches trying to solve this problem. Many of these approaches, however, make use of features that are related to or influenced by the topic of the documents. Therefore, it may accidentally happen that their verification results are based not on the writing style (the actual focus of AV), but on the topic of the documents. To address this problem, we propose an alternative AV approach that considers only topic-agnostic features in its classification decision. In addition, we present a post-hoc interpretation method that allows to understand which particular features have contributed to the prediction of the proposed AV method. To evaluate the performance of our AV method, we compared it with ten competing baselines (including the current state of the art) on four challenging data sets. The results show that our approach outperforms all baselines in two cases (with a maximum accuracy of 84%), while in the other two cases it performs as well as the strongest baseline.
An Improved Topic Masking Technique for Authorship Analysis
May 02, 2020

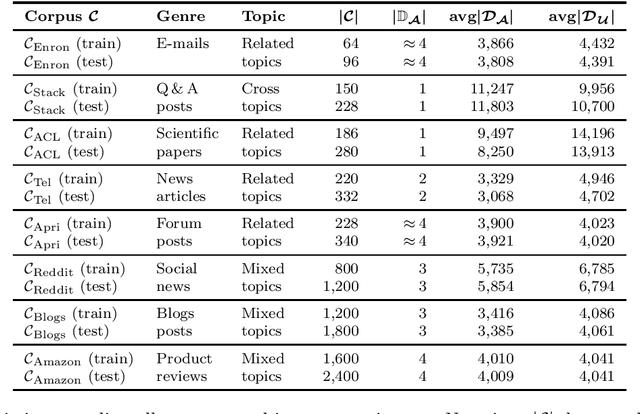
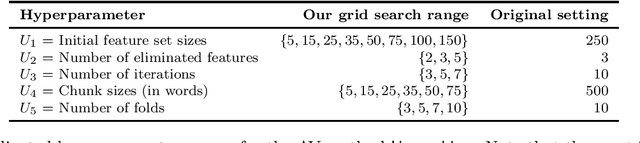
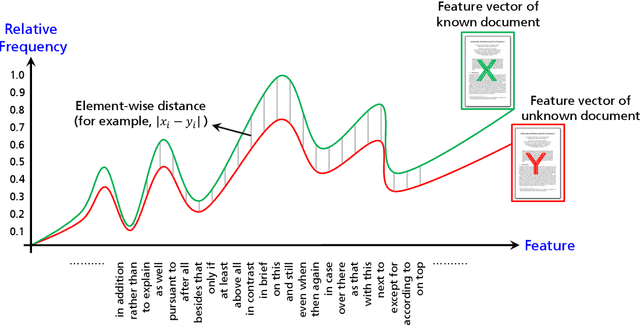
Abstract:Authorship verification (AV) is an important sub-area of digital text forensics and has been researched for more than two decades. The fundamental question addressed by AV is whether two documents were written by the same person. A serious problem that has received little attention in the literature so far is the question if AV methods actually focus on the writing style during classification, or whether they are unintentionally distorted by the topic of the documents. To counteract this problem, we propose an effective technique called POSNoise, which aims to mask topic-related content in documents. In this way, AV methods are forced to focus on those text units that are more related to the author's writing style. Based on a comprehensive evaluation with eight existing AV methods applied to eight corpora, we demonstrate that POSNoise is able to outperform a well-known topic masking approach in 51 out of 64 cases with up to 12.5% improvement in terms of accuracy. Furthermore, we show that for corpora preprocessed with POSNoise, the AV methods examined often achieve higher accuracies (improvement of up to 20.6%) compared to the original corpora.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge