Robert Abbas
Hybrid Deep Learning-Federated Learning Powered Intrusion Detection System for IoT/5G Advanced Edge Computing Network
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:The exponential expansion of IoT and 5G-Advanced applications has enlarged the attack surface for DDoS, malware, and zero-day intrusions. We propose an intrusion detection system that fuses a convolutional neural network (CNN), a bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM), and an autoencoder (AE) bottleneck within a privacy-preserving federated learning (FL) framework. The CNN-BiLSTM branch captures local and gated cross-feature interactions, while the AE emphasizes reconstruction-based anomaly sensitivity. Training occurs across edge devices without sharing raw data. On UNSW-NB15 (binary), the fused model attains AUC 99.59 percent and F1 97.36 percent; confusion-matrix analysis shows balanced error rates with high precision and recall. Average inference time is approximately 0.0476 ms per sample on our test hardware, which is well within the less than 10 ms URLLC budget, supporting edge deployment. We also discuss explainability, drift tolerance, and FL considerations for compliant, scalable 5G-Advanced IoT security.
A Novel Zero-Touch, Zero-Trust, AI/ML Enablement Framework for IoT Network Security
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:The IoT facilitates a connected, intelligent, and sustainable society; therefore, it is imperative to protect the IoT ecosystem. The IoT-based 5G and 6G will leverage the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence (ML/AI) more to pave the way for autonomous and collaborative secure IoT networks. Zero-touch, zero-trust IoT security with AI and machine learning (ML) enablement frameworks offers a powerful approach to securing the expanding landscape of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This paper presents a novel framework based on the integration of Zero Trust, Zero Touch, and AI/ML powered for the detection, mitigation, and prevention of DDoS attacks in modern IoT ecosystems. The focus will be on the new integrated framework by establishing zero trust for all IoT traffic, fixed and mobile 5G/6G IoT network traffic, and data security (quarantine-zero touch and dynamic policy enforcement). We perform a comparative analysis of five machine learning models, namely, XGBoost, Random Forest, K-Nearest Neighbors, Stochastic Gradient Descent, and Native Bayes, by comparing these models based on accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC. Results show that the best performance in detecting and mitigating different DDoS vectors comes from the ensemble-based approaches.
IoT Security: Botnet detection in IoT using Machine learning
Apr 06, 2021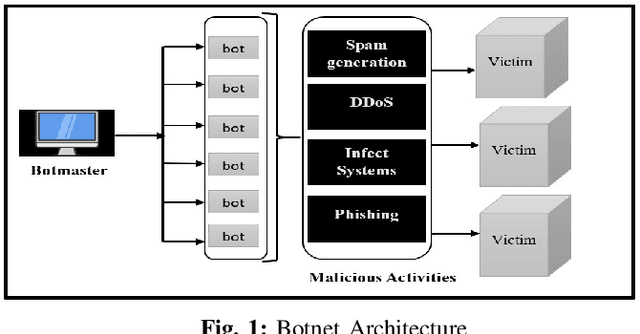
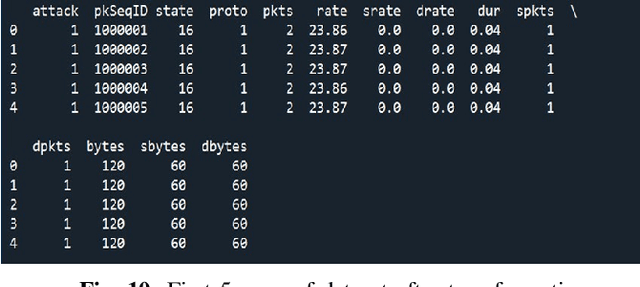
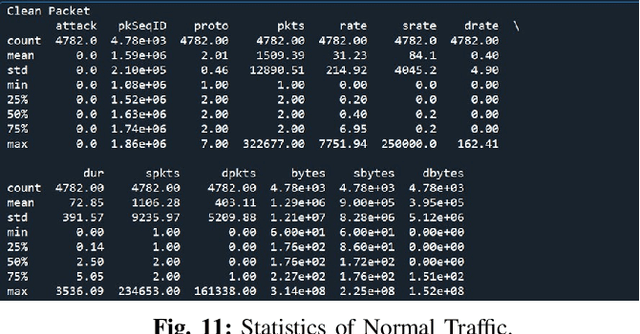
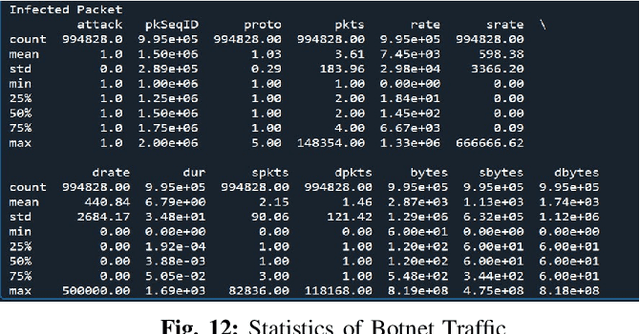
Abstract:The acceptance of Internet of Things (IoT) applications and services has seen an enormous rise of interest in IoT. Organizations have begun to create various IoT based gadgets ranging from small personal devices such as a smart watch to a whole network of smart grid, smart mining, smart manufacturing, and autonomous driver-less vehicles. The overwhelming amount and ubiquitous presence have attracted potential hackers for cyber-attacks and data theft. Security is considered as one of the prominent challenges in IoT. The key scope of this research work is to propose an innovative model using machine learning algorithm to detect and mitigate botnet-based distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack in IoT network. Our proposed model tackles the security issue concerning the threats from bots. Different machine learning algorithms such as K- Nearest Neighbour (KNN), Naive Bayes model and Multi-layer Perception Artificial Neural Network (MLP ANN) were used to develop a model where data are trained by BoT-IoT dataset. The best algorithm was selected by a reference point based on accuracy percentage and area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (ROC AUC) score. Feature engineering and Synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) were combined with machine learning algorithms (MLAs). Performance comparison of three algorithms used was done in class imbalance dataset and on the class balanced dataset.
Machine Learning based Anomaly Detection for 5G Networks
Mar 07, 2020



Abstract:Protecting the networks of tomorrow is set to be a challenging domain due to increasing cyber security threats and widening attack surfaces created by the Internet of Things (IoT), increased network heterogeneity, increased use of virtualisation technologies and distributed architectures. This paper proposes SDS (Software Defined Security) as a means to provide an automated, flexible and scalable network defence system. SDS will harness current advances in machine learning to design a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) using NAS (Neural Architecture Search) to detect anomalous network traffic. SDS can be applied to an intrusion detection system to create a more proactive and end-to-end defence for a 5G network. To test this assumption, normal and anomalous network flows from a simulated environment have been collected and analyzed with a CNN. The results from this method are promising as the model has identified benign traffic with a 100% accuracy rate and anomalous traffic with a 96.4% detection rate. This demonstrates the effectiveness of network flow analysis for a variety of common malicious attacks and also provides a viable option for detection of encrypted malicious network traffic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge