Richard Mar
Pre and Post Counting for Scalable Statistical-Relational Model Discovery
Oct 19, 2021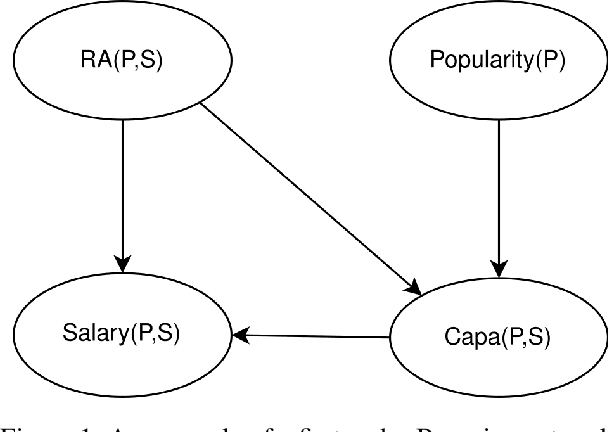
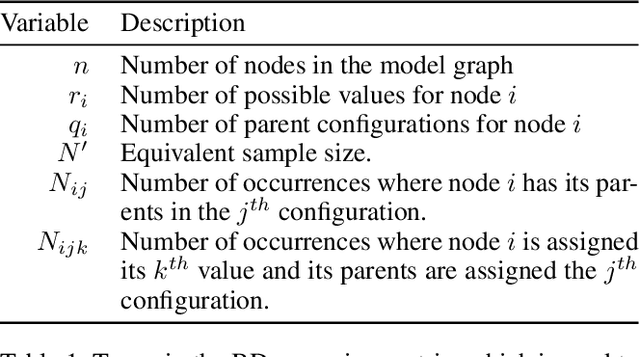
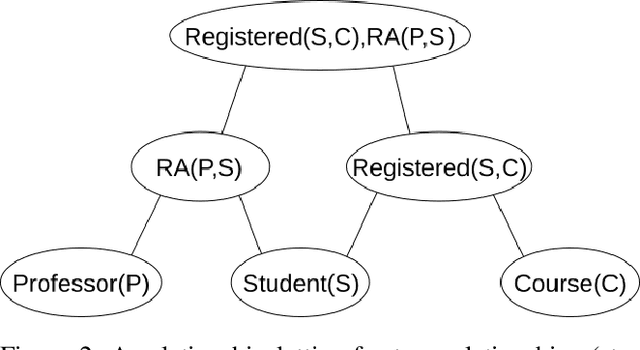
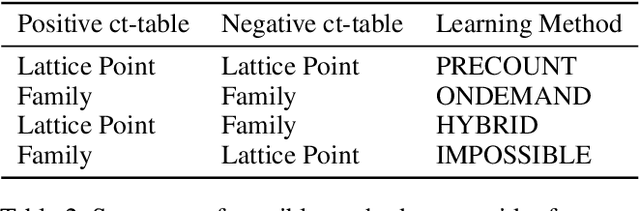
Abstract:Statistical-Relational Model Discovery aims to find statistically relevant patterns in relational data. For example, a relational dependency pattern may stipulate that a user's gender is associated with the gender of their friends. As with propositional (non-relational) graphical models, the major scalability bottleneck for model discovery is computing instantiation counts: the number of times a relational pattern is instantiated in a database. Previous work on propositional learning utilized pre-counting or post-counting to solve this task. This paper takes a detailed look at the memory and speed trade-offs between pre-counting and post-counting strategies for relational learning. A pre-counting approach computes and caches instantiation counts for a large set of relational patterns before model search. A post-counting approach computes an instantiation count dynamically on-demand for each candidate pattern generated during the model search. We describe a novel hybrid approach, tailored to relational data, that achieves a sweet spot with pre-counting for patterns involving positive relationships (e.g. pairs of users who are friends) and post-counting for patterns involving negative relationships (e.g. pairs of users who are not friends). Our hybrid approach scales model discovery to millions of data facts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge