Reinhard Stolle
Towards Automated Safety Requirements Derivation Using Agent-based RAG
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:We study the automated derivation of safety requirements in a self-driving vehicle use case, leveraging LLMs in combination with agent-based retrieval-augmented generation. Conventional approaches that utilise pre-trained LLMs to assist in safety analyses typically lack domain-specific knowledge. Existing RAG approaches address this issue, yet their performance deteriorates when handling complex queries and it becomes increasingly harder to retrieve the most relevant information. This is particularly relevant for safety-relevant applications. In this paper, we propose the use of agent-based RAG to derive safety requirements and show that the retrieved information is more relevant to the queries. We implement an agent-based approach on a document pool of automotive standards and the Apollo case study, as a representative example of an automated driving perception system. Our solution is tested on a data set of safety requirement questions and answers, extracted from the Apollo data. Evaluating a set of selected RAG metrics, we present and discuss advantages of a agent-based approach compared to default RAG methods.
* 9 pages, 3 figures
Radar Classification of Vehicles Using a Ground-Reflection Model
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:Classification of road users is important for traffic monitoring. The usability of a height estimate based on the two-ray ground-reflection model as a feature for the classification of vehicles is analyzed in this paper. The four-ray ground-reflection model for fast chirp ramp sequence waveforms of FMCW radars is derived and simplified to the well-known two-ray ground-reflection model. A spectrum from which the height of a target can be derived is obtained using the Lomb-Scargle periodogram. Measurements with two vehicle classes illustrate the approach and show that the model could be used as a feature to distinguish vehicles based on their height.
FMCW Radar Height Estimation of Moving Vehicles by Analyzing Multipath Reflections
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:Target classification is an important task of automotive radar systems. In this work, a concept for estimating the height of vehicles to allow for a differentiation between passenger cars, trucks, and others, is presented and discussed. Fixed installed radar sensors for traffic monitoring in the 77 GHz band are used to track and analyze radar echoes from individual vehicles as they move relative to the radar. Considering multipath propagation, which includes the ground reflection, the height of individual radar targets is estimated by analyzing the periodicity of the resulting amplitude modulation (AM) of the echo signal as a function of the horizontal distance from the radar. Two approaches have been realized to integrate the concept into an automotive FMCW signal processing scheme. Measurements in a test field using a trihedral corner reflector as an idealized target in heights from 0 to 2.5 m suggest, that the concept is suitable for height estimation in an automotive context.
A High-Level Track Fusion Scheme for Circular Quantities
Jan 10, 2022



Abstract:As sensors get more and more integrated, signal processing functions, like tracking, are performed closer to the sensor. Consequently, high level fusion is on the rise. Presented here is a high level fusion scheme incorporating not only linear,but circular quantities as well. Monte Carlo experiments are used to verify our novel fusion operators that work as a weighted average for the Wrapped Normal and the von-Mises distribution. To further verify the new fusion operators, we implemented a full track level fusion scheme and tested it by fusing the measurements of two RADAR sensors.
Cooperative RADAR Sensors for the Digital Test Field A9 (KoRA9): Algorithmic Recap and Lessons Learned
Jan 04, 2022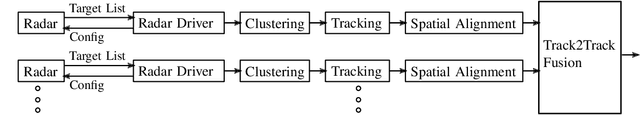
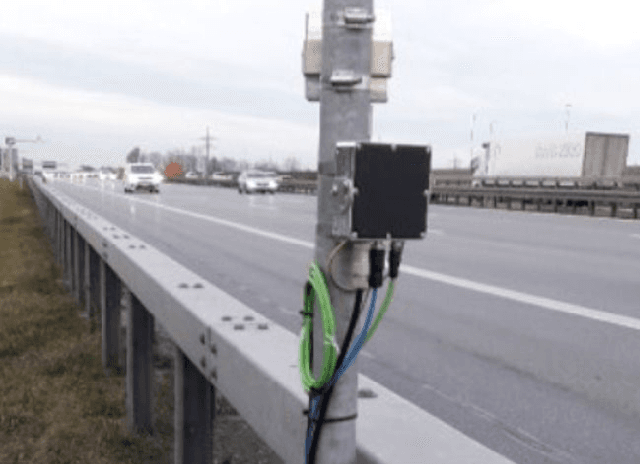

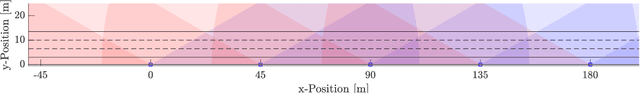
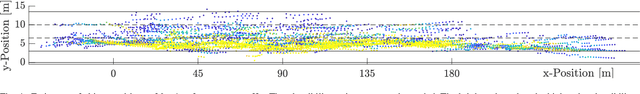
Abstract:Infrastructure sensing systems in combination with Infrastructure-to-Vehicle communication can be used to enhance sensor data obtained from the perspective of a vehicle, only. This paper presents a system consisting of a radar sensor network installed at the side of the street, together with an Edge Processing Unit to fuse the data of different sensors. Measurements taken by the demonstrator are shown, the system architecture is discussed, and some lessons learned are presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge