Regina Berretta
mQAPViz: A divide-and-conquer multi-objective optimization algorithm to compute large data visualizations
Oct 30, 2018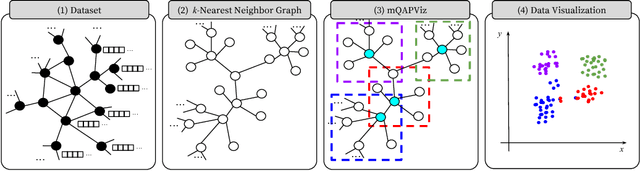


Abstract:Algorithms for data visualizations are essential tools for transforming data into useful narratives. Unfortunately, very few visualization algorithms can handle the large datasets of many real-world scenarios. In this study, we address the visualization of these datasets as a Multi-Objective Optimization Problem. We propose mQAPViz, a divide-and-conquer multi-objective optimization algorithm to compute large-scale data visualizations. Our method employs the Multi-Objective Quadratic Assignment Problem (mQAP) as the mathematical foundation to solve the visualization task at hand. The algorithm applies advanced sampling techniques originating from the field of machine learning and efficient data structures to scale to millions of data objects. The algorithm allocates objects onto a 2D grid layout. Experimental results on real-world and large datasets demonstrate that mQAPViz is a competitive alternative to existing techniques.
PasMoQAP: A Parallel Asynchronous Memetic Algorithm for solving the Multi-Objective Quadratic Assignment Problem
Jun 27, 2017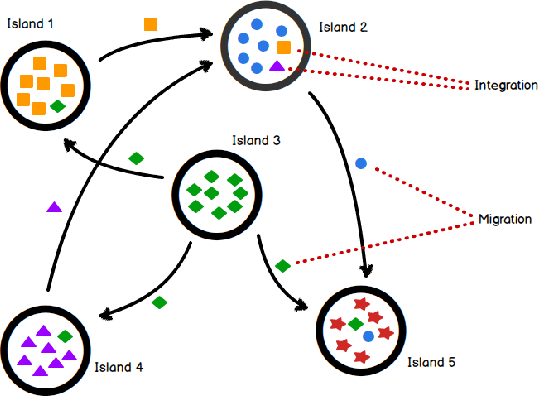
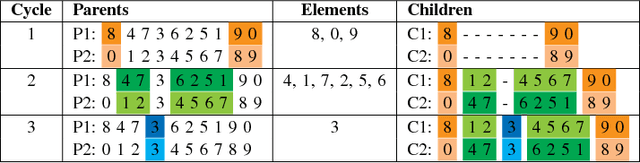
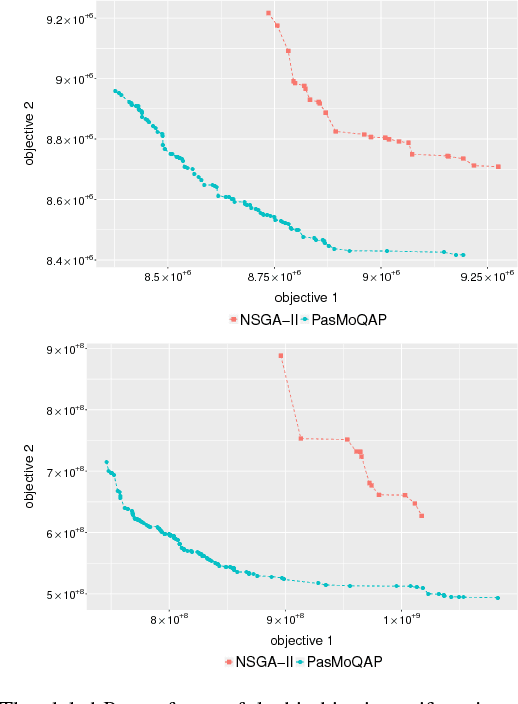
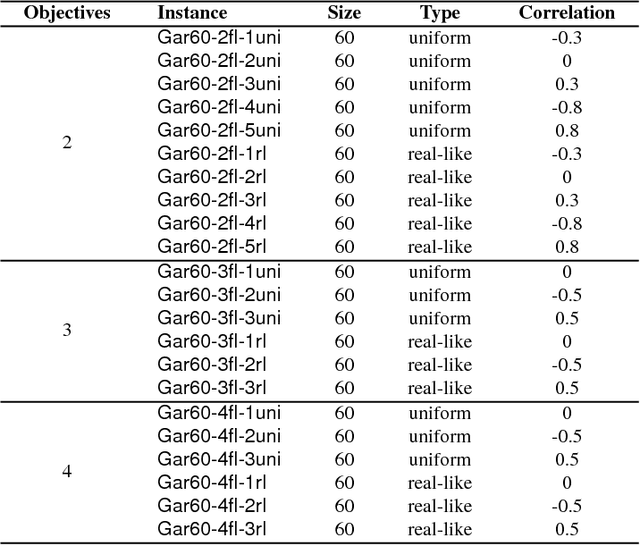
Abstract:Multi-Objective Optimization Problems (MOPs) have attracted growing attention during the last decades. Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms (MOEAs) have been extensively used to address MOPs because are able to approximate a set of non-dominated high-quality solutions. The Multi-Objective Quadratic Assignment Problem (mQAP) is a MOP. The mQAP is a generalization of the classical QAP which has been extensively studied, and used in several real-life applications. The mQAP is defined as having as input several flows between the facilities which generate multiple cost functions that must be optimized simultaneously. In this study, we propose PasMoQAP, a parallel asynchronous memetic algorithm to solve the Multi-Objective Quadratic Assignment Problem. PasMoQAP is based on an island model that structures the population by creating sub-populations. The memetic algorithm on each island individually evolve a reduced population of solutions, and they asynchronously cooperate by sending selected solutions to the neighboring islands. The experimental results show that our approach significatively outperforms all the island-based variants of the multi-objective evolutionary algorithm NSGA-II. We show that PasMoQAP is a suitable alternative to solve the Multi-Objective Quadratic Assignment Problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge