Ray-Kuang Lee
Machine learning transfer efficiencies for noisy quantum walks
Feb 18, 2020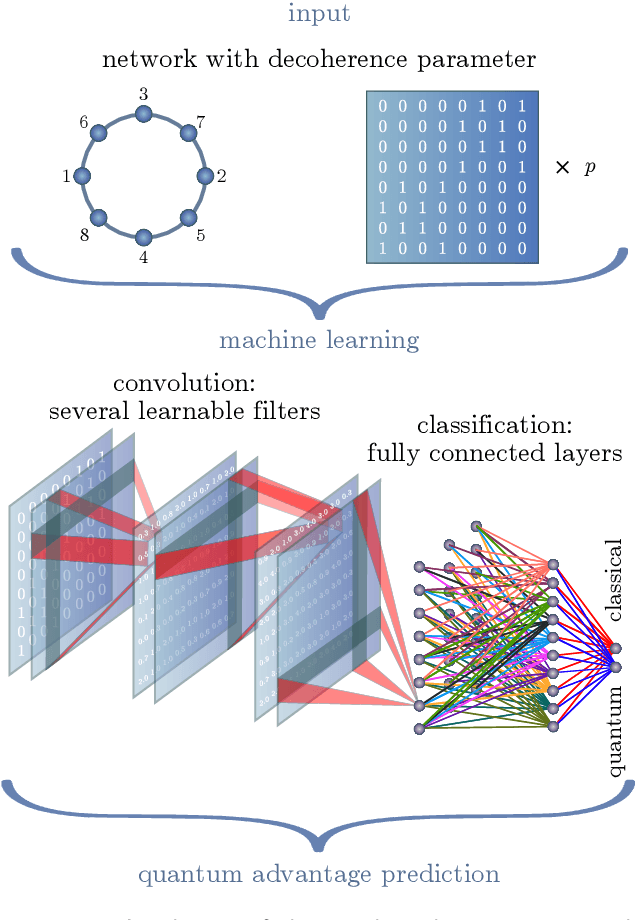
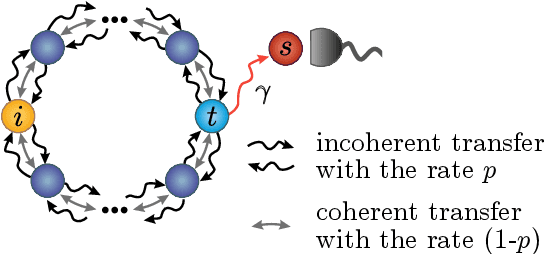
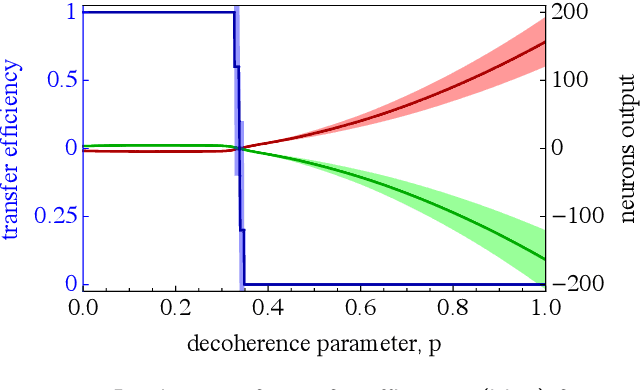
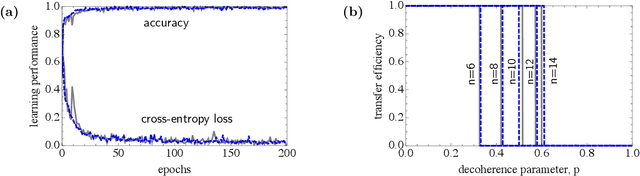
Abstract:Quantum effects are known to provide an advantage in particle transfer across networks. In order to achieve this advantage, requirements on both a graph type and a quantum system coherence must be found. Here we show that the process of finding these requirements can be automated by learning from simulated examples. The automation is done by using a convolutional neural network of a particular type that learns to understand with which network and under which coherence requirements quantum advantage is possible. Our machine learning approach is applied to study noisy quantum walks on cycle graphs of different sizes. We found that it is possible to predict the existence of quantum advantage for the entire decoherence parameter range, even for graphs outside of the training set. Our results are of importance for demonstration of advantage in quantum experiments and pave the way towards automating scientific research and discoveries.
* 6 pages, 4 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge