Raveena R Kumar
A POS Tagger for Code Mixed Indian Social Media Text - ICON-2016 NLP Tools Contest Entry from Surukam
Dec 31, 2016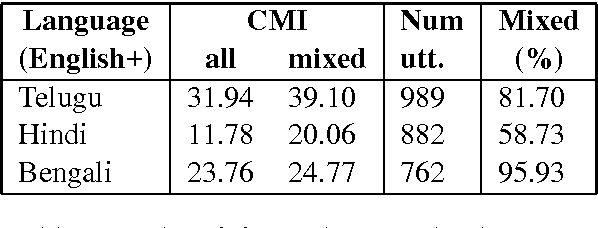
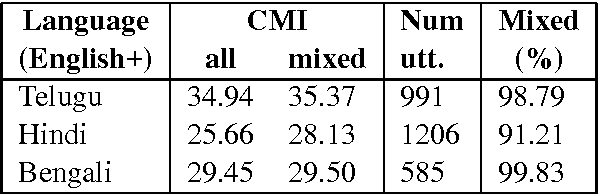
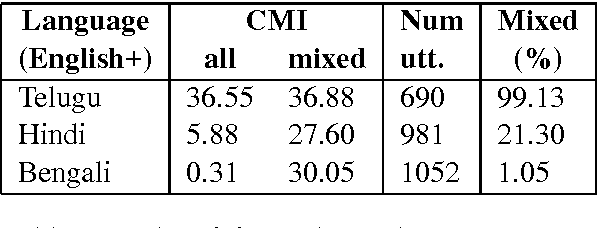
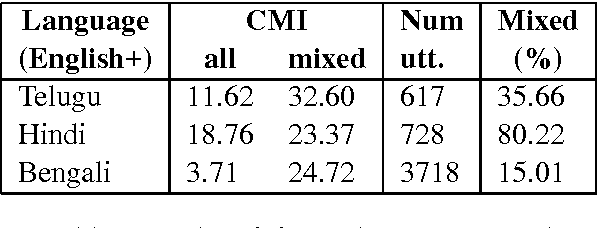
Abstract:Building Part-of-Speech (POS) taggers for code-mixed Indian languages is a particularly challenging problem in computational linguistics due to a dearth of accurately annotated training corpora. ICON, as part of its NLP tools contest has organized this challenge as a shared task for the second consecutive year to improve the state-of-the-art. This paper describes the POS tagger built at Surukam to predict the coarse-grained and fine-grained POS tags for three language pairs - Bengali-English, Telugu-English and Hindi-English, with the text spanning three popular social media platforms - Facebook, WhatsApp and Twitter. We employed Conditional Random Fields as the sequence tagging algorithm and used a library called sklearn-crfsuite - a thin wrapper around CRFsuite for training our model. Among the features we used include - character n-grams, language information and patterns for emoji, number, punctuation and web-address. Our submissions in the constrained environment,i.e., without making any use of monolingual POS taggers or the like, obtained an overall average F1-score of 76.45%, which is comparable to the 2015 winning score of 76.79%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge