Ramzi Al-Sharawi
Real, fake and synthetic faces -- does the coin have three sides?
Apr 02, 2024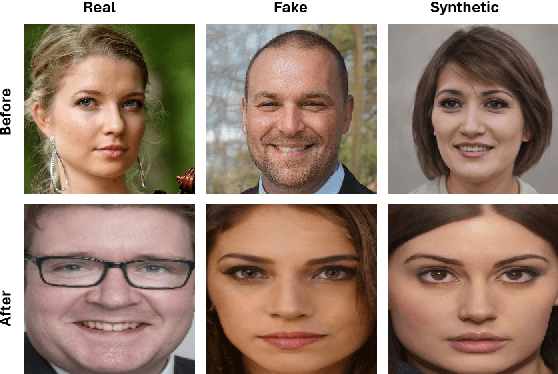
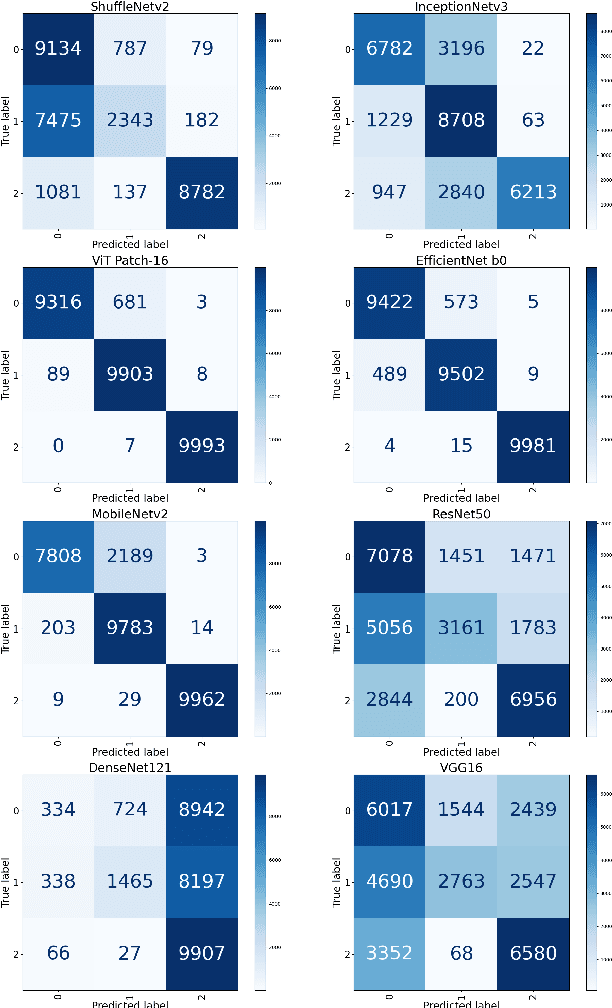
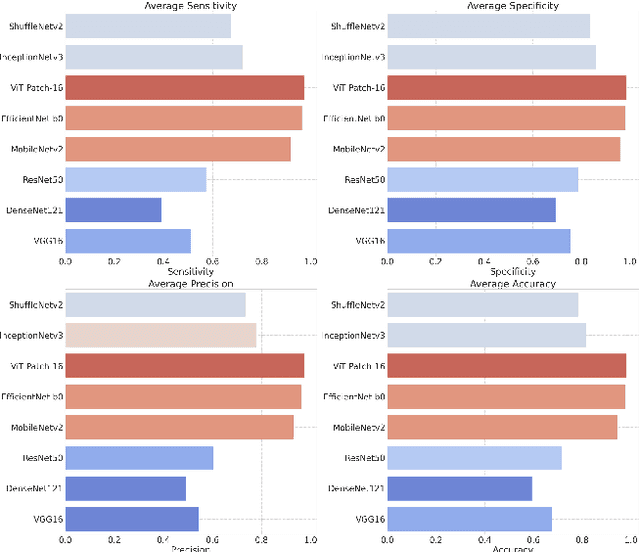
Abstract:With the ever-growing power of generative artificial intelligence, deepfake and artificially generated (synthetic) media have continued to spread online, which creates various ethical and moral concerns regarding their usage. To tackle this, we thus present a novel exploration of the trends and patterns observed in real, deepfake and synthetic facial images. The proposed analysis is done in two parts: firstly, we incorporate eight deep learning models and analyze their performances in distinguishing between the three classes of images. Next, we look to further delve into the similarities and differences between these three sets of images by investigating their image properties both in the context of the entire image as well as in the context of specific regions within the image. ANOVA test was also performed and provided further clarity amongst the patterns associated between the images of the three classes. From our findings, we observe that the investigated deeplearning models found it easier to detect synthetic facial images, with the ViT Patch-16 model performing best on this task with a class-averaged sensitivity, specificity, precision, and accuracy of 97.37%, 98.69%, 97.48%, and 98.25%, respectively. This observation was supported by further analysis of various image properties. We saw noticeable differences across the three category of images. This analysis can help us build better algorithms for facial image generation, and also shows that synthetic, deepfake and real face images are indeed three different classes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge