Raj Ratn Pranesh
TweetBLM: A Hate Speech Dataset and Analysis of Black Lives Matter-related Microblogs on Twitter
Aug 27, 2021



Abstract:In the past few years, there has been a significant rise in toxic and hateful content on various social media platforms. Recently Black Lives Matter movement came into the picture, causing an avalanche of user generated responses on the internet. In this paper, we have proposed a Black Lives Matter related tweet hate speech dataset TweetBLM. Our dataset comprises 9165 manually annotated tweets that target the Black Lives Matter movement. We annotated the tweets into two classes, i.e., HATE and NONHATE based on their content related to racism erupted from the movement for the black community. In this work, we also generated useful statistical insights on our dataset and performed a systematic analysis of various machine learning models such as Random Forest, CNN, LSTM, BiLSTM, Fasttext, BERTbase, and BERTlarge for the classification task on our dataset. Through our work, we aim at contributing to the substantial efforts of the research community for the identification and mitigation of hate speech on the internet. The dataset is publicly available.
Looking for COVID-19 misinformation in multilingual social media texts
May 03, 2021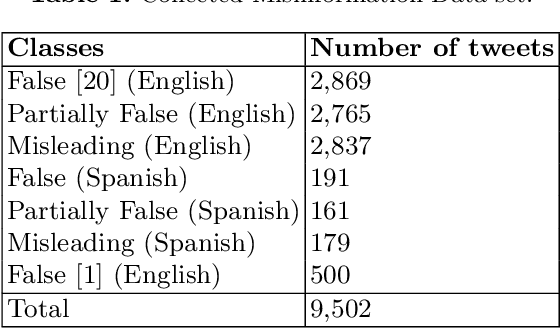
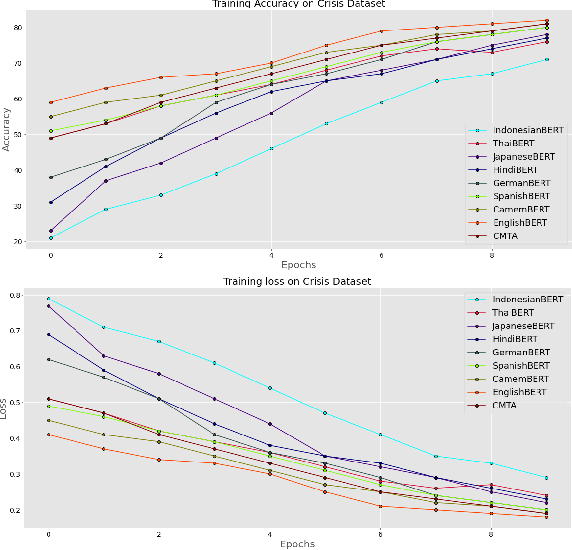
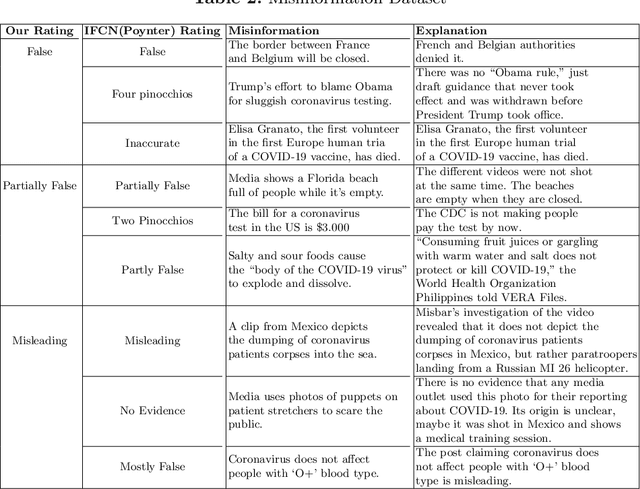
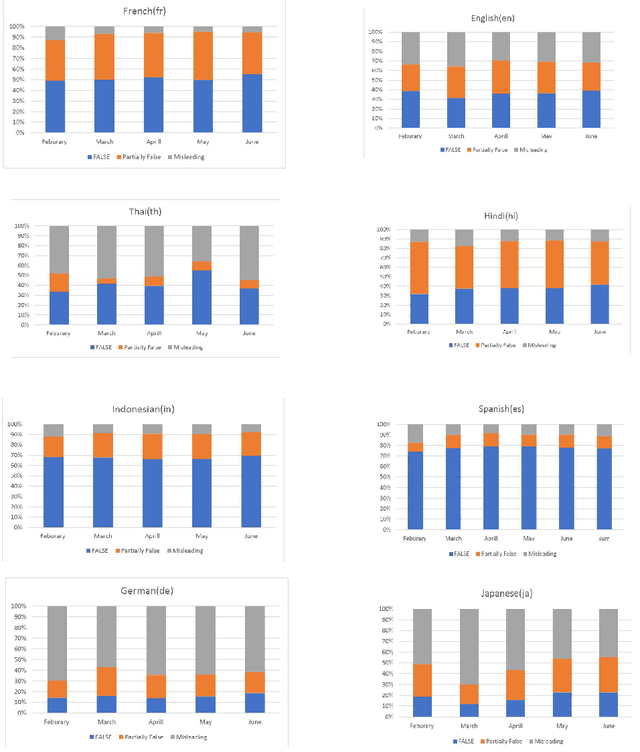
Abstract:This paper presents the Multilingual COVID-19 Analysis Method (CMTA) for detecting and observing the spread of misinformation about this disease within texts. CMTA proposes a data science (DS) pipeline that applies machine learning models for processing, classifying (Dense-CNN) and analyzing (MBERT) multilingual (micro)-texts. DS pipeline data preparation tasks extract features from multilingual textual data and categorize it into specific information classes (i.e., 'false', 'partly false', 'misleading'). The CMTA pipeline has been experimented with multilingual micro-texts (tweets), showing misinformation spread across different languages. To assess the performance of CMTA and put it in perspective, we performed a comparative analysis of CMTA with eight monolingual models used for detecting misinformation. The comparison shows that CMTA has surpassed various monolingual models and suggests that it can be used as a general method for detecting misinformation in multilingual micro-texts. CMTA experimental results show misinformation trends about COVID-19 in different languages during the first pandemic months.
A Conglomerate of Multiple OCR Table Detection and Extraction
Oct 16, 2020

Abstract:Information representation as tables are compact and concise method that eases searching, indexing, and storage requirements. Extracting and cloning tables from parsable documents is easier and widely used, however industry still faces challenge in detecting and extracting tables from OCR documents or images. This paper proposes an algorithm that detects and extracts multiple tables from OCR document. The algorithm uses a combination of image processing techniques, text recognition and procedural coding to identify distinct tables in same image and map the text to appropriate corresponding cell in dataframe which can be stored as Comma-separated values, Database, Excel and multiple other usable formats.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge