Rahat Masum
A Review On Game Theory With Smart Grid Security
Apr 23, 2023Abstract:Smart grid is the modern two way mechanism combining the power grid, control center, smart metering facility, energy routing and customer demand response services. The system being complicated, security vulnerabilities are paramount for the sound operation and process continuation. Since smart grid connects with the end user to the energy providers, these two parties can interact with each other within the whole energy management work flow. In this regard, game theory provides effective insights in the analysis of security measures for smart grid. The mentioned parties will be the players in the game model to provide a solution for the various threats to the grid aspects. In this work, a brief review has presented with the existing approaches to the threat models for divergent sectors of the smart grid. The solution approaches to these threats are based on the game theoretical approaches that connect the attackers and defenders in the scenarios.
Cyber Security in Smart Manufacturing (Threats, Landscapes Challenges)
Apr 20, 2023Abstract:Industry 4.0 is a blend of the hyper-connected digital industry within two world of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT). With this amalgamate opportunity, smart manufacturing involves production assets with the manufacturing equipment having its own intelligence, while the system-wide intelligence is provided by the cyber layer. However Smart manufacturing now becomes one of the prime targets of cyber threats due to vulnerabilities in the existing process of operation. Since smart manufacturing covers a vast area of production industries from cyber physical system to additive manufacturing, to autonomous vehicles, to cloud based IIoT (Industrial IoT), to robotic production, cyber threat stands out with this regard questioning about how to connect manufacturing resources by network, how to integrate a whole process chain for a factory production etc. Cybersecurity confidentiality, integrity and availability expose their essential existence for the proper operational thread model known as digital thread ensuring secure manufacturing. In this work, a literature survey is presented from the existing threat models, attack vectors and future challenges over the digital thread of smart manufacturing.
Expansion of Cyber Attack Data From Unbalanced Datasets Using Generative Techniques
Dec 10, 2019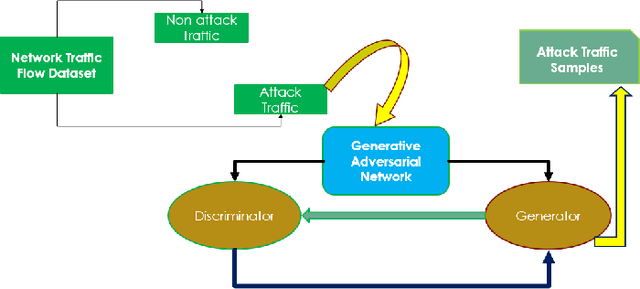
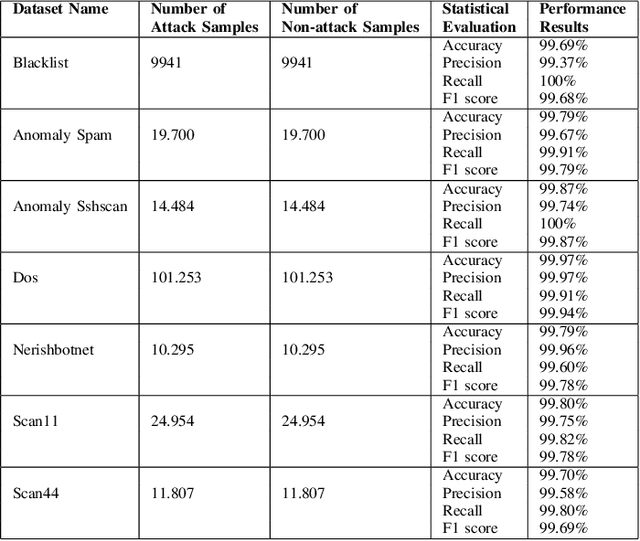
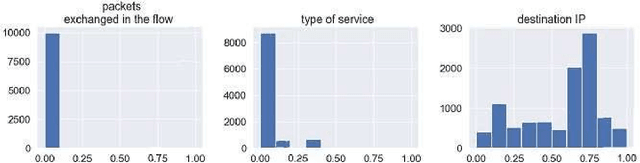
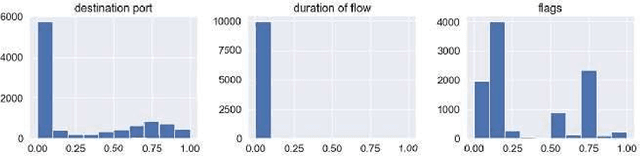
Abstract:Machine learning techniques help to understand patterns of a dataset to create a defense mechanism against cyber attacks. However, it is difficult to construct a theoretical model due to the imbalances in the dataset for discriminating attacks from the overall dataset. Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) technique will provide improvement in accuracy and increase the performance of detecting the attack and benign data from a balanced dataset. We have worked on the UGR'16 dataset publicly available for this work. Data wrangling has been done due to prepare test set from in the original set. We fed the neural network classifier larger input to the neural network in an increasing manner (i.e. 10000, 50000, 1 million) to see the distribution of features over the accuracy. We have implemented a GAN model that can produce samples of different attack labels (e.g. blacklist, anomaly spam, ssh scan). We have been able to generate as many samples as necessary based on the data sample we have taken from the UGR'16. We have tested the accuracy of our model with the imbalance dataset initially and then with the increasing the attack samples and found improvement of classification performance for the latter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge