Priyanka Meel
Is Dynamic Rumor Detection on social media Viable? An Unsupervised Perspective
Nov 23, 2021

Abstract:With the growing popularity and ease of access to the internet, the problem of online rumors is escalating. People are relying on social media to gain information readily but fall prey to false information. There is a lack of credibility assessment techniques for online posts to identify rumors as soon as they arrive. Existing studies have formulated several mechanisms to combat online rumors by developing machine learning and deep learning algorithms. The literature so far provides supervised frameworks for rumor classification that rely on huge training datasets. However, in the online scenario where supervised learning is exigent, dynamic rumor identification becomes difficult. Early detection of online rumors is a challenging task, and studies relating to them are relatively few. It is the need of the hour to identify rumors as soon as they appear online. This work proposes a novel framework for unsupervised rumor detection that relies on an online post's content and social features using state-of-the-art clustering techniques. The proposed architecture outperforms several existing baselines and performs better than several supervised techniques. The proposed method, being lightweight, simple, and robust, offers the suitability of being adopted as a tool for online rumor identification.
A Review of Web Infodemic Analysis and Detection Trends across Multi-modalities using Deep Neural Networks
Nov 23, 2021
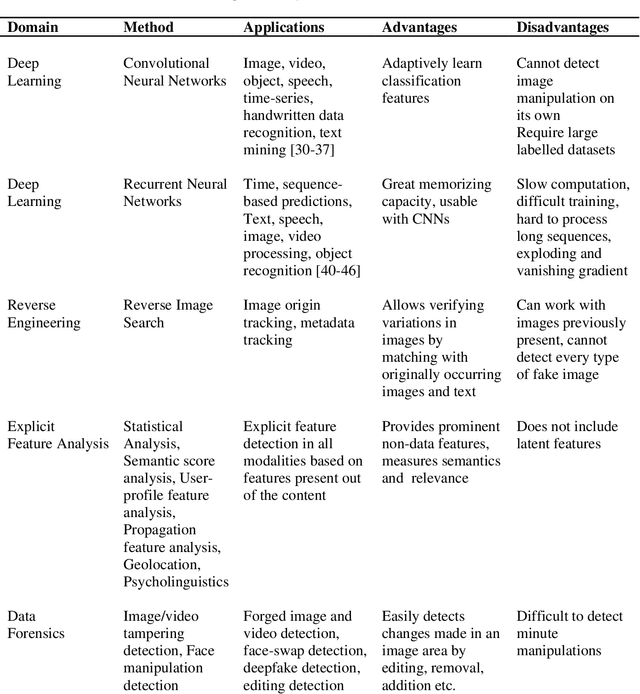

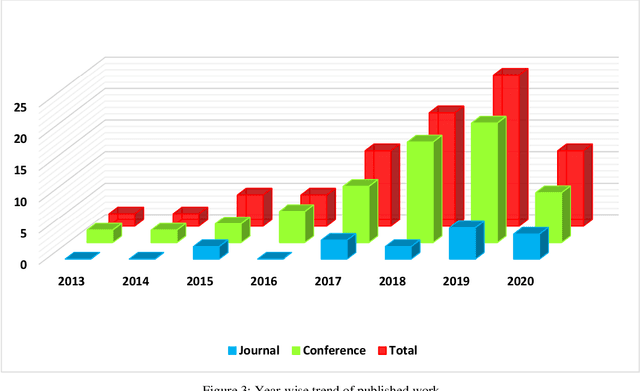
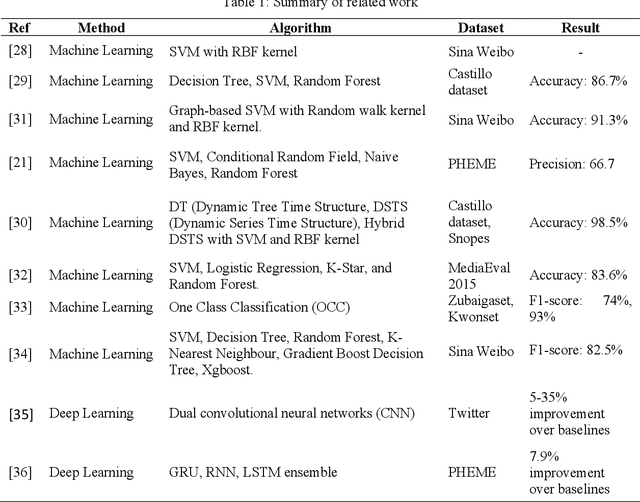
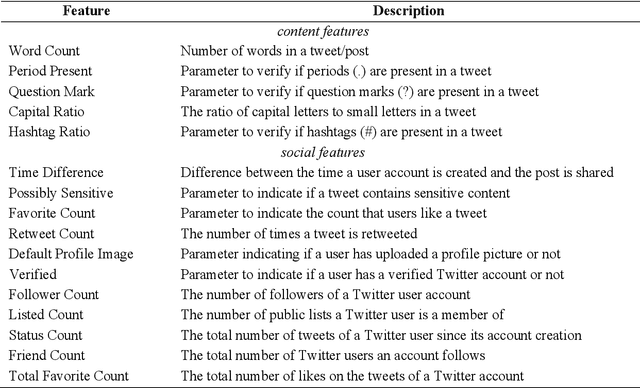
Abstract:Fake news and misinformation are a matter of concern for people around the globe. Users of the internet and social media sites encounter content with false information much frequently. Fake news detection is one of the most analyzed and prominent areas of research. These detection techniques apply popular machine learning and deep learning algorithms. Previous work in this domain covers fake news detection vastly among text circulating online. Platforms that have extensively been observed and analyzed include news websites and Twitter. Facebook, Reddit, WhatsApp, YouTube, and other social applications are gradually gaining attention in this emerging field. Researchers are analyzing online data based on multiple modalities composed of text, image, video, speech, and other contributing factors. The combination of various modalities has resulted in efficient fake news detection. At present, there is an abundance of surveys consolidating textual fake news detection algorithms. This review primarily deals with multi-modal fake news detection techniques that include images, videos, and their combinations with text. We provide a comprehensive literature survey of eighty articles presenting state-of-the-art detection techniques, thereby identifying research gaps and building a pathway for researchers to further advance this domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge