Pranav M. Pawar
Distributed Deep Reinforcement Learning for Collaborative Spectrum Sharing
Apr 06, 2021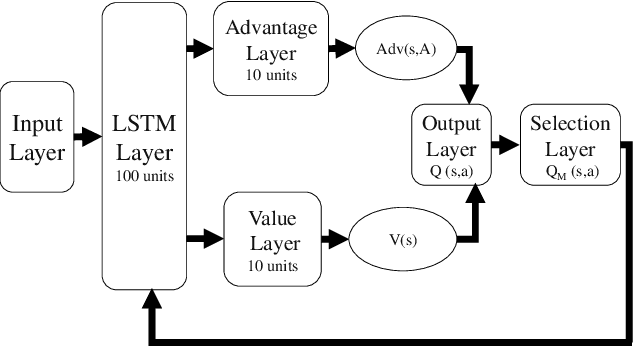
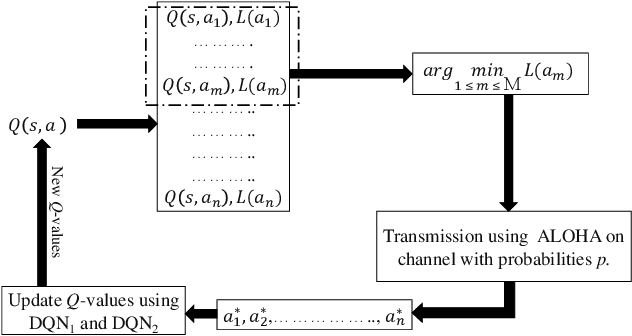
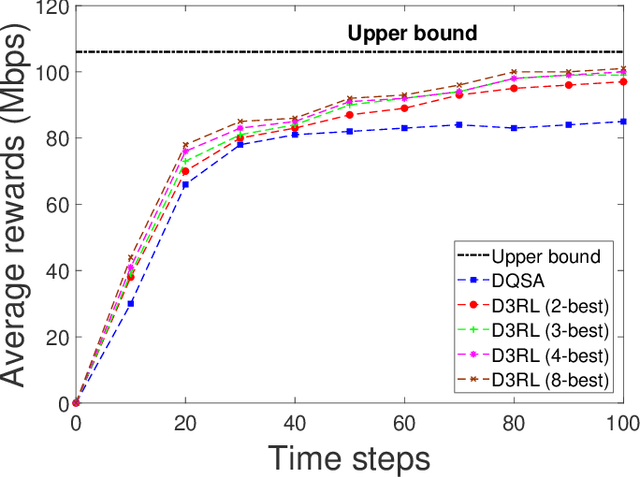
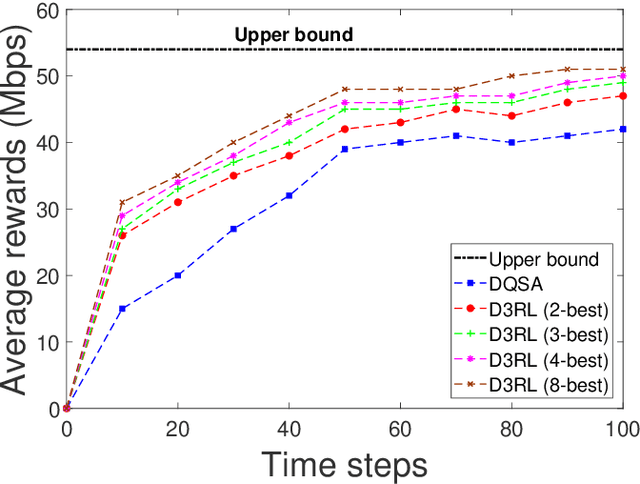
Abstract:Spectrum sharing among users is a fundamental problem in the management of any wireless network. In this paper, we discuss the problem of distributed spectrum collaboration without central management under general unknown channels. Since the cost of communication, coordination and control is rapidly increasing with the number of devices and the expanding bandwidth used there is an obvious need to develop distributed techniques for spectrum collaboration where no explicit signaling is used. In this paper, we combine game-theoretic insights with deep Q-learning to provide a novel asymptotically optimal solution to the spectrum collaboration problem. We propose a deterministic distributed deep reinforcement learning(D3RL) mechanism using a deep Q-network (DQN). It chooses the channels using the Q-values and the channel loads while limiting the options available to the user to a few channels with the highest Q-values and among those, it selects the least loaded channel. Using insights from both game theory and combinatorial optimization we show that this technique is asymptotically optimal for large overloaded networks. The selected channel and the outcome of the successful transmission are fed back into the learning of the deep Q-network to incorporate it into the learning of the Q-values. We also analyzed performance to understand the behavior of D3RL in differ
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge