Prakash S. Prasad
Automated Diabetic Retinopathy Grading using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Apr 14, 2020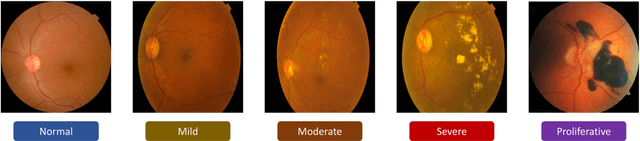
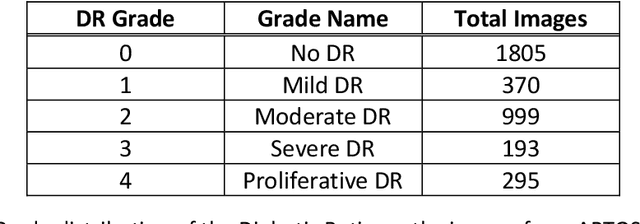


Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy is a global health problem, influences 100 million individuals worldwide, and in the next few decades, these incidences are expected to reach epidemic proportions. Diabetic Retinopathy is a subtle eye disease that can cause sudden, irreversible vision loss. The early-stage Diabetic Retinopathy diagnosis can be challenging for human experts, considering the visual complexity of fundus photography retinal images. However, Early Stage detection of Diabetic Retinopathy can significantly alter the severe vision loss problem. The competence of computer-aided detection systems to accurately detect the Diabetic Retinopathy had popularized them among researchers. In this study, we have utilized a pre-trained DenseNet121 network with several modifications and trained on APTOS 2019 dataset. The proposed method outperformed other state-of-the-art networks in early-stage detection and achieved 96.51% accuracy in severity grading of Diabetic Retinopathy for multi-label classification and achieved 94.44% accuracy for single-class classification method. Moreover, the precision, recall, f1-score, and quadratic weighted kappa for our network was reported as 86%, 87%, 86%, and 91.96%, respectively. Our proposed architecture is simultaneously very simple, accurate, and efficient concerning computational time and space.
Advances in Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy
Sep 21, 2019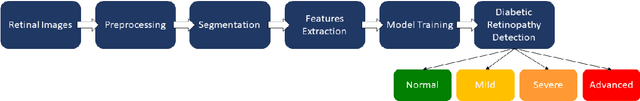
Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy is a critical health problem influences 100 million individuals worldwide, and these figures are expected to rise, particularly in Asia. Diabetic Retinopathy is a chronic eye disease which can lead to irreversible vision loss. Considering the visual complexity of retinal images, the early-stage diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy can be challenging for human experts. However, Early detection of Diabetic Retinopathy can significantly help to avoid permanent vision loss. The capability of computer-aided detection systems to accurately and efficiently detect the diabetic retinopathy had popularized them among researchers. In this review paper, the literature search was conducted on PubMed, Google Scholar, IEEE Explorer with a focus on the computer-aided detection of Diabetic Retinopathy using either of Machine Learning or Deep Learning algorithms. Moreover, this study also explores the typical methodology utilized for the computer-aided diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy. This review paper is aimed to direct the researchers about the limitations of current methods and identify the specific areas in the field to boost future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge