Phayung Meesad
Terrorism Event Classification Using Fuzzy Inference Systems
Apr 11, 2010

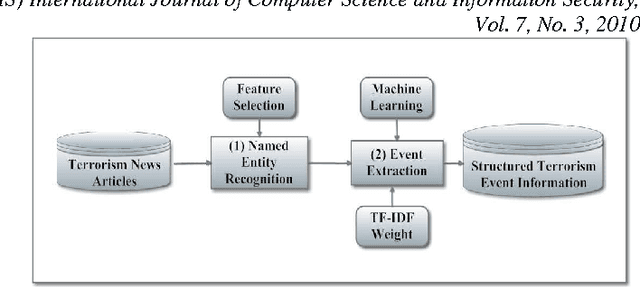
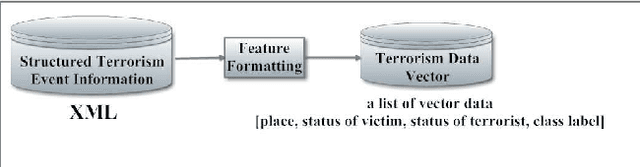
Abstract:Terrorism has led to many problems in Thai societies, not only property damage but also civilian casualties. Predicting terrorism activities in advance can help prepare and manage risk from sabotage by these activities. This paper proposes a framework focusing on event classification in terrorism domain using fuzzy inference systems (FISs). Each FIS is a decision-making model combining fuzzy logic and approximate reasoning. It is generated in five main parts: the input interface, the fuzzification interface, knowledge base unit, decision making unit and output defuzzification interface. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) is a FIS model adapted by combining the fuzzy logic and neural network. The ANFIS utilizes automatic identification of fuzzy logic rules and adjustment of membership function (MF). Moreover, neural network can directly learn from data set to construct fuzzy logic rules and MF implemented in various applications. FIS settings are evaluated based on two comparisons. The first evaluation is the comparison between unstructured and structured events using the same FIS setting. The second comparison is the model settings between FIS and ANFIS for classifying structured events. The data set consists of news articles related to terrorism events in three southern provinces of Thailand. The experimental results show that the classification performance of the FIS resulting from structured events achieves satisfactory accuracy and is better than the unstructured events. In addition, the classification of structured events using ANFIS gives higher performance than the events using only FIS in the prediction of terrorism events.
* IEEE Publication format, ISSN 1947 5500, http://sites.google.com/site/ijcsis/
Ontology-supported processing of clinical text using medical knowledge integration for multi-label classification of diagnosis coding
Apr 08, 2010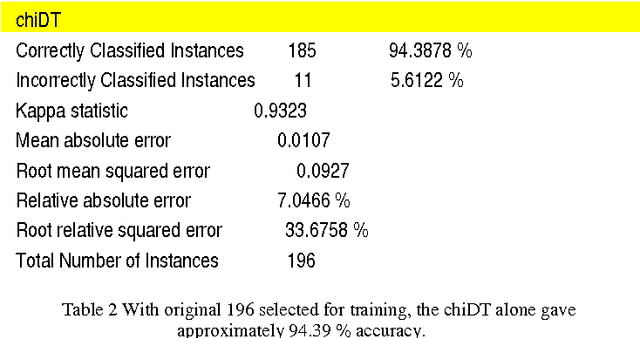
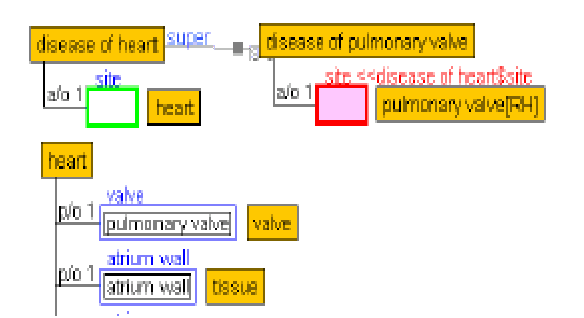
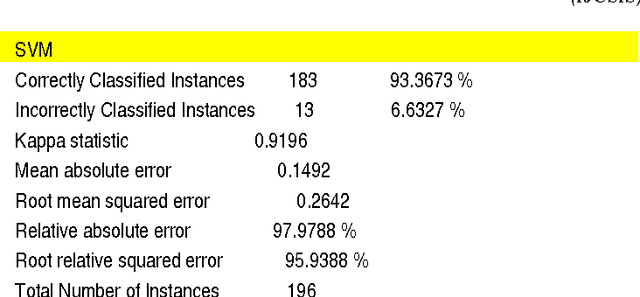
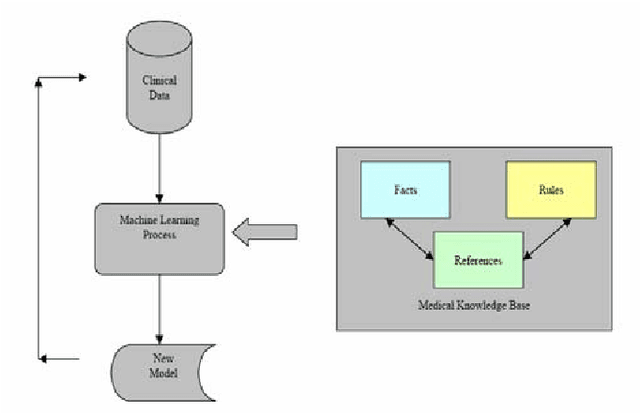
Abstract:This paper discusses the knowledge integration of clinical information extracted from distributed medical ontology in order to ameliorate a machine learning-based multi-label coding assignment system. The proposed approach is implemented using a decision tree based cascade hierarchical technique on the university hospital data for patients with Coronary Heart Disease (CHD). The preliminary results obtained show a satisfactory finding.
* IEEE Publication format, ISSN 1947 5500, http://sites.google.com/site/ijcsis/
Hierarchical Web Page Classification Based on a Topic Model and Neighboring Pages Integration
Mar 07, 2010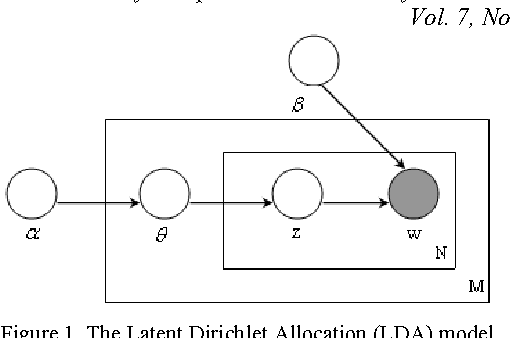
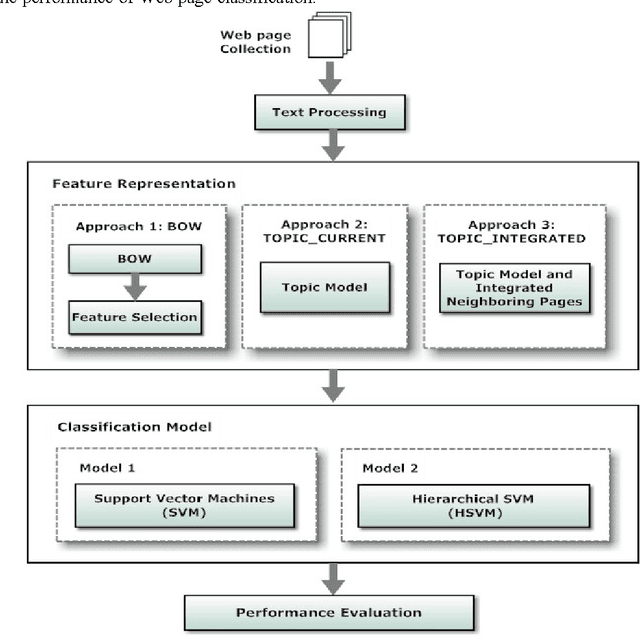
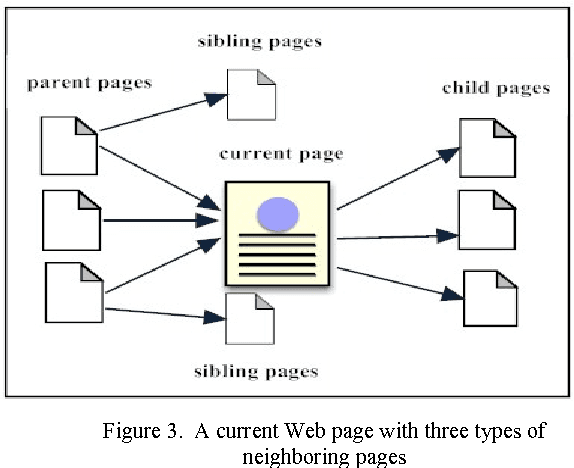
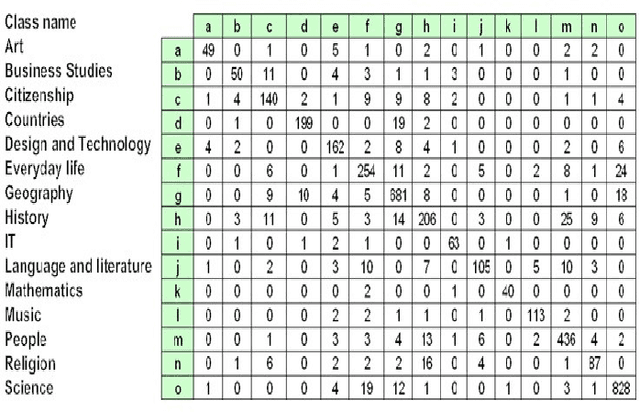
Abstract:Most Web page classification models typically apply the bag of words (BOW) model to represent the feature space. The original BOW representation, however, is unable to recognize semantic relationships between terms. One possible solution is to apply the topic model approach based on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation algorithm to cluster the term features into a set of latent topics. Terms assigned into the same topic are semantically related. In this paper, we propose a novel hierarchical classification method based on a topic model and by integrating additional term features from neighboring pages. Our hierarchical classification method consists of two phases: (1) feature representation by using a topic model and integrating neighboring pages, and (2) hierarchical Support Vector Machines (SVM) classification model constructed from a confusion matrix. From the experimental results, the approach of using the proposed hierarchical SVM model by integrating current page with neighboring pages via the topic model yielded the best performance with the accuracy equal to 90.33% and the F1 measure of 90.14%; an improvement of 5.12% and 5.13% over the original SVM model, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge