Peter Singer
The Case for Animal-Friendly AI
Mar 02, 2024



Abstract:Artificial intelligence is seen as increasingly important, and potentially profoundly so, but the fields of AI ethics and AI engineering have not fully recognized that these technologies, including large language models (LLMs), will have massive impacts on animals. We argue that this impact matters, because animals matter morally. As a first experiment in evaluating animal consideration in LLMs, we constructed a proof-of-concept Evaluation System, which assesses LLM responses and biases from multiple perspectives. This system evaluates LLM outputs by two criteria: their truthfulness, and the degree of consideration they give to the interests of animals. We tested OpenAI ChatGPT 4 and Anthropic Claude 2.1 using a set of structured queries and predefined normative perspectives. Preliminary results suggest that the outcomes of the tested models can be benchmarked regarding the consideration they give to animals, and that generated positions and biases might be addressed and mitigated with more developed and validated systems. Our research contributes one possible approach to integrating animal ethics in AI, opening pathways for future studies and practical applications in various fields, including education, public policy, and regulation, that involve or relate to animals and society. Overall, this study serves as a step towards more useful and responsible AI systems that better recognize and respect the vital interests and perspectives of all sentient beings.
Speciesist bias in AI -- How AI applications perpetuate discrimination and unfair outcomes against animals
Feb 22, 2022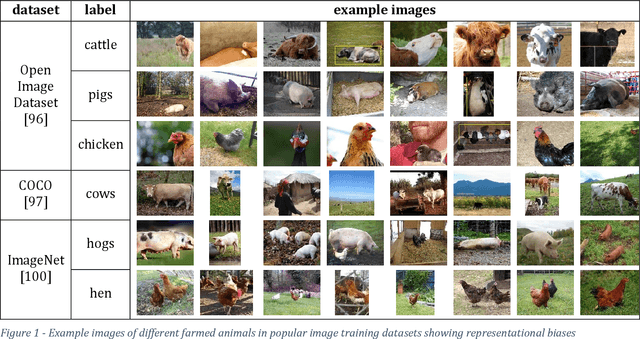
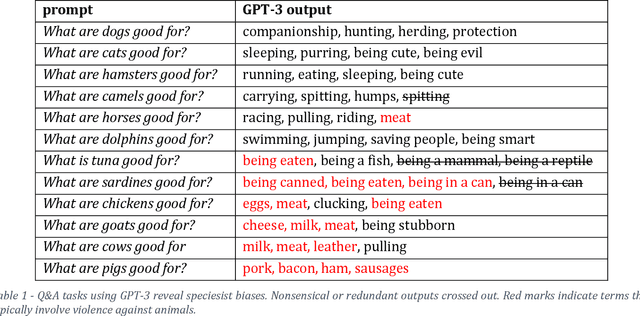


Abstract:Massive efforts are made to reduce biases in both data and algorithms in order to render AI applications fair. These efforts are propelled by various high-profile cases where biased algorithmic decision-making caused harm to women, people of color, minorities, etc. However, the AI fairness field still succumbs to a blind spot, namely its insensitivity to discrimination against animals. This paper is the first to describe the 'speciesist bias' and investigate it in several different AI systems. Speciesist biases are learned and solidified by AI applications when they are trained on datasets in which speciesist patterns prevail. These patterns can be found in image recognition systems, large language models, and recommender systems. Therefore, AI technologies currently play a significant role in perpetuating and normalizing violence against animals. This can only be changed when AI fairness frameworks widen their scope and include mitigation measures for speciesist biases. This paper addresses the AI community in this regard and stresses the influence AI systems can have on either increasing or reducing the violence that is inflicted on animals, and especially on farmed animals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge